Rotational Kinetic Energy Equation
The rotational kinetic energy equation is a fundamental concept in physics, describing the energy associated with the rotation of an object around a fixed axis. This concept is crucial in understanding various phenomena, from the spinning of tops to the rotation of celestial bodies. In this article, we will delve into the rotational kinetic energy equation, exploring its components, applications, and significance in the realm of physics.
Understanding Rotational Kinetic Energy

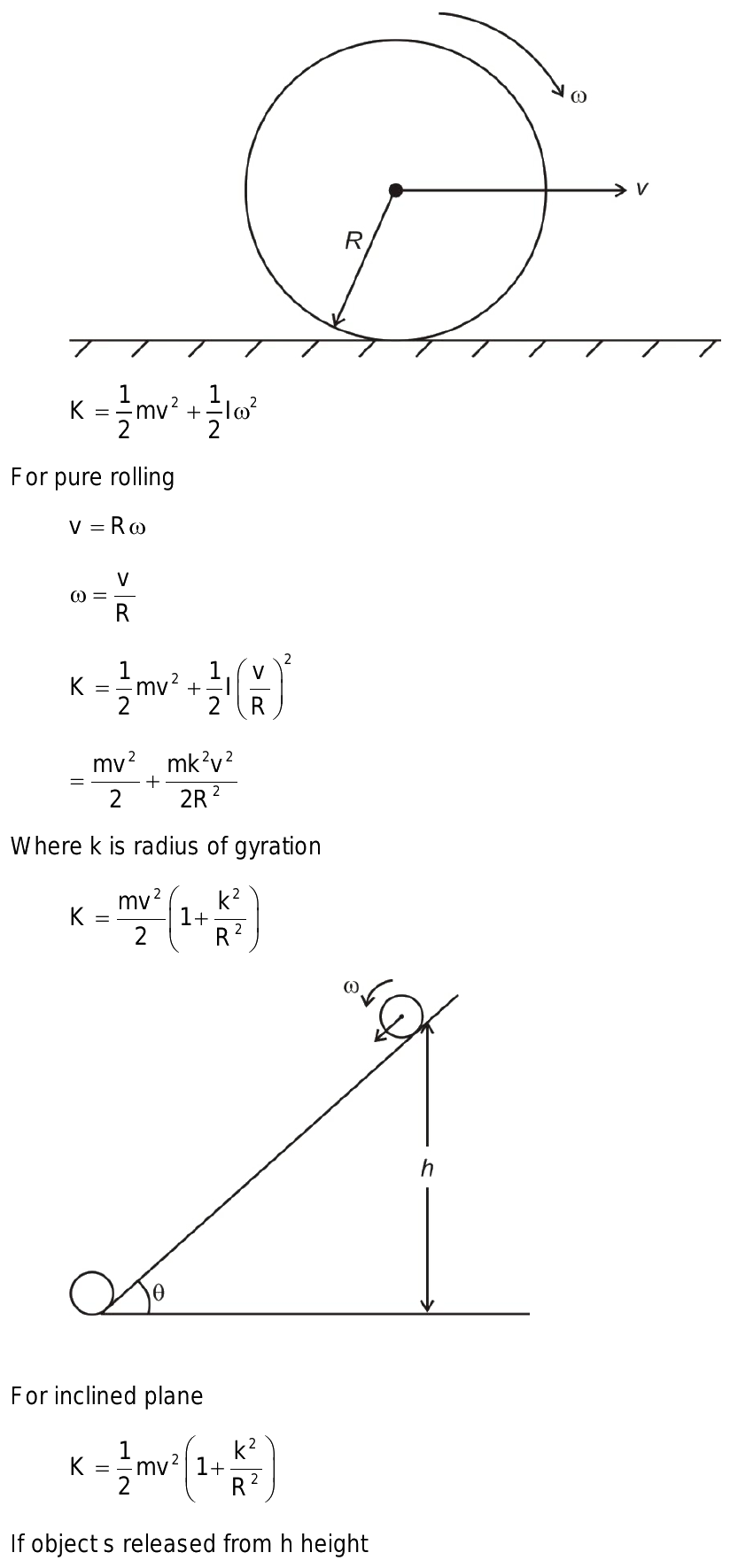
Rotational kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its rotation. It is a form of kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. Unlike translational kinetic energy, which is associated with an object moving in a straight line, rotational kinetic energy is associated with an object rotating around a fixed axis. The amount of rotational kinetic energy an object has depends on its moment of inertia and its angular velocity.
Moment of Inertia and Angular Velocity
The moment of inertia (I) of an object is a measure of its resistance to changes in its rotation. It depends on the mass distribution of the object and the distance of the mass from the axis of rotation. The angular velocity (ω) is a measure of how fast the object is rotating. It is typically measured in radians per second. The rotational kinetic energy equation combines these two parameters to calculate the energy of rotation.
The rotational kinetic energy (KE_rot) equation is given by:
KE_rot = (1/2)Iω^2
This equation shows that the rotational kinetic energy is directly proportional to the moment of inertia and the square of the angular velocity. Understanding and applying this equation is essential in various fields, including engineering, astronomy, and sports science.
Applications of Rotational Kinetic Energy
The concept of rotational kinetic energy has numerous applications across different disciplines. In engineering, it is used in the design of rotating machinery, such as turbines and generators, to optimize their performance and efficiency. In astronomy, the rotational kinetic energy of celestial bodies, like planets and stars, helps in understanding their formation, evolution, and dynamics. In sports science, the rotational kinetic energy of athletes, particularly in sports involving rotation like gymnastics and figure skating, is analyzed to improve performance and reduce injury risk.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Engineering | Design of rotating machinery for optimal performance |
| Astronomy | Understanding celestial body dynamics and evolution |
| Sports Science | Analysis of athlete rotation to improve performance and safety |

Calculating Rotational Kinetic Energy
Calculating the rotational kinetic energy of an object involves knowing its moment of inertia and angular velocity. The moment of inertia can be calculated using the formula I = mr^2 for a point mass, where m is the mass and r is the distance from the axis of rotation. For more complex objects, the moment of inertia can be calculated using the integral of the mass elements times the square of their distances from the axis of rotation.
Once the moment of inertia is determined, and the angular velocity is known, the rotational kinetic energy can be calculated using the rotational kinetic energy equation. This calculation is crucial in understanding the dynamics of rotating systems and in predicting their behavior under different conditions.
Technical Specifications and Performance Analysis
In the context of engineering and design, understanding the rotational kinetic energy of a system is essential for its technical specifications and performance analysis. For instance, in the design of a wind turbine, the rotational kinetic energy of the blades is critical in determining the turbine’s efficiency and power output. Similarly, in the design of a car engine, the rotational kinetic energy of the crankshaft and camshaft is vital for the engine’s performance and fuel efficiency.
The analysis of rotational kinetic energy also involves considering factors like friction and energy loss. In real-world applications, not all of the rotational kinetic energy can be converted into useful work due to energy losses. Understanding these losses and how to minimize them is a key aspect of optimizing the design and performance of rotating machinery.
What is the formula for calculating rotational kinetic energy?
+The formula for rotational kinetic energy is KE_rot = (1⁄2)Iω^2, where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity.
What factors affect the rotational kinetic energy of an object?
+The rotational kinetic energy of an object is affected by its moment of inertia and its angular velocity. The design and material of the object, as well as external factors like friction, can also influence its rotational kinetic energy.
How is rotational kinetic energy used in real-world applications?
+Rotational kinetic energy is used in various real-world applications, including the design of rotating machinery like turbines and generators, understanding celestial body dynamics in astronomy, and analyzing athlete performance in sports science.
