What Is Rotational Kinetic Energy Formula? Simplified

The rotational kinetic energy of an object is the energy it possesses due to its rotation. This form of energy is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it is crucial for understanding the behavior of rotating systems. The rotational kinetic energy formula is a mathematical expression that describes the relationship between the energy of a rotating object and its rotational parameters.
Rotational Kinetic Energy Formula
The rotational kinetic energy formula is given by:
Ek = (1/2) \* I \* ω^2
where:
- Ek is the rotational kinetic energy of the object
- I is the moment of inertia of the object
- ω is the angular velocity of the object
Moment of Inertia (I)
The moment of inertia (I) is a measure of an object's resistance to changes in its rotation. It depends on the mass distribution of the object and the axis of rotation. For a point mass, the moment of inertia is given by:
I = m \* r^2
where:
- m is the mass of the object
- r is the distance from the axis of rotation to the object
For more complex objects, the moment of inertia can be calculated using the following formulas:
| Object | Moment of Inertia (I) |
|---|---|
| Solid sphere | (2/5) \* m \* r^2 |
| Hollow sphere | (2/3) \* m \* r^2 |
| Solid cylinder | (1/2) \* m \* r^2 |
| Ring | m \* r^2 |
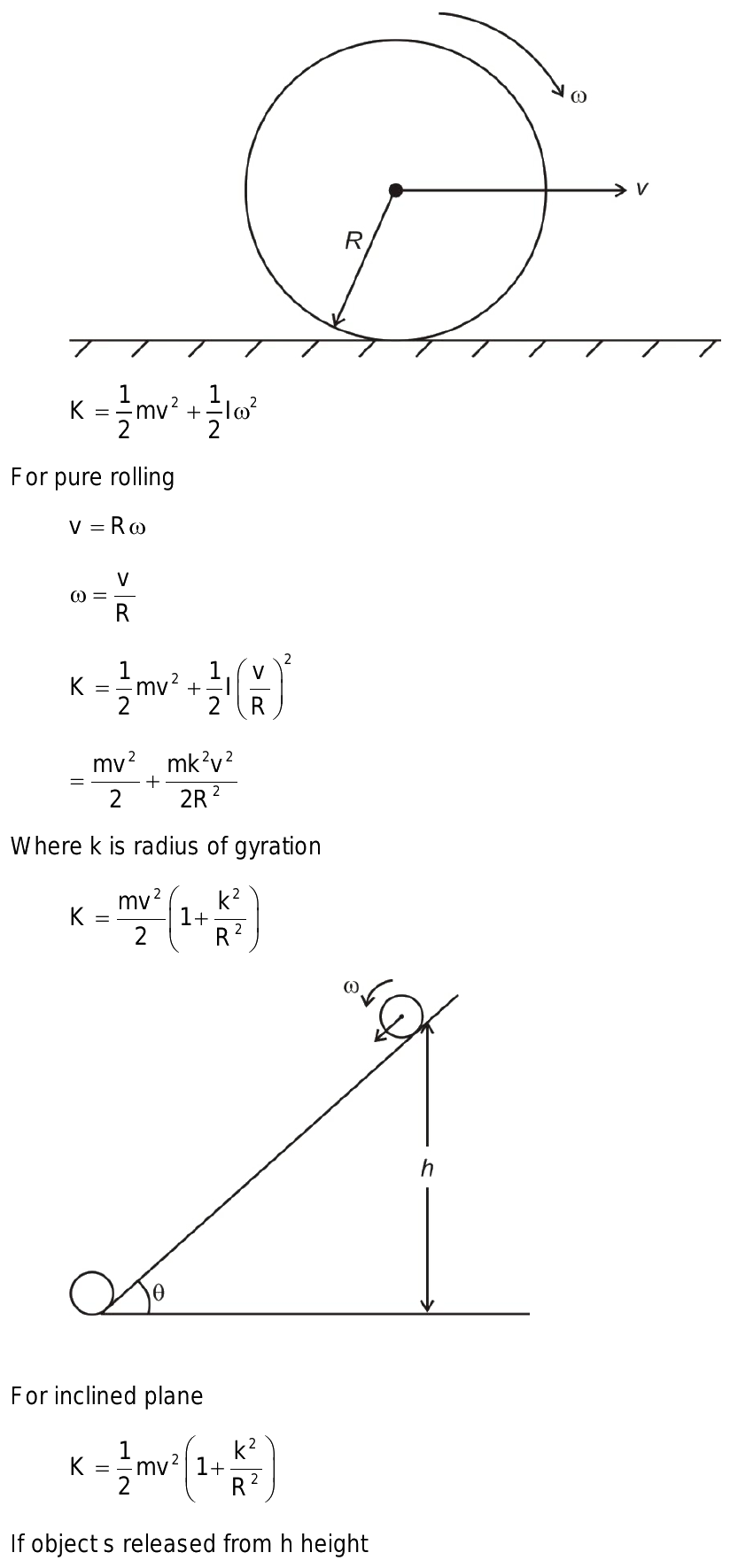
Angular Velocity (ω)
The angular velocity (ω) is a measure of an object’s rate of rotation. It is typically expressed in units of radians per second (rad/s). The angular velocity can be calculated using the following formula:
ω = θ / t
where:
- θ is the angular displacement of the object
- t is the time over which the displacement occurs
Applications of Rotational Kinetic Energy
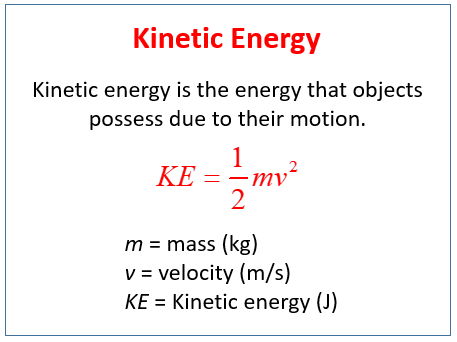
The rotational kinetic energy formula has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and technology. Some examples include:
- Designing more efficient wind turbines and hydroelectric generators
- Optimizing the performance of electric motors and gearboxes
- Understanding the behavior of rotating shafts and bearings in machinery
- Analyzing the stability of rotating systems, such as gyroscopes and flywheels
In conclusion, the rotational kinetic energy formula is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering. By understanding the relationship between the energy of a rotating object and its rotational parameters, we can design more efficient and effective systems, and optimize the performance of rotating machinery.
What is the rotational kinetic energy formula?
+
The rotational kinetic energy formula is given by Ek = (1⁄2) * I * ω^2, where Ek is the rotational kinetic energy, I is the moment of inertia, and ω is the angular velocity.
What is the moment of inertia (I)?
+
The moment of inertia (I) is a measure of an object’s resistance to changes in its rotation. It depends on the mass distribution of the object and the axis of rotation.
What is the angular velocity (ω)?
+
The angular velocity (ω) is a measure of an object’s rate of rotation. It is typically expressed in units of radians per second (rad/s).