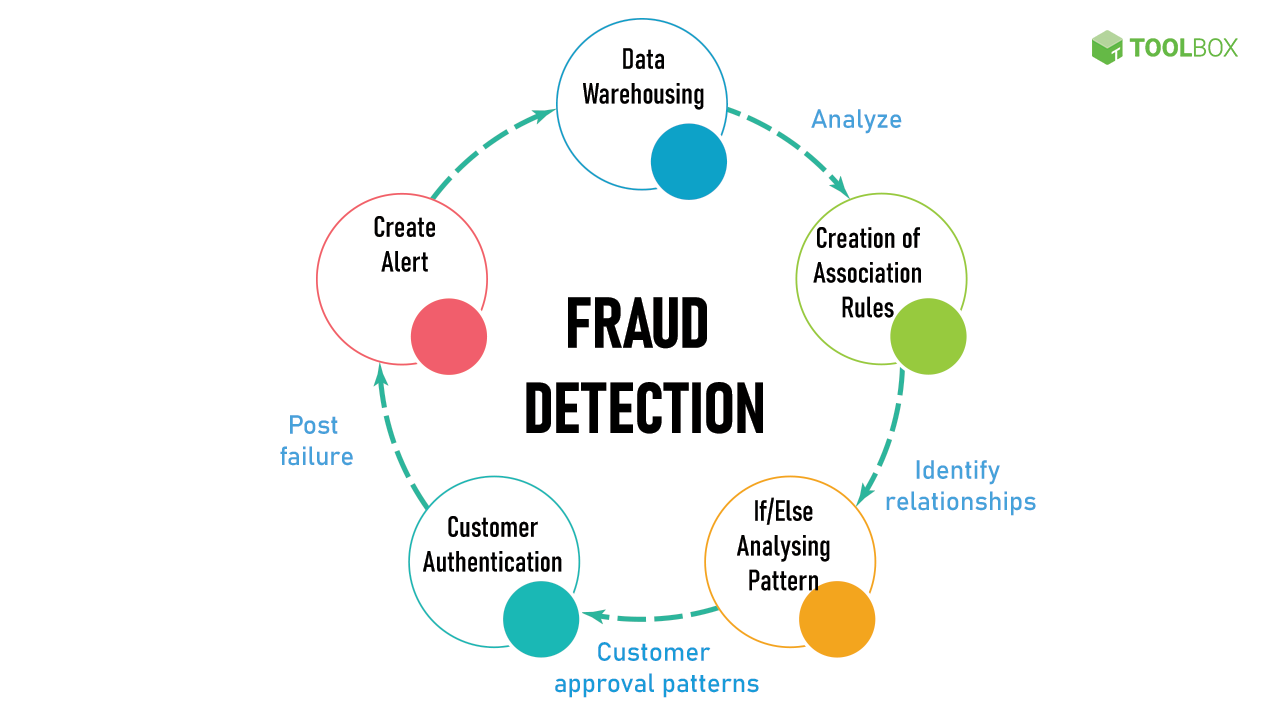
What Is Density? Understanding Science Made Easy

Density is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of matter. It is defined as the amount of mass per unit volume of a substance. In simpler terms, density is a measure of how tightly packed the molecules of a substance are. The density of an object determines its weight and how it interacts with other objects. Understanding density is essential in various fields, including engineering, chemistry, and materials science. In this article, we will delve into the world of density, exploring its definition, types, and applications.
What is Density?

Density is a physical property of a substance that is calculated by dividing its mass by its volume. The formula for density is: density = mass / volume. The unit of density is typically measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). Density is an intensive property, meaning it does not depend on the size or amount of the substance. For example, the density of a small rock and a large rock of the same material will be the same.
Types of Density
There are several types of density, including:
- True density: The density of a substance without any air pockets or voids.
- Bulk density: The density of a substance, including any air pockets or voids.
- Apparent density: The density of a substance as it appears to be, taking into account any air pockets or voids.
- Relative density: The ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water.
Understanding the different types of density is crucial in various applications, such as engineering and materials science. For instance, the bulk density of a material can affect its strength and durability, while the apparent density can impact its buoyancy and flotation.
Applications of Density
Density has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Engineering: Density is used to calculate the weight and stress of materials, ensuring the stability and safety of structures.
- Chemistry: Density is used to identify and analyze substances, as well as to determine their purity and concentration.
- Materials Science: Density is used to develop new materials with specific properties, such as strength, conductivity, and optical properties.
- Geology: Density is used to study the Earth’s crust and mantle, as well as to locate mineral deposits and underground water reservoirs.
The applications of density are vast and diverse, and its importance cannot be overstated. By understanding density, scientists and engineers can develop new technologies, materials, and solutions that transform our daily lives.
Density in Everyday Life
Density is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications in our daily lives. For example:
- Shipping and transportation: Density affects the weight and volume of cargo, impacting shipping costs and logistics.
- Cooking and food processing: Density is used to determine the texture and consistency of food products, such as bread, cakes, and sauces.
- Medical applications: Density is used in medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays and CT scans, to diagnose and treat diseases.
- Environmental science: Density is used to study ocean currents, water pollution, and climate change.
The examples above illustrate the significance of density in various aspects of our lives, from the food we eat to the medical treatments we receive.
| Substance | Density (kg/m³) |
|---|---|
| Air | 1.2 |
| Water | 1000 |
| Steel | 7800 |
| Gold | 19300 |

Measuring Density
Measuring density can be done using various methods, including:
- Hydrometer: A device that measures the density of a liquid by floating it in a cylinder.
- Pycnometer: A device that measures the density of a solid or liquid by measuring its volume and mass.
- Archimedes’ principle: A method that measures the density of an object by measuring its weight in air and water.
Understanding how to measure density is essential in various applications, from materials science to environmental monitoring. By using the right measurement techniques, scientists and engineers can determine the density of substances with high accuracy.
Challenges and Limitations
While density is a fundamental concept, there are challenges and limitations to its measurement and application. For example:
- Uncertainty: Density measurements can be affected by various factors, such as temperature, pressure, and humidity.
- Complexity: Density can be difficult to measure in complex systems, such as porous materials or mixtures.
- Scalability: Density measurements can be challenging to scale up or down, depending on the size and complexity of the system.
Despite these challenges, scientists and engineers continue to develop new techniques and technologies to measure and apply density in various fields.
What is the difference between density and specific gravity?
+
Density and specific gravity are related but distinct concepts. Density is a measure of the mass per unit volume of a substance, while specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water.
How does density affect the behavior of materials?
+
Density affects the behavior of materials in various ways, including their strength, conductivity, and optical properties. For example, materials with high density tend to be stronger and more durable, while those with low density tend to be more flexible and prone to deformation.
What are some common applications of density in everyday life?
+
Density has numerous applications in everyday life, including shipping and transportation, cooking and food processing, medical applications, and environmental science. Understanding density is essential in these fields, as it affects the behavior and properties of materials and substances.