Element Mixtures: Understand Differences Fast
Element mixtures are a fundamental concept in chemistry, referring to the combination of two or more elements in a physical or chemical state. Understanding the differences between various element mixtures is crucial for chemists, researchers, and students alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of element mixtures, exploring their types, properties, and significance in various fields.
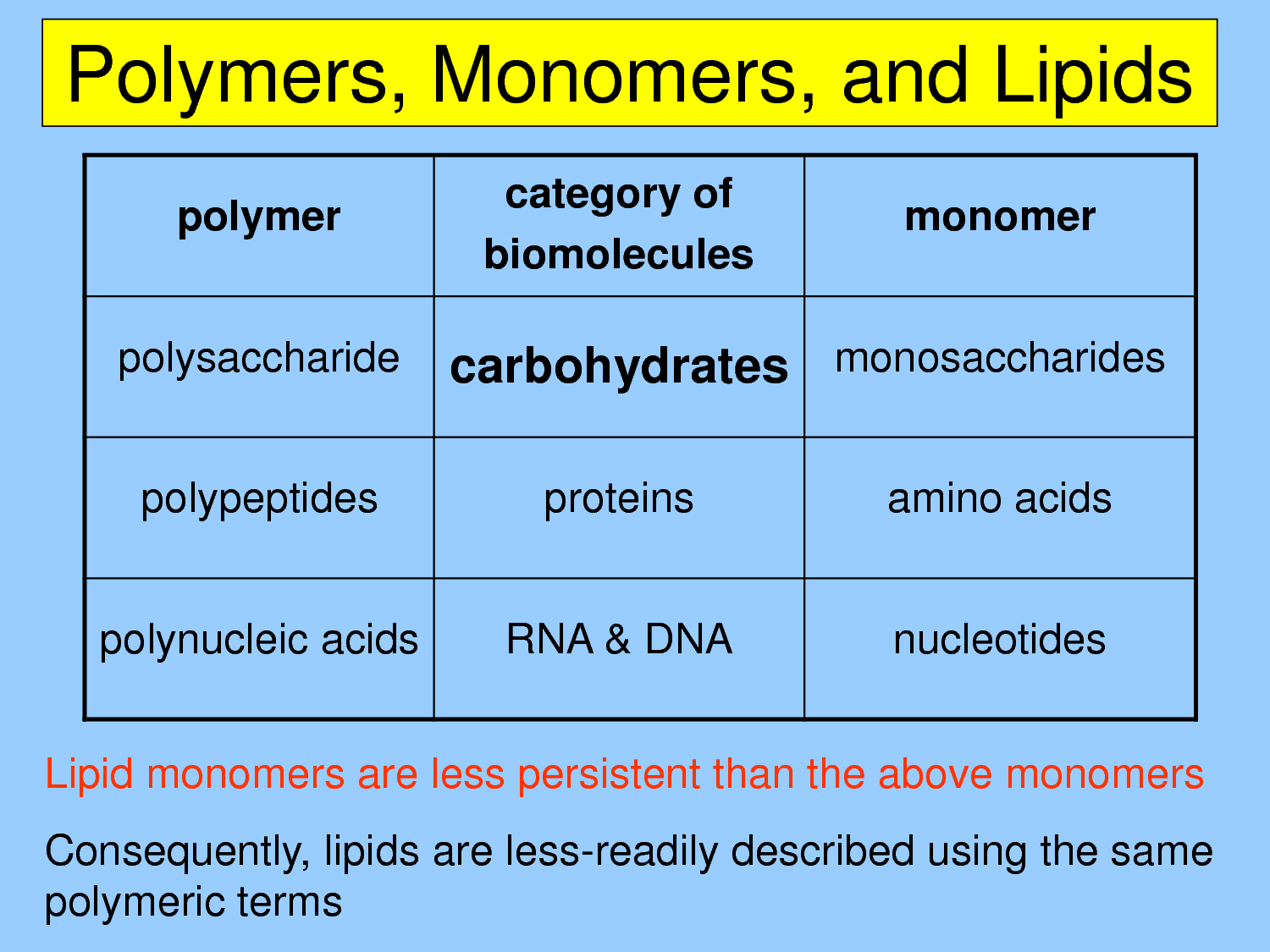
Types of Element Mixtures
There are several types of element mixtures, each with distinct characteristics and applications. The primary categories include:
- Solutions: A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where one substance is dissolved in another. Examples include sugar water and saline solution.
- Suspensions: A heterogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where particles of one substance are suspended in another. Examples include mud water and blood.
- Colloids: A mixture of two or more substances, where particles of one substance are dispersed in another, with sizes ranging from 1-1000 nanometers. Examples include milk and fog.
Each type of element mixture has unique properties and behaviors, which are essential to understand for various applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Properties of Element Mixtures
The properties of element mixtures depend on the type of mixture, the elements involved, and their proportions. Some key properties include:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | The proportion of each element in the mixture. |
| Physical State | The state of the mixture, such as solid, liquid, or gas. |
| Chemical Reactivity | The ability of the mixture to react with other substances. |
Understanding these properties is vital for predicting the behavior of element mixtures in various situations, such as chemical reactions, phase transitions, and separation processes.
Significance of Element Mixtures
Element mixtures play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Materials Science: Element mixtures are used to create materials with unique properties, such as alloys, composites, and nanomaterials.
- Chemical Engineering: Element mixtures are used in various chemical processes, such as separation, reaction, and purification.
- Biotechnology: Element mixtures are used in biomedical applications, such as drug delivery, imaging, and diagnostics.
The significance of element mixtures extends to various industries, including energy, environment, and healthcare, where they are used to develop innovative solutions and products.
Real-World Applications
Element mixtures have numerous real-world applications, including:
The production of alloys, such as steel, which is a mixture of iron and carbon, used in construction, transportation, and manufacturing. The development of composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment. The creation of nanomaterials, such as nanoparticles and nanotubes, used in electronics, energy, and biomedical applications.
These examples demonstrate the importance of element mixtures in modern technology and industry, where they are used to create materials with unique properties and applications.
What is the difference between a solution and a suspension?
+A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where one substance is dissolved in another, whereas a suspension is a heterogeneous mixture, where particles of one substance are suspended in another.
What are the properties of a colloid?
+A colloid is a mixture of two or more substances, where particles of one substance are dispersed in another, with sizes ranging from 1-1000 nanometers. Colloids have unique properties, such as stability, optical activity, and surface tension.
What are some real-world applications of element mixtures?
+Element mixtures have numerous real-world applications, including the production of alloys, composite materials, and nanomaterials, used in various industries, such as energy, environment, and healthcare.