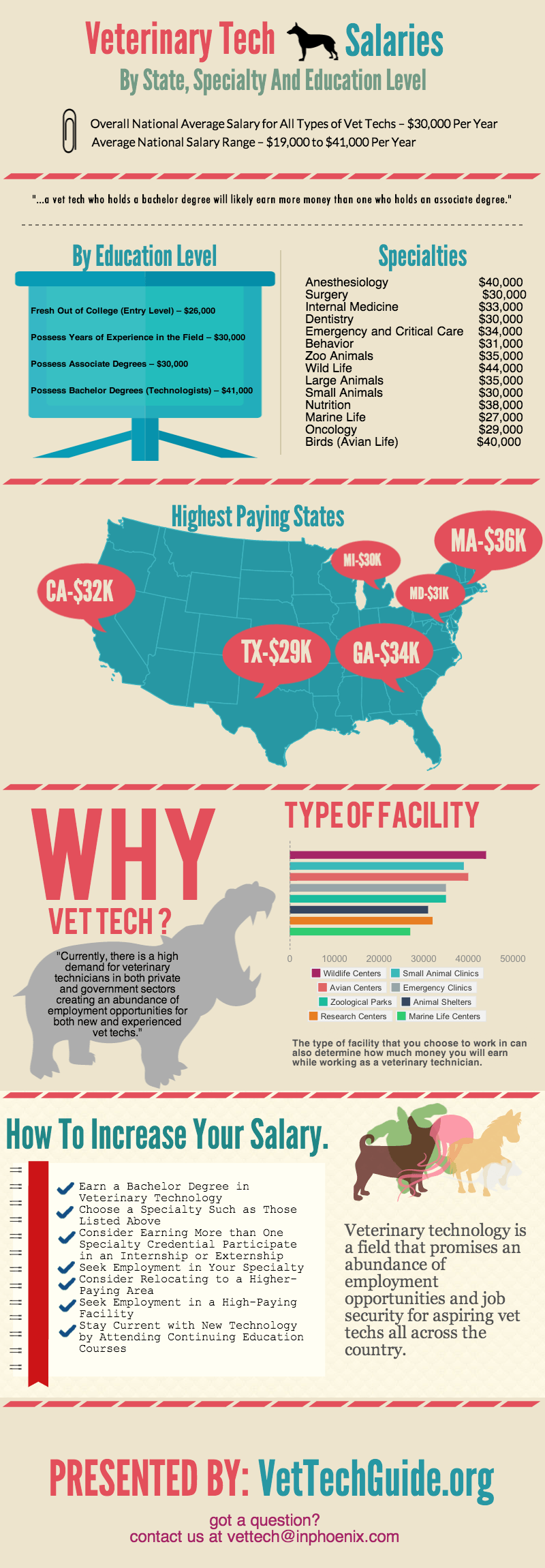
What Is Icd 10 Code For Hypomagnesemia? Accurate Diagnosis
Hypomagnesemia, a condition characterized by low magnesium levels in the blood, is a significant electrolyte imbalance that can lead to various clinical manifestations, including muscle weakness, fatigue, and cardiac arrhythmias. Accurate diagnosis and coding of hypomagnesemia are crucial for appropriate patient management and billing purposes. The ICD-10 code for hypomagnesemia is E83.41, which is used to indicate a diagnosis of hypomagnesemia in the patient's medical record.
Understanding ICD-10 Coding for Hypomagnesemia
The ICD-10 coding system, which stands for the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, is a comprehensive system used globally for coding and classifying diseases, symptoms, and procedures. It provides a standardized way of documenting patient data, which is essential for clinical, administrative, and epidemiological purposes. The code E83.41 specifically pertains to hypomagnesemia, distinguishing it from other electrolyte imbalances.
Importance of Accurate Coding
Accurate coding of hypomagnesemia with the ICD-10 code E83.41 is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that the patient receives the correct treatment plan, as the diagnosis directly influences the choice of therapeutic interventions. Secondly, it facilitates communication among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care. Finally, accurate coding is essential for billing and insurance claims, as it verifies the medical necessity of the services provided.
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| E83.41 | Hypomagnesemia |
| E83.40 | Magnesium deficiency, unspecified |
| E87.1 | Hypomagnesemia in hyperaldosteronism |
The diagnosis of hypomagnesemia involves clinical evaluation and laboratory testing, particularly measuring serum magnesium levels. However, the interpretation of these levels must consider the patient's overall clinical picture, as symptoms can vary widely. Mild cases might be asymptomatic, while severe hypomagnesemia can lead to life-threatening complications, such as respiratory failure or cardiac arrest.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
Clinical manifestations of hypomagnesemia can include muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, and neuromuscular excitability. In severe cases, patients might experience seizures or cardiac arrhythmias. The diagnosis is typically made by measuring the serum magnesium level, which is considered low if it falls below 1.8 mg/dL (or 0.74 mmol/L).
Treatment and Management
Treatment of hypomagnesemia involves magnesium supplementation, either orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the deficiency and the presence of symptoms. It’s crucial to identify and address the underlying cause of the magnesium deficiency to prevent recurrence. In some cases, particularly where hypomagnesemia is a result of an underlying condition, treating the primary disorder is essential for managing the magnesium levels.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis and coding of hypomagnesemia using the ICD-10 code E83.41 are critical for patient care, communication among healthcare providers, and administrative purposes. Understanding the clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of hypomagnesemia can help in providing high-quality care and ensuring that patients receive appropriate management for their condition.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypomagnesemia?
+
The ICD-10 code for hypomagnesemia is E83.41.
What are the symptoms of hypomagnesemia?
+
Symptoms can include muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, and in severe cases, seizures or cardiac arrhythmias.
How is hypomagnesemia diagnosed?
+
Diagnosis is typically made by measuring the serum magnesium level, which is considered low if it falls below 1.8 mg/dL (or 0.74 mmol/L).