Sas If Then And: Master Decision Making Codes
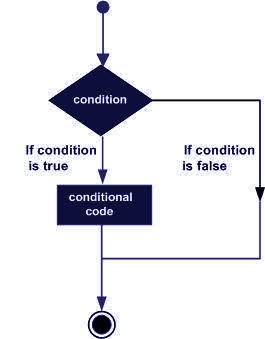
The SAS programming language is a powerful tool for data manipulation and analysis, and one of its most useful features is the IF-THEN statement. This statement allows users to make decisions based on conditions and perform different actions accordingly. In this article, we will explore the IF-THEN statement and its variations, including the IF-THEN-ELSE statement and the use of the AND operator.
Introduction to IF-THEN Statements
The IF-THEN statement is a fundamental construct in SAS programming that enables users to execute different blocks of code based on conditions. The basic syntax of an IF-THEN statement is:
IF condition THEN action;
In this syntax, the condition is a logical expression that evaluates to either true or false, and the action is the code that is executed if the condition is true. For example:
IF x > 10 THEN y = 2 * x;
In this example, if the value of x is greater than 10, then the value of y is set to twice the value of x.
IF-THEN-ELSE Statements
The IF-THEN-ELSE statement is a variation of the IF-THEN statement that allows users to specify an alternative action if the condition is false. The syntax of an IF-THEN-ELSE statement is:
IF condition THEN action1;
ELSE action2;
In this syntax, action1 is the code that is executed if the condition is true, and action2 is the code that is executed if the condition is false. For example:
IF x > 10 THEN y = 2 * x;
ELSE y = x / 2;
In this example, if the value of x is greater than 10, then the value of y is set to twice the value of x, otherwise the value of y is set to half the value of x.
Using the AND Operator
The AND operator is a logical operator that allows users to combine multiple conditions in an IF-THEN statement. The syntax of an IF-THEN statement with the AND operator is:
IF condition1 AND condition2 THEN action;
In this syntax, condition1 and condition2 are logical expressions that are evaluated together, and the action is executed only if both conditions are true. For example:
IF x > 10 AND y < 5 THEN z = x + y;
In this example, if the value of x is greater than 10 and the value of y is less than 5, then the value of z is set to the sum of x and y.
Multiple Conditions
SAS also allows users to specify multiple conditions in an IF-THEN statement using the OR operator or the IN operator. The syntax of an IF-THEN statement with multiple conditions is:
IF condition1 OR condition2 THEN action;
or
IF variable IN (value1, value2, ...) THEN action;
In the first syntax, condition1 and condition2 are logical expressions that are evaluated separately, and the action is executed if either condition is true. In the second syntax, variable is a variable that is compared to a list of values, and the action is executed if the variable matches any of the values in the list. For example:
IF x > 10 OR y < 5 THEN z = x + y;
or
IF color IN ('red', 'blue', 'green') THEN category = 'primary';
In the first example, if the value of x is greater than 10 or the value of y is less than 5, then the value of z is set to the sum of x and y. In the second example, if the value of color is 'red', 'blue', or 'green', then the value of category is set to 'primary'.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| AND | Logical AND operator |
| OR | Logical OR operator |
| IN | Membership operator |
| = | Equality operator |
| <> | Inequality operator |
| < | Less than operator |
| <= | Less than or equal to operator |
| > | Greater than operator |
| >= | Greater than or equal to operator |
Best Practices for Using IF-THEN Statements
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when using IF-THEN statements in SAS:
- Use clear and concise conditions that are easy to understand
- Avoid using complex conditions that are hard to read
- Use comments to explain the purpose of the IF-THEN statement
- Test the IF-THEN statement thoroughly to ensure it works as expected
- Use the AND and OR operators to simplify complex conditions
- Avoid using unnecessary parentheses, which can make the code harder to read
By following these best practices, you can write effective and efficient IF-THEN statements that make your SAS code more readable and maintainable.
What is the purpose of the IF-THEN statement in SAS?
+
The IF-THEN statement is used to execute different blocks of code based on conditions. It allows users to make decisions based on data and perform different actions accordingly.
How do I use the AND operator in an IF-THEN statement?
+
The AND operator is used to combine multiple conditions in an IF-THEN statement. The syntax is: IF condition1 AND condition2 THEN action. This means that the action is executed only if both conditions are true.
What is the difference between the IF-THEN and IF-THEN-ELSE statements?
+
The IF-THEN statement executes an action if a condition is true, while the IF-THEN-ELSE statement executes an action if a condition is true and another action if the condition is false.