Rotational Energy Equation: Solve Problems Fast

The rotational energy equation is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the energy associated with an object's rotation. It is a crucial aspect of understanding various phenomena in mechanics, engineering, and other fields. In this article, we will delve into the rotational energy equation, its derivation, and how to solve problems related to it efficiently.
Introduction to Rotational Energy

Rotational energy, also known as rotational kinetic energy, is the energy an object possesses due to its rotation. It is a form of kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. The rotational energy of an object depends on its moment of inertia, angular velocity, and the distance of the object’s mass from the axis of rotation. Understanding rotational energy is essential for analyzing and solving problems in physics, engineering, and other disciplines.
Moment of Inertia and Angular Velocity
The moment of inertia (I) is a measure of an object’s resistance to changes in its rotation. It depends on the object’s mass distribution and the distance of the mass from the axis of rotation. The angular velocity (ω) is a measure of the rate of change of an object’s angular position. The rotational energy equation is given by:
E = (1/2)Iω^2
where E is the rotational energy, I is the moment of inertia, and ω is the angular velocity.
Derivation of the Rotational Energy Equation

The rotational energy equation can be derived by considering a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. The kinetic energy of the body can be calculated by summing the kinetic energies of its individual particles. Using the concept of moment of inertia and angular velocity, the rotational energy equation can be derived as follows:
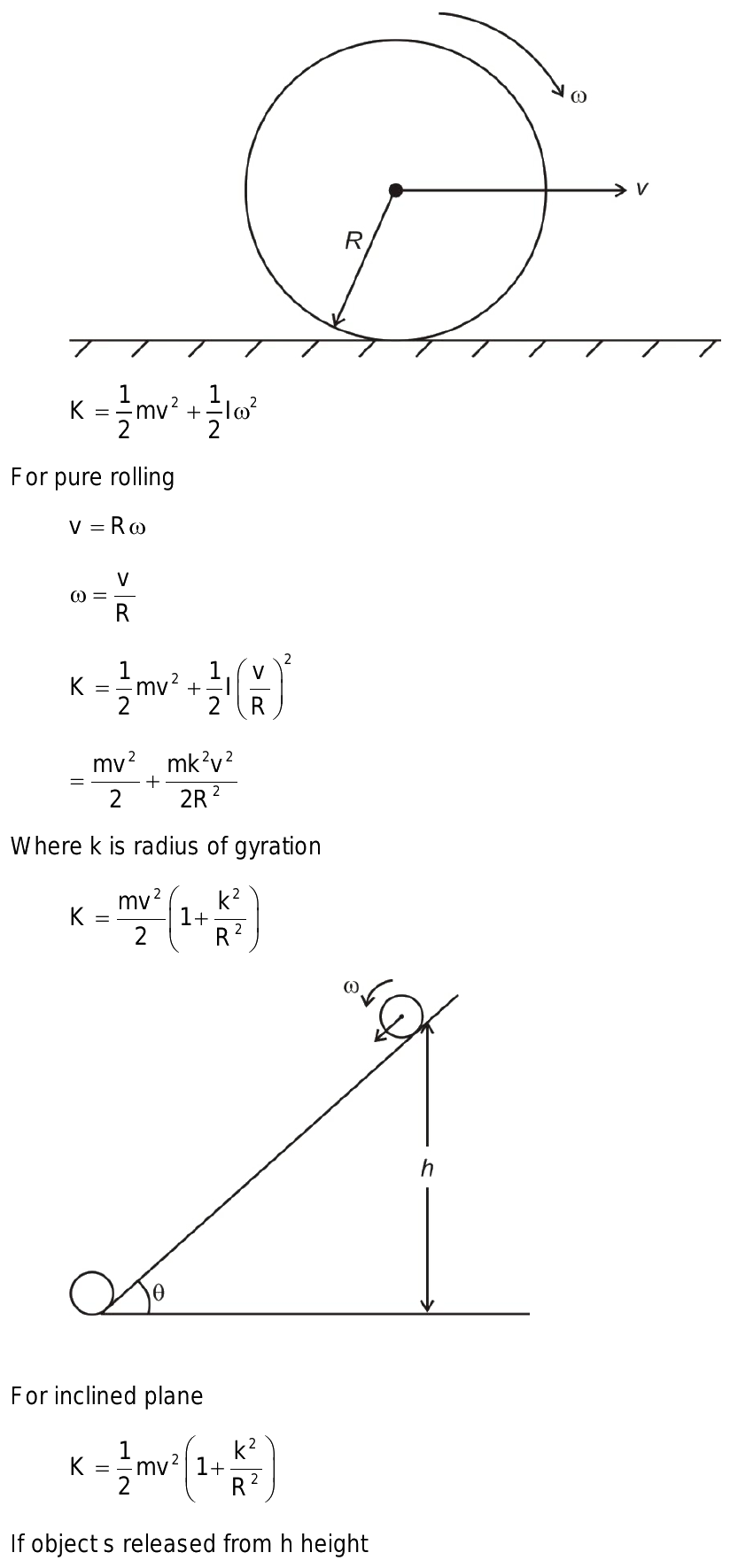
Let's consider a rigid body of mass m, rotating about a fixed axis with an angular velocity ω. The kinetic energy of the body can be calculated as:
K = (1/2)m(v^2)
where v is the linear velocity of the body. Using the relationship between linear velocity and angular velocity (v = rω), we can rewrite the kinetic energy equation as:
K = (1/2)m(rω)^2
Since the moment of inertia I is defined as the sum of the products of the masses and the squares of their distances from the axis of rotation, we can rewrite the kinetic energy equation as:
K = (1/2)Iω^2
This is the rotational energy equation, which describes the energy associated with an object's rotation.
Solving Problems with the Rotational Energy Equation
To solve problems related to rotational energy, we need to apply the rotational energy equation and use the given information to find the unknown quantities. Here are some steps to follow:
- Read the problem carefully and identify the given information, such as the moment of inertia, angular velocity, and rotational energy.
- Use the rotational energy equation to relate the given quantities and find the unknown quantities.
- Apply the concept of moment of inertia and angular velocity to analyze the problem and find the solution.
Let's consider an example problem:
A solid sphere of mass 2 kg and radius 0.5 m is rotating about its central axis with an angular velocity of 10 rad/s. What is its rotational energy?
We can solve this problem by using the rotational energy equation and the given information:
E = (1/2)Iω^2
First, we need to find the moment of inertia of the sphere. The moment of inertia of a solid sphere is given by:
I = (2/5)mr^2
where m is the mass and r is the radius of the sphere. Substituting the given values, we get:
I = (2/5)(2 kg)(0.5 m)^2 = 0.2 kg m^2
Now, we can substitute the values of I and ω into the rotational energy equation:
E = (1/2)(0.2 kg m^2)(10 rad/s)^2 = 10 J
Therefore, the rotational energy of the sphere is 10 J.
Applications of Rotational Energy
Rotational energy has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Mechanics: Rotational energy is used to analyze the motion of rigid bodies and solve problems related to rotational motion.
- Engineering: Rotational energy is used in the design and analysis of rotating machines, such as motors, generators, and turbines.
- Physics: Rotational energy is used to study the behavior of rotating systems and understand various phenomena, such as gyroscopic motion and precession.
Understanding rotational energy and its applications is crucial for solving problems and analyzing phenomena in various fields.
Comparison with Translational Energy
Rotational energy is similar to translational energy, which is the energy associated with an object’s motion in a straight line. However, there are some key differences between the two:
| Energy Type | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Translational Energy | K = (1/2)mv^2 | Energy associated with an object's motion in a straight line. |
| Rotational Energy | E = (1/2)Iω^2 | Energy associated with an object's rotation. |
While translational energy depends on the object's mass and linear velocity, rotational energy depends on the object's moment of inertia and angular velocity.
Future Implications and Emerging Trends
Rotational energy has numerous applications in various fields, and its understanding is crucial for solving problems and analyzing phenomena. As technology advances, the importance of rotational energy will continue to grow, and new applications will emerge. Some of the emerging trends and future implications include:
- Advances in materials science and engineering: New materials with unique properties will be developed, enabling the creation of more efficient and powerful rotating machines.
- Increased focus on sustainability: Rotational energy will play a crucial role in the development of sustainable technologies, such as wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants.
- Growing importance of robotics and mechatronics: Rotational energy will be used to analyze and optimize the motion of robots and mechatronic systems.
Understanding rotational energy and its applications will be essential for addressing the challenges and opportunities of the future.
What is the difference between rotational energy and translational energy?
+
Rotational energy is the energy associated with an object’s rotation, while translational energy is the energy associated with an object’s motion in a straight line. Rotational energy depends on the object’s moment of inertia and angular velocity, while translational energy depends on the object’s mass and linear velocity.
How is rotational energy used in real-world applications?
+
Rotational energy is used in various real-world applications, including the design and analysis of rotating machines, such as motors, generators, and turbines. It is also used in the study of gyroscopic motion and precession, and in the development of sustainable technologies, such as wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants.
What are some of the key concepts related to rotational energy?
+
Some of the key concepts related to rotational energy include moment of inertia, angular velocity, and rotational kinematics. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing and solving problems related to rotational energy.

