10 Lipid Monomers For Better Health
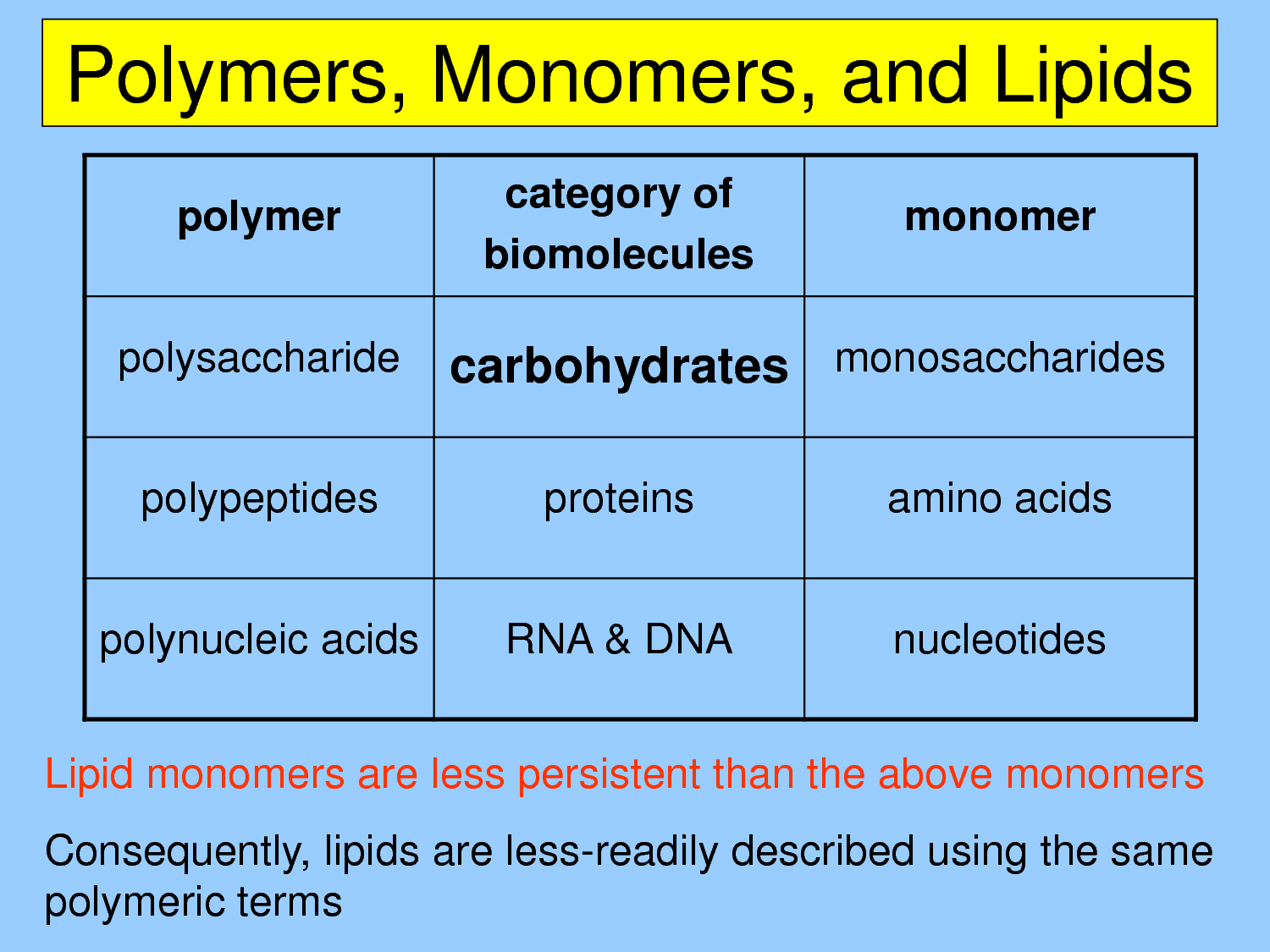
Lipid monomers are the building blocks of lipids, which are essential for various bodily functions, including energy storage, cell membrane structure, and signaling pathways. A diet rich in lipid monomers can have numerous health benefits, ranging from improved heart health to enhanced cognitive function. In this article, we will delve into the world of lipid monomers and explore 10 key types that can contribute to better health.
Introduction to Lipid Monomers

Lipid monomers are simple lipids that can be combined to form more complex lipids, such as triglycerides and phospholipids. They are typically composed of a glycerol backbone and one or more fatty acid chains. Lipid monomers can be found in various food sources, including nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. A balanced intake of these monomers is crucial for maintaining optimal health, as they play a vital role in energy production, cell signaling, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Types of Lipid Monomers
There are several types of lipid monomers, each with unique properties and functions. The following are 10 key lipid monomers that can contribute to better health:
- Glycerol: A simple lipid monomer that serves as the backbone for triglycerides and phospholipids.
- Palmitic acid: A saturated fatty acid that is abundant in palm oil and plays a role in energy production.
- Stearic acid: A saturated fatty acid found in animal fats and vegetable oils, which can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Oleic acid: A monounsaturated fatty acid abundant in olive oil, which can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Linoleic acid: A polyunsaturated fatty acid found in nuts and seeds, which is essential for skin and hair health.
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): A polyunsaturated fatty acid found in flaxseeds and chia seeds, which can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): A polyunsaturated fatty acid found in fatty fish, which can help reduce inflammation and improve brain function.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): A polyunsaturated fatty acid found in fatty fish, which is essential for brain and eye health.
- Arachidonic acid: A polyunsaturated fatty acid found in meat and dairy products, which plays a role in inflammation and immune function.
- Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA): A polyunsaturated fatty acid found in evening primrose oil, which can help reduce inflammation and improve skin health.
Health Benefits of Lipid Monomers
The health benefits of lipid monomers are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key benefits include:
Improved heart health: Lipid monomers such as oleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid can help reduce inflammation and improve lipid profiles, which can lower the risk of heart disease.
Enhanced cognitive function: Lipid monomers such as DHA and EPA can help improve brain function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Reduced inflammation: Lipid monomers such as linoleic acid and gamma-linolenic acid can help reduce inflammation, which can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as arthritis and diabetes.
Improved skin and hair health: Lipid monomers such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid can help improve skin and hair health by reducing inflammation and promoting healthy cell growth.
| Lipid Monomer | Food Sources | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | Nuts, seeds, avocados | Energy production, cell signaling |
| Palmitic acid | Palm oil, meat, dairy products | Energy production, cell membrane structure |
| Stearic acid | Animal fats, vegetable oils | Lowering cholesterol levels, improving heart health |
| Oleic acid | Olive oil, nuts, seeds | Reducing inflammation, improving heart health |
| Linoleic acid | Nuts, seeds, vegetable oils | Improving skin and hair health, reducing inflammation |
| Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) | Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts | Reducing inflammation, improving heart health |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | Fatty fish, fish oil supplements | Reducing inflammation, improving brain function |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | Fatty fish, fish oil supplements | Improving brain and eye health, reducing inflammation |
| Arachidonic acid | Meat, dairy products, egg yolks | Improving skin and hair health, reducing inflammation |
| Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) | Evening primrose oil, borage oil | Reducing inflammation, improving skin health |

Conclusion and Future Implications
In conclusion, lipid monomers play a vital role in maintaining optimal health. A diet rich in these essential lipids can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve cognitive function, and promote overall well-being. Further research is needed to fully understand the benefits and mechanisms of lipid monomers, but the existing evidence suggests that they are a crucial component of a healthy diet.
Lipid monomers are a fascinating field of study, and their potential health benefits are vast. As our understanding of these molecules grows, we can expect to see new developments in the prevention and treatment of various diseases. By incorporating a balanced mix of lipid monomers into our diets, we can take a proactive approach to maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
What are lipid monomers?
+Lipid monomers are the building blocks of lipids, which are essential for various bodily functions, including energy storage, cell membrane structure, and signaling pathways.
What are the health benefits of lipid monomers?
+The health benefits of lipid monomers include improved heart health, enhanced cognitive function, reduced inflammation, and improved skin and hair health.
What food sources are rich in lipid monomers?
+Food sources rich in lipid monomers include nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil, fatty fish, and whole grains.
