Cordyceps Last Of Us
The Cordyceps fungus, a real-world organism, has gained significant attention due to its fictional depiction in the popular video game and TV series, The Last of Us. In the game, the Cordyceps fungus is portrayed as a mutated strain that infects humans, turning them into zombie-like creatures. However, in reality, the Cordyceps fungus is a fascinating organism with unique properties and potential benefits.
Cordyceps Fungus: A Real-World Organism

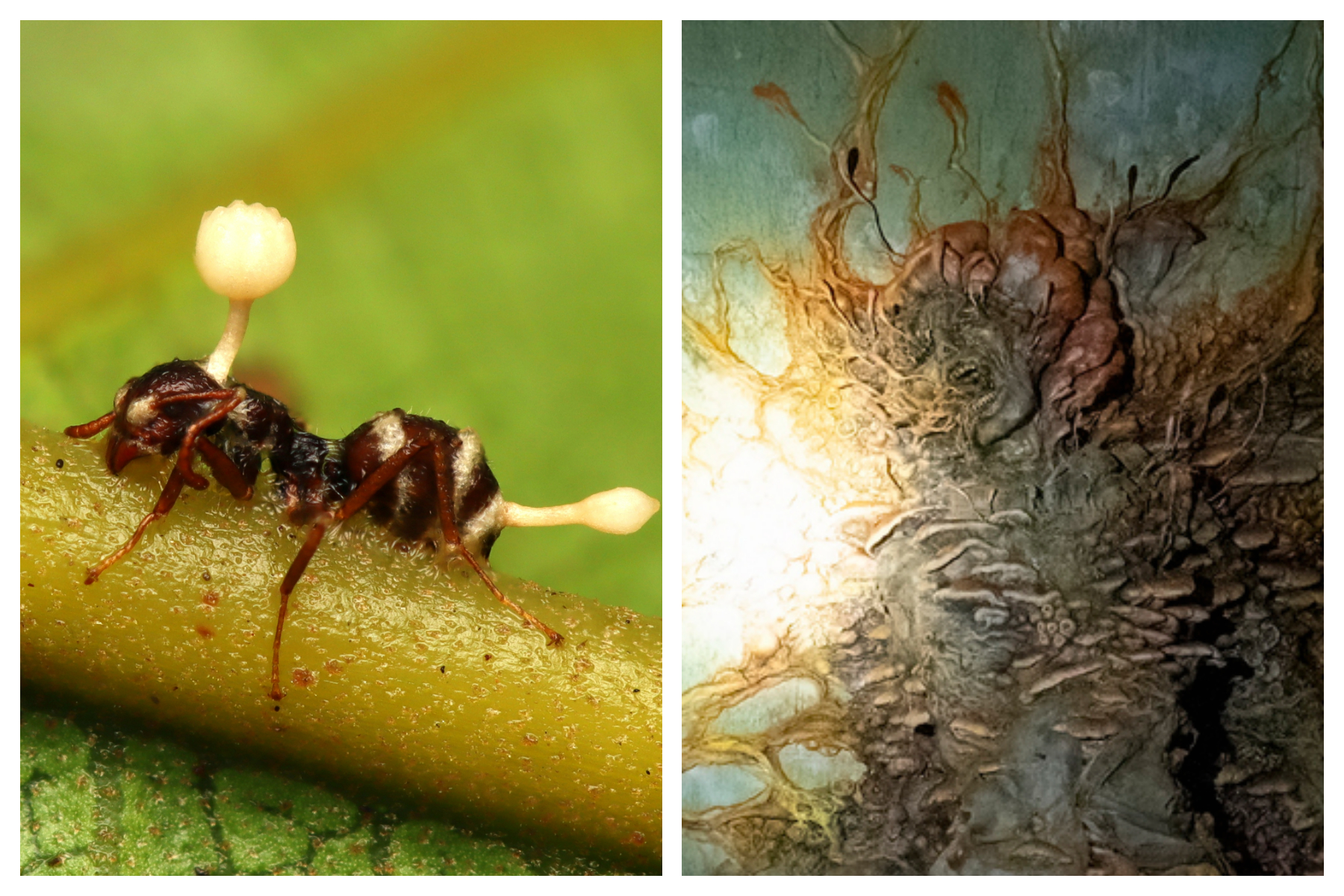
The Cordyceps fungus, also known as Cordyceps sinensis, is a type of fungus that grows in the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas and other parts of Asia. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, where it is valued for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties. The fungus grows by infecting the larvae of certain insects, eventually killing them and using their bodies as a nutrient source.
Unique Properties of Cordyceps
Cordyceps has several unique properties that make it an interesting subject of study. One of its most notable features is its ability to manipulate the behavior of its insect hosts. The fungus infects the larvae and eventually takes control of their bodies, causing them to climb to high locations before producing fruiting bodies. This behavior is thought to be an adaptation to increase the fungus’s chances of spreading its spores. In addition, Cordyceps has been found to have a range of potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving immune function, and increasing exercise performance.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | Potential to reduce inflammation and improve immune function |
| Antioxidant | Ability to neutralize free radicals and protect against cell damage |
| Immune-boosting | Potential to stimulate the immune system and increase its response to infection |

The Last of Us: A Fictional Depiction

In the world of The Last of Us, the Cordyceps fungus has mutated into a highly infectious and deadly strain that infects humans. The fungus grows inside the human body, eventually taking control of the host’s brain and turning them into zombie-like creatures. The game’s fictional depiction of Cordyceps is certainly thrilling, but it bears little resemblance to the real-world fungus.
A Comparison of Real and Fictional Cordyceps
While the real-world Cordyceps fungus is a fascinating organism with potential health benefits, the fictional depiction in The Last of Us is a highly exaggerated and distorted representation. In reality, Cordyceps is not capable of infecting humans or manipulating their behavior in the way depicted in the game. However, the game’s use of Cordyceps as a fictional villain has helped to raise awareness of the fungus and its unique properties.
- Real-world Cordyceps: a fungus that infects insects and has potential health benefits
- Fictional Cordyceps: a mutated strain that infects humans and turns them into zombie-like creatures
- Key differences: the real-world fungus is not infectious to humans and does not manipulate behavior in the same way as the fictional strain
What is the real-world Cordyceps fungus?
+
The real-world Cordyceps fungus is a type of fungus that grows in the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas and other parts of Asia. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, where it is valued for its potential health benefits.
How does the fictional depiction of Cordyceps in The Last of Us differ from the real-world fungus?
+
The fictional depiction of Cordyceps in The Last of Us is a highly exaggerated and distorted representation of the real-world fungus. In reality, Cordyceps is not capable of infecting humans or manipulating their behavior in the way depicted in the game.
What are the potential health benefits of Cordyceps?
+
Cordyceps has been found to have a range of potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving immune function, and increasing exercise performance. However, further research is needed to fully understand the effects of Cordyceps on human health.