When To Use C Vs F? Temperature Tips Inside

Temperature is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, and understanding when to use Celsius (C) versus Fahrenheit (F) is essential for accurate communication and measurement. The choice between these two temperature scales often depends on the context, location, and specific application. In this article, we will delve into the history of both scales, their differences, and provide temperature tips on when to use each.
History of Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
The Celsius scale, formerly known as the centigrade scale, was introduced by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. It is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, where 0°C is the freezing point and 100°C is the boiling point. On the other hand, the Fahrenheit scale was developed by German physicist Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724. It is also based on the freezing and boiling points of water, but with 32°F as the freezing point and 212°F as the boiling point.
Differences Between Celsius and Fahrenheit
The main difference between the two scales is the size of the degree. A Celsius degree is larger than a Fahrenheit degree, with 1°C equal to 1.8°F. This means that a temperature change of 1°C is equivalent to a change of 1.8°F. Additionally, the Celsius scale is more widely used in scientific and international applications, while the Fahrenheit scale is more commonly used in everyday applications in the United States.
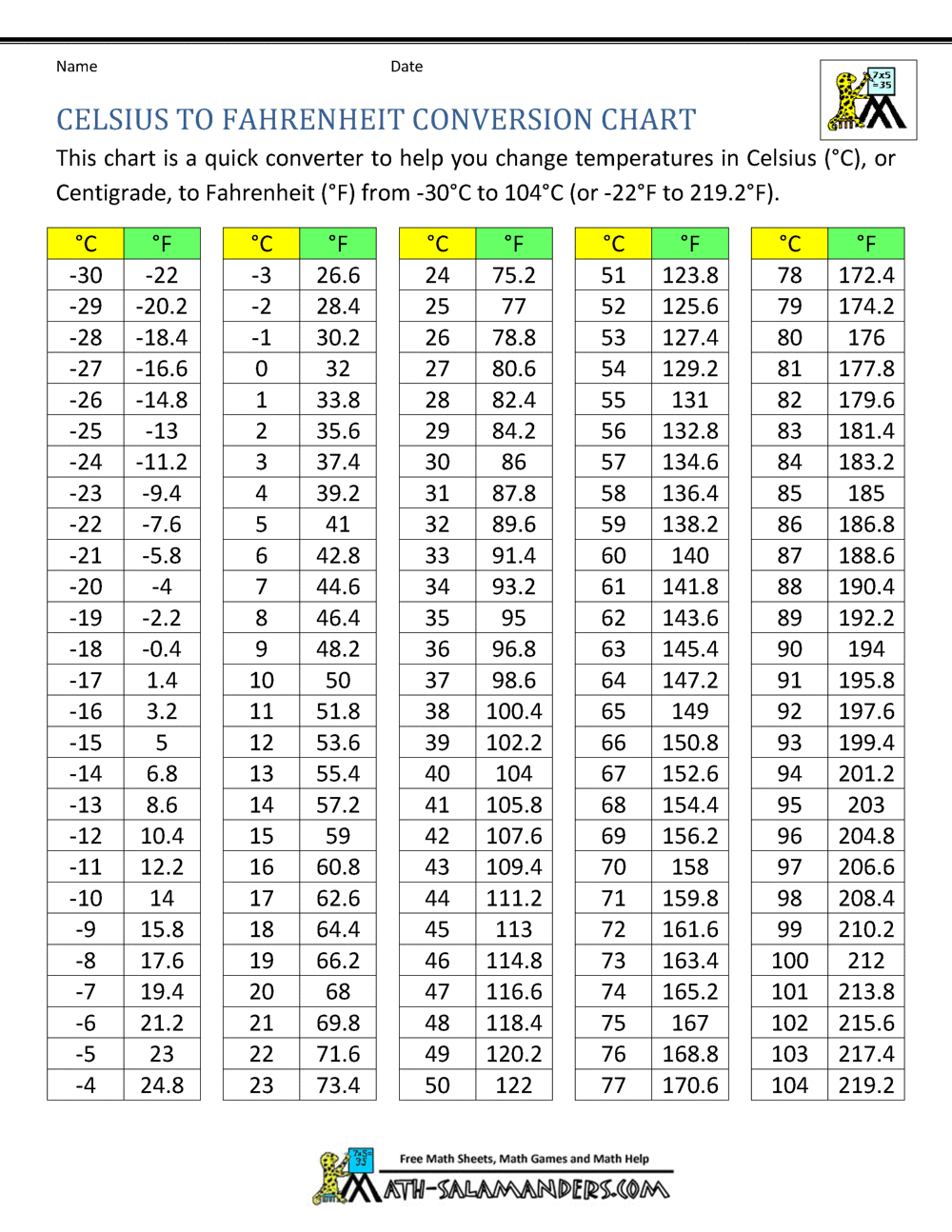
The following table illustrates the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit for common temperatures:
| Celsius | Fahrenheit |
|---|---|
| -20°C | -4°F |
| 0°C | 32°F |
| 20°C | 68°F |
| 37°C | 98.6°F |
| 100°C | 212°F |

When to Use Celsius

Celsius is the preferred temperature scale in most scientific and international applications. It is widely used in:
- Scientific research and experiments
- Weather forecasting and meteorology
- International trade and commerce
- Cooking and food safety guidelines
In these contexts, Celsius provides a more precise and consistent measurement of temperature, which is critical for accurate calculations and predictions.
Examples of Celsius in Everyday Life
Celsius is commonly used in everyday applications such as:
Cooking: Recipes often specify temperatures in Celsius, such as 180°C for baking or 100°C for boiling water. Thermometers used in cooking typically display temperatures in Celsius.
Weather forecasting: Weather reports and forecasts usually provide temperatures in Celsius, such as "today's high will be 25°C." Temperature fluctuations are also measured in Celsius, helping to predict weather patterns.
When to Use Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit is commonly used in everyday applications in the United States, particularly in:
- Weather forecasting and temperature measurement
- Cooking and food preparation
- Heating and cooling systems
In these contexts, Fahrenheit provides a more familiar and intuitive measurement of temperature, which is often preferred by the general public.
Examples of Fahrenheit in Everyday Life
Fahrenheit is commonly used in everyday applications such as:
Heating and cooling systems: Thermostats and temperature controls often display temperatures in Fahrenheit, such as 72°F for a comfortable indoor temperature. Air conditioning units and heating systems typically use Fahrenheit for temperature settings.
Weather forecasting: While Celsius is widely used in scientific applications, Fahrenheit is still commonly used in weather forecasts and temperature measurements in the United States, such as "today's high will be 77°F." Temperature records are also often reported in Fahrenheit, such as the highest temperature ever recorded in a particular region.
What is the difference between Celsius and Fahrenheit?
+The main difference between the two scales is the size of the degree. A Celsius degree is larger than a Fahrenheit degree, with 1°C equal to 1.8°F.
When should I use Celsius?
+Celsius is the preferred temperature scale in most scientific and international applications, such as scientific research, weather forecasting, and international trade.
When should I use Fahrenheit?
+Fahrenheit is commonly used in everyday applications in the United States, particularly in weather forecasting, cooking, and heating and cooling systems.
