Msds Sheet For Sodium Hydroxide
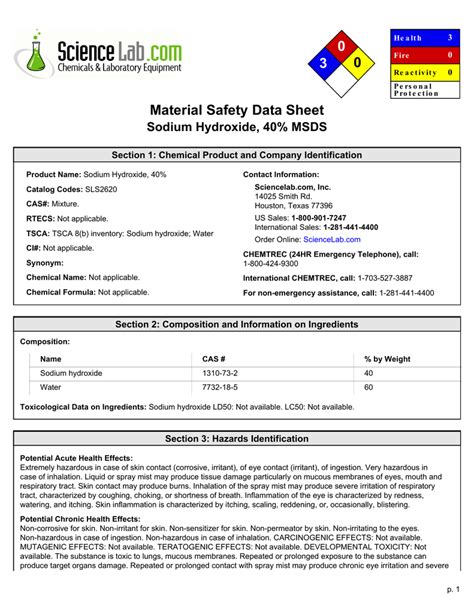
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye or caustic soda, is a highly corrosive and toxic substance that requires careful handling and storage. The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for sodium hydroxide provides critical information on the safe handling, use, storage, and disposal of this chemical.
Introduction to Sodium Hydroxide
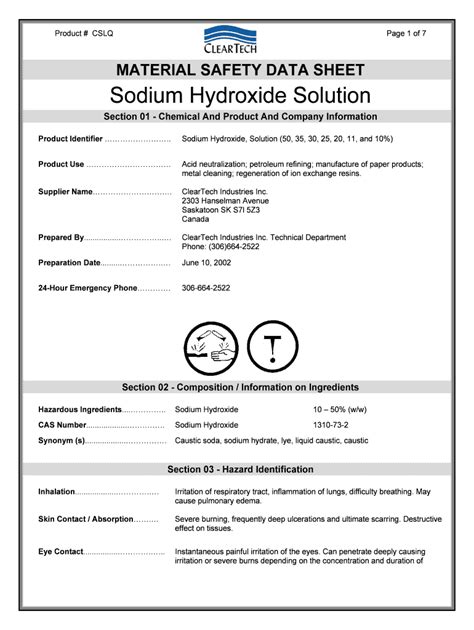
Sodium hydroxide is a white, odorless, and highly caustic solid that is commonly used in various industrial applications, including the manufacture of paper, textiles, and soap. It is also used in the production of biodiesel and as a drain cleaner. The chemical formula for sodium hydroxide is NaOH, and it has a molecular weight of 40.00 g/mol.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Sodium hydroxide is highly soluble in water and has a melting point of 318°C (604°F). It is a strong base that can neutralize acids and is highly reactive with many substances, including metals and organic compounds. The physical and chemical properties of sodium hydroxide are as follows:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | NaOH |
| Molecular Weight | 40.00 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 318°C (604°F) |
| Boiling Point | 1388°C (2530°F) |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble |

Hazards and Risks

Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive and toxic substance that can cause severe burns and eye damage. It can also release toxic fumes when it comes into contact with acids or other substances. The hazards and risks associated with sodium hydroxide are as follows:
Corrosive Properties: Sodium hydroxide can cause severe burns and eye damage, including permanent vision loss. It can also damage skin and mucous membranes, leading to pain, redness, and blistering.
Toxicity: Sodium hydroxide is highly toxic and can be fatal if ingested. It can cause respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and other systemic problems.
Environmental Hazards: Sodium hydroxide can contaminate soil, water, and air, and can harm aquatic life and other organisms.
Safe Handling and Storage
To minimize the risks associated with sodium hydroxide, it is essential to handle and store it safely. The following precautions should be taken:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear protective clothing, including gloves, safety glasses, and a face mask, when handling sodium hydroxide.
Storage: Store sodium hydroxide in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from incompatible substances and heat sources.
Handling: Handle sodium hydroxide with care, avoiding skin contact and inhalation of fumes. Use a fork lift or other mechanical equipment to move large quantities.
First Aid and Emergency Procedures
In the event of an accident or exposure to sodium hydroxide, the following first aid and emergency procedures should be followed:
Eye Exposure: Flush eyes with water for at least 15 minutes, and seek medical attention immediately.
Skin Exposure: Wash affected area with soap and water, and seek medical attention if irritation persists.
Inhalation: Move to fresh air, and seek medical attention if respiratory symptoms occur.
Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting, and seek medical attention immediately.
Disposal and Spill Response
Sodium hydroxide should be disposed of in accordance with local and national regulations. In the event of a spill, the following procedures should be followed:
Containment: Contain the spill using absorbent materials, such as sand or vermiculite.
Cleanup: Neutralize the spill with a weak acid, such as vinegar or citric acid, and dispose of the waste in accordance with regulations.
What are the hazards associated with sodium hydroxide?
+
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive and toxic substance that can cause severe burns and eye damage. It can also release toxic fumes when it comes into contact with acids or other substances.
How should sodium hydroxide be stored?
+
Sodium hydroxide should be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from incompatible substances and heat sources.
What should be done in case of skin exposure to sodium hydroxide?
+
Wash the affected area with soap and water, and seek medical attention if irritation persists.