Oxidation No Explained: Master Chemistry
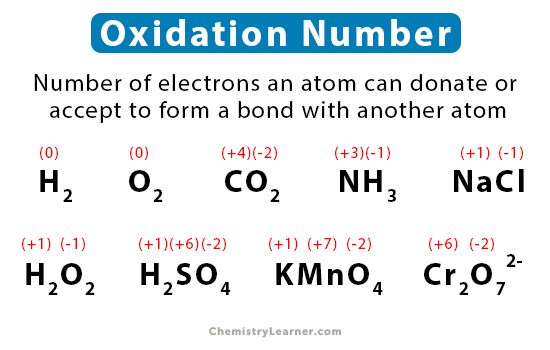
Oxidation numbers are a fundamental concept in chemistry, used to describe the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The oxidation number, also known as the oxidation state, is a numerical value that represents the number of electrons an atom has gained or lost to form a chemical bond. Understanding oxidation numbers is crucial in mastering chemistry, as it helps chemists predict the properties and reactivity of compounds.
Introduction to Oxidation Numbers

Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms in a compound based on a set of rules. The rules are as follows: the oxidation number of a free element is zero, the oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge, and the oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2, except in peroxides where it is -1. The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, except in hydrides where it is -1. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is zero, and the sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
Assigning Oxidation Numbers
Assigning oxidation numbers to atoms in a compound can be a challenging task, especially for complex compounds. However, by following the rules and using a systematic approach, it is possible to determine the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a compound. For example, in the compound sodium chloride (NaCl), the oxidation number of sodium is +1, and the oxidation number of chlorine is -1. In the compound calcium carbonate (CaCO3), the oxidation number of calcium is +2, the oxidation number of carbon is +4, and the oxidation number of oxygen is -2.
| Element | Oxidation Number |
|---|---|
| Sodium (Na) | +1 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | -1 |
| Calcium (Ca) | +2 |
| Carbon (C) | +4 |
| Oxygen (O) | -2 |

Types of Oxidation Reactions

Oxidation reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another, resulting in a change in the oxidation number of the atoms involved. There are several types of oxidation reactions, including combustion reactions, displacement reactions, and redox reactions. Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen, resulting in the release of heat and light. Displacement reactions involve the reaction of a more reactive element with a less reactive element, resulting in the displacement of the less reactive element. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another, resulting in a change in the oxidation number of the atoms involved.
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions are a type of oxidation reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one species to another. Redox reactions can be further categorized into two types: oxidation and reduction. Oxidation involves the loss of electrons, resulting in an increase in the oxidation number of the atom. Reduction involves the gain of electrons, resulting in a decrease in the oxidation number of the atom. For example, in the reaction between sodium and chlorine to form sodium chloride, sodium is oxidized (loses electrons), and chlorine is reduced (gains electrons).
- Oxidation: loss of electrons, increase in oxidation number
- Reduction: gain of electrons, decrease in oxidation number
Applications of Oxidation Numbers
Oxidation numbers have numerous applications in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and pharmacology. Understanding oxidation numbers is essential in predicting the properties and reactivity of compounds, which is critical in the development of new materials and pharmaceuticals. Oxidation numbers are also used in the identification of unknown compounds, as they can provide valuable information about the structure and composition of the compound.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Oxidation numbers play a critical role in the development of new pharmaceuticals. Understanding the oxidation numbers of atoms in a compound can help predict its reactivity and potential toxicity. For example, compounds with high oxidation numbers may be more reactive and potentially toxic, while compounds with low oxidation numbers may be less reactive and safer. By mastering oxidation numbers, pharmaceutical companies can develop safer and more effective drugs.
What is the oxidation number of oxygen in a peroxide?
+
The oxidation number of oxygen in a peroxide is -1.
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
+
Oxidation involves the loss of electrons, resulting in an increase in the oxidation number of the atom, while reduction involves the gain of electrons, resulting in a decrease in the oxidation number of the atom.
How are oxidation numbers used in pharmaceutical development?
+
Oxidation numbers are used in pharmaceutical development to predict the reactivity and potential toxicity of compounds. By understanding the oxidation numbers of atoms in a compound, pharmaceutical companies can develop safer and more effective drugs.


