What Is Inverse Square Law? Simplified Formula
The Inverse Square Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes how the intensity of a physical quantity, such as light, sound, or radiation, decreases with distance from the source. This law states that the intensity of the quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source. In simpler terms, as you move further away from the source, the intensity of the quantity decreases rapidly.
Understanding the Inverse Square Law

The Inverse Square Law can be mathematically expressed as: I ∝ 1/r^2, where I is the intensity of the quantity and r is the distance from the source. This means that if you double the distance from the source, the intensity of the quantity will decrease to one-quarter of its original value. The law applies to various physical phenomena, including electromagnetic radiation, sound waves, and gravitational forces.
Derivation of the Inverse Square Law
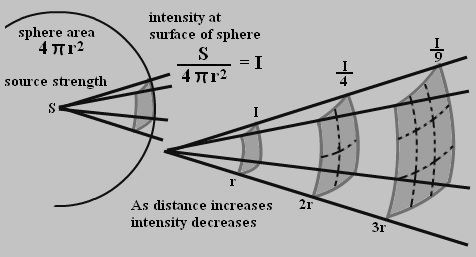
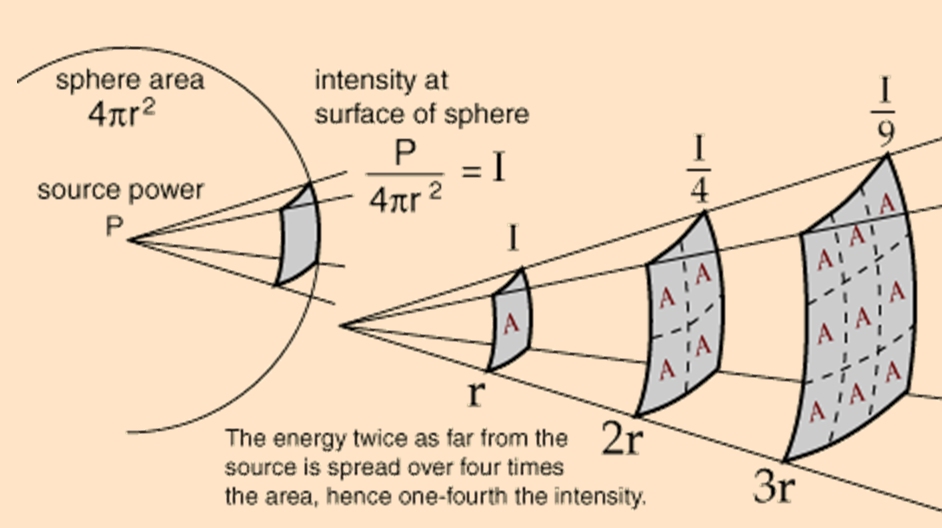
The Inverse Square Law can be derived by considering the surface area of a sphere. Imagine a point source of light or radiation at the center of a sphere. The intensity of the radiation is proportional to the amount of energy that passes through a unit area of the sphere’s surface. As the distance from the source increases, the surface area of the sphere increases, and the energy is spread out over a larger area, resulting in a decrease in intensity.
The formula for the surface area of a sphere (A = 4πr^2) shows that the area increases with the square of the radius. Since the intensity is inversely proportional to the area, it decreases with the square of the distance. This leads to the simplified formula: I = k / r^2, where k is a constant of proportionality.
| Distance from Source | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 1 meter | 100% |
| 2 meters | 25% |
| 4 meters | 6.25% |

Applications of the Inverse Square Law
The Inverse Square Law has numerous practical applications in fields such as:
- Photography: understanding how light intensity decreases with distance helps photographers adjust their camera settings for optimal exposure.
- Radiation Safety: the law is used to calculate the safe distance from radiation sources and to design protective shielding.
- Acoustics: the Inverse Square Law explains how sound intensity decreases with distance, which is essential for designing auditoriums and concert halls.
- Astronomy: the law is used to calculate the brightness of celestial objects, such as stars and galaxies, based on their distance from Earth.
Limitations and Exceptions
While the Inverse Square Law is a fundamental principle, it has limitations and exceptions. For example, in certain situations, such as in the presence of obstacles or reflective surfaces, the law may not apply. Additionally, the law assumes a point source and a homogeneous medium, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios.
In optics, the Inverse Square Law is used to describe the decrease in light intensity with distance. However, when dealing with diffuse reflection or scattering, the law may not accurately predict the intensity of the reflected or scattered light.
What is the Inverse Square Law in simple terms?
+The Inverse Square Law states that the intensity of a physical quantity, such as light or sound, decreases rapidly as you move further away from the source.
What are some practical applications of the Inverse Square Law?
+The Inverse Square Law has applications in photography, radiation safety, acoustics, and astronomy, among other fields.
Are there any limitations or exceptions to the Inverse Square Law?
+Yes, the law has limitations and exceptions, such as in the presence of obstacles or reflective surfaces, and when dealing with diffuse reflection or scattering.