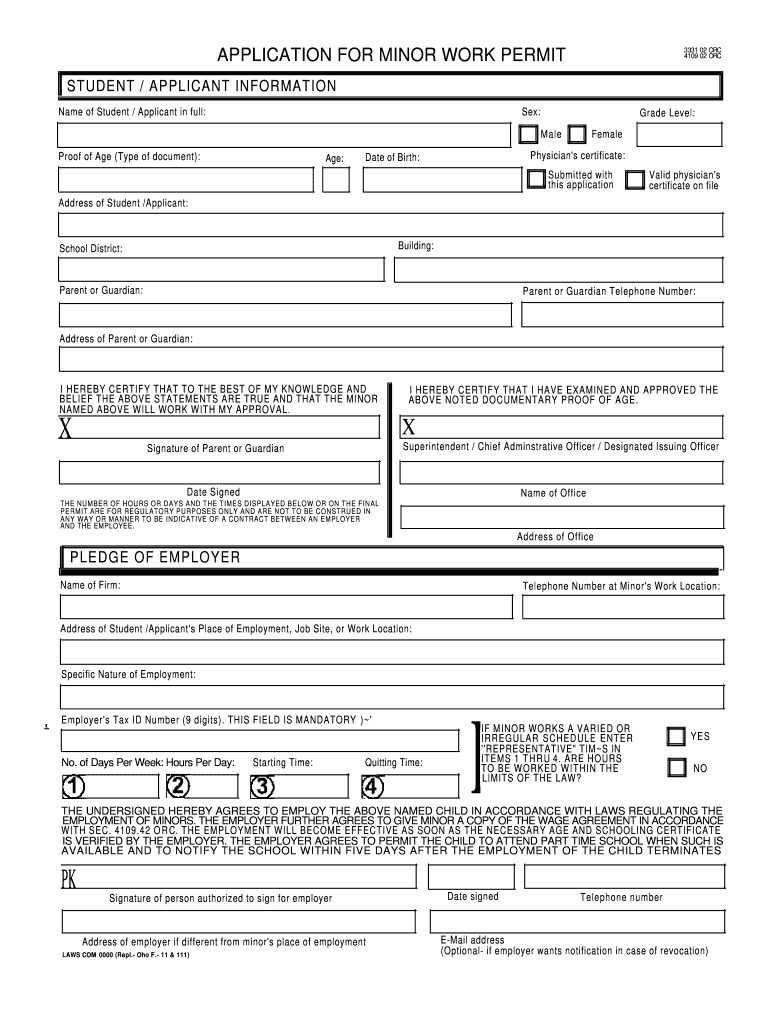
Work Permit For Minors

The process of obtaining a work permit for minors is a crucial aspect of ensuring that young individuals are protected and safe in the workplace. In the United States, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) regulates the employment of minors, and each state has its own set of rules and regulations regarding work permits. The FLSA sets a minimum age of 14 for non-agricultural employment, but some states have higher minimum age requirements.
Types of Work Permits for Minors

There are several types of work permits that minors can obtain, depending on the type of employment and the state in which they reside. The most common types of work permits include:
- Entertainment Work Permit: This permit is required for minors who work in the entertainment industry, such as in film, television, or theater productions.
- Agricultural Work Permit: This permit is required for minors who work in agricultural jobs, such as on farms or in orchards.
- Non-Agricultural Work Permit: This permit is required for minors who work in non-agricultural jobs, such as in retail, food service, or office settings.
Requirements for Obtaining a Work Permit
To obtain a work permit, minors must meet certain requirements, which vary by state. Some common requirements include:
- Age: Minors must be at least 14 years old to apply for a work permit, although some states have higher minimum age requirements.
- Proof of Age: Minors must provide proof of age, such as a birth certificate or passport.
- Proof of Residency: Minors must provide proof of residency, such as a utility bill or lease agreement.
- Parental Consent: Minors must obtain parental consent to work, which is typically provided on the work permit application.
| State | Minimum Age Requirement | Work Permit Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| California | 14 | Proof of age, proof of residency, parental consent |
| New York | 14 | Proof of age, proof of residency, parental consent |
| Texas | 14 | Proof of age, proof of residency, parental consent |

Child Labor Laws and Regulations
Child labor laws and regulations are in place to protect minors from exploitation and ensure their safety in the workplace. Some key aspects of child labor laws include:
- Hours of Work: Minors are restricted from working certain hours, such as during school hours or late at night.
- Types of Jobs: Minors are prohibited from working in certain jobs, such as those that involve hazardous materials or equipment.
- Wages and Benefits: Minors are entitled to minimum wage and other benefits, such as workers’ compensation and unemployment insurance.
Consequences of Violating Child Labor Laws
Employers who violate child labor laws can face serious consequences, including:
- Fines and Penalties: Employers can be fined and penalized for violating child labor laws.
- Lawsuits and Litigation: Employers can be sued by minors or their parents for violating child labor laws.
- Loss of Business License: Employers can lose their business license for violating child labor laws.
What is the minimum age requirement for obtaining a work permit?
+The minimum age requirement for obtaining a work permit varies by state, but most states require minors to be at least 14 years old.
What types of jobs are prohibited for minors?
+Minors are prohibited from working in jobs that involve hazardous materials or equipment, such as construction or manufacturing jobs.
What are the consequences of violating child labor laws?
+Employers who violate child labor laws can face fines and penalties, lawsuits and litigation, and loss of business license.