Standard Distribution Table
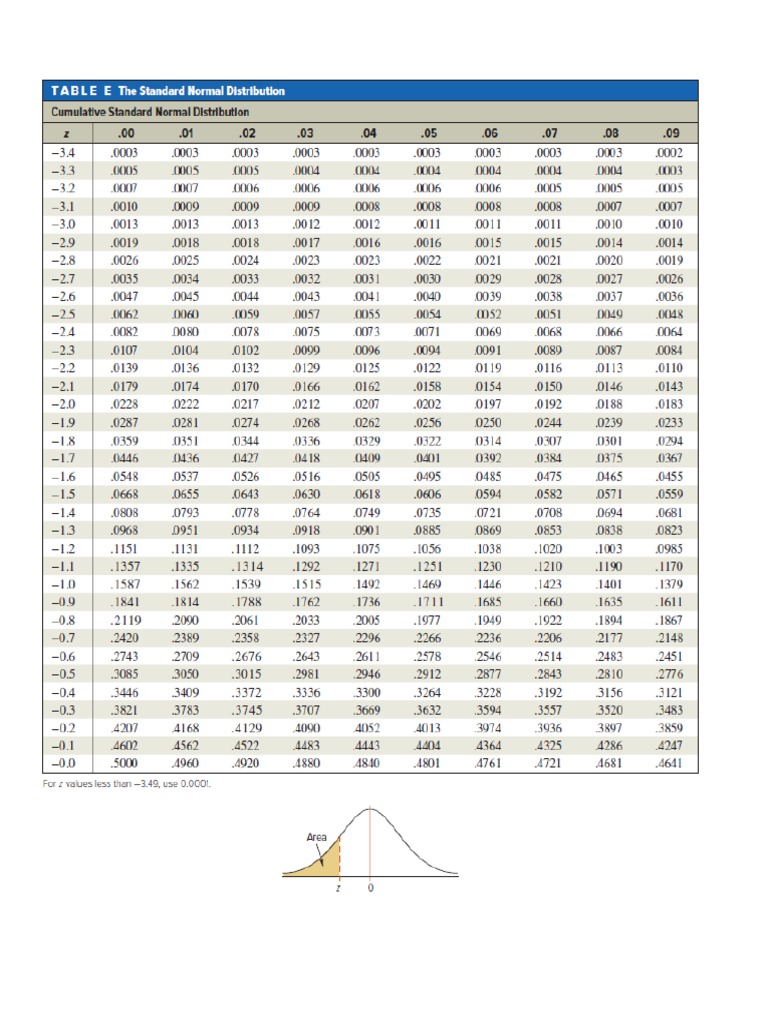
The standard distribution table, also known as the z-table, is a statistical tool used to find the probability that a random variable with a normal distribution will fall within a certain range. It is a crucial concept in statistics and is widely used in various fields such as business, economics, and social sciences. In this article, we will delve into the world of standard distribution tables, exploring their definition, construction, and application in real-world scenarios.
What is a Standard Distribution Table?

A standard distribution table is a table that shows the area under the standard normal curve to the left of a given z-score. The standard normal curve, also known as the z-distribution, is a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. The z-table is used to find the probability that a random variable with a normal distribution will fall within a certain range, given its mean and standard deviation.
Construction of a Standard Distribution Table
The construction of a standard distribution table involves calculating the area under the standard normal curve to the left of a given z-score. This is typically done using numerical integration or other approximation methods. The resulting table shows the area under the curve to the left of a given z-score, which can be used to find the probability that a random variable will fall within a certain range.
The table is typically organized with z-scores ranging from -3 to 3, with increments of 0.01. Each z-score corresponds to a specific area under the curve, which is represented as a decimal value between 0 and 1. For example, a z-score of 1.96 corresponds to an area under the curve of approximately 0.975, indicating that there is a 97.5% probability that a random variable with a standard normal distribution will fall below a z-score of 1.96.
| Z-Score | Area Under the Curve |
|---|---|
| -3.00 | 0.0013 |
| -2.00 | 0.0228 |
| -1.00 | 0.1587 |
| 0.00 | 0.5000 |
| 1.00 | 0.8413 |
| 2.00 | 0.9772 |
| 3.00 | 0.9987 |

Applications of Standard Distribution Tables

Standard distribution tables have a wide range of applications in various fields, including business, economics, and social sciences. Some of the most common applications include:
- Hypothesis testing: Standard distribution tables are used to determine the probability of rejecting a null hypothesis, given a specific test statistic and significance level.
- Confidence intervals: Standard distribution tables are used to construct confidence intervals for population parameters, such as the mean and proportion.
- Predictive modeling: Standard distribution tables are used to predict the behavior of random variables and make informed decisions based on probability estimates.
Real-World Examples
Standard distribution tables have numerous real-world applications. For example, in business, they can be used to predict sales forecasts and determine the probability of meeting sales targets. In economics, they can be used to analyze the behavior of economic indicators, such as inflation and unemployment rates. In social sciences, they can be used to study the behavior of social phenomena, such as crime rates and population growth.
For instance, suppose a company wants to determine the probability that its sales will exceed $1 million in a given quarter. Using historical data, the company can calculate the mean and standard deviation of its sales and use a standard distribution table to find the probability that its sales will exceed $1 million. This information can be used to make informed decisions about production and marketing strategies.
What is the purpose of a standard distribution table?
+
The purpose of a standard distribution table is to find the probability that a random variable with a normal distribution will fall within a certain range, given its mean and standard deviation.
How is a standard distribution table constructed?
+
A standard distribution table is constructed by calculating the area under the standard normal curve to the left of a given z-score, typically using numerical integration or other approximation methods.
What are some common applications of standard distribution tables?
+
Standard distribution tables have a wide range of applications, including hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and predictive modeling. They are used in various fields, such as business, economics, and social sciences.



