Oxidation And Reduction
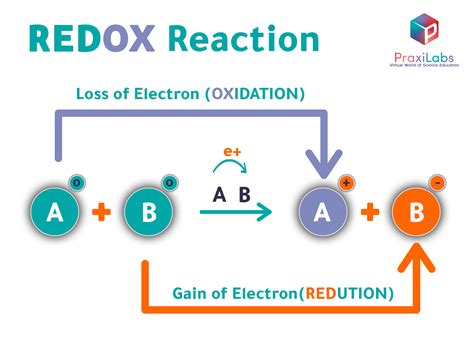
Oxidation and reduction are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that describe the loss and gain of electrons by atoms, molecules, or ions. These processes are essential in various chemical reactions, including those that occur in living organisms, industries, and the environment. In this article, we will delve into the world of oxidation and reduction, exploring their definitions, mechanisms, and significance in different fields.
Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction

Oxidation is defined as the loss of one or more electrons by an atom, molecule, or ion, resulting in an increase in its oxidation state. On the other hand, reduction is the gain of one or more electrons, leading to a decrease in its oxidation state. These two processes are often coupled, meaning that one species is oxidized while another is reduced, resulting in a transfer of electrons between them. The combination of oxidation and reduction reactions is known as a redox reaction.
Oxidation States and Redox Reactions
The oxidation state of an atom, molecule, or ion is a measure of the number of electrons it has gained or lost. It is typically denoted by a positive or negative integer, with a higher value indicating a greater loss of electrons. In a redox reaction, the oxidation states of the reactants change as they gain or lose electrons. For example, in the reaction between sodium and chlorine, sodium loses an electron to form a positive ion (Na+), while chlorine gains an electron to form a negative ion (Cl-).
| Reactant | Product | Oxidation State |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium (Na) | Sodium ion (Na+) | 0 to +1 |
| Chlorine (Cl2) | Chloride ion (Cl-) | 0 to -1 |

Types of Redox Reactions
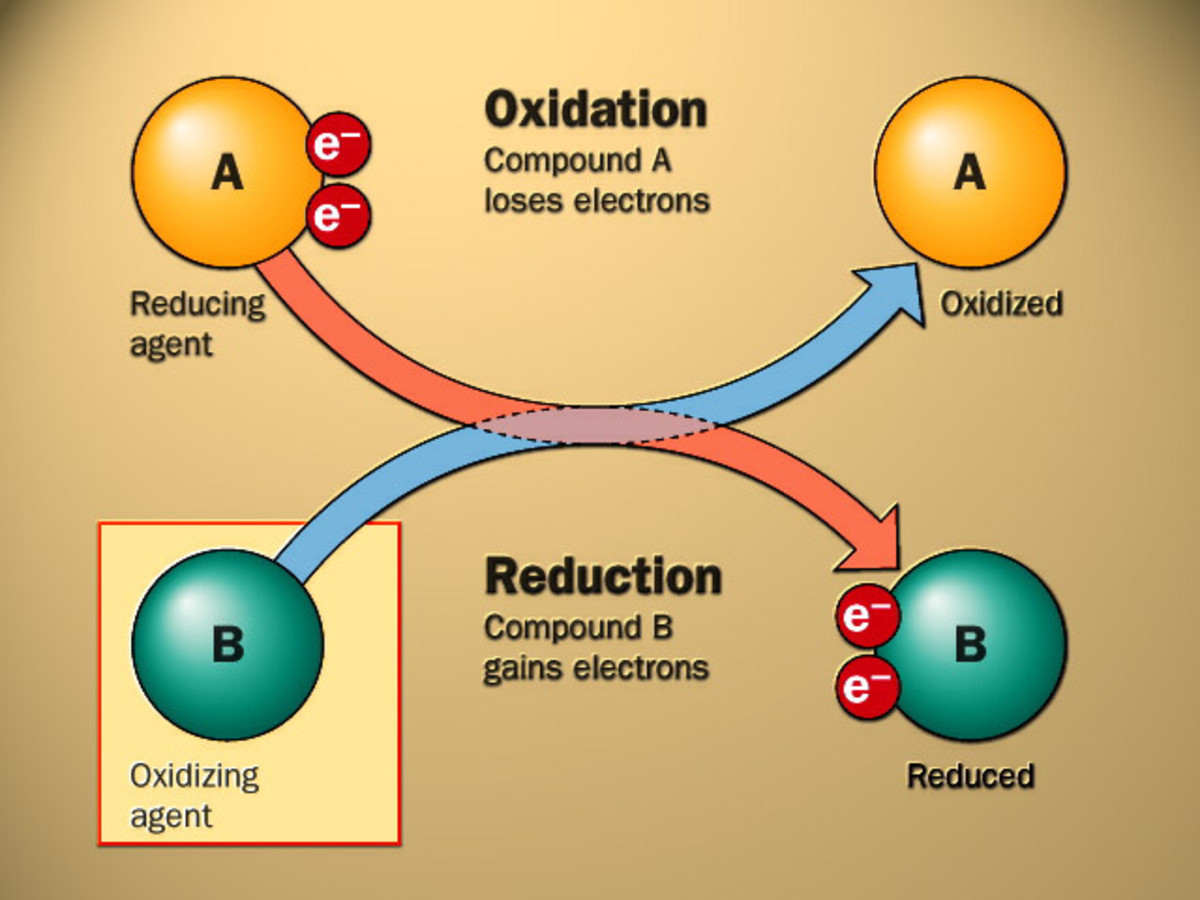
Redox reactions can be classified into different types based on the nature of the reactants and products. Some common types of redox reactions include:
- Combination reactions: These involve the combination of two or more reactants to form a single product, often with the transfer of electrons. Examples include the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water.
- Decomposition reactions: These involve the breakdown of a single reactant into two or more products, often with the transfer of electrons. Examples include the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Displacement reactions: These involve the replacement of one reactant by another, often with the transfer of electrons. Examples include the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate, where zinc displaces copper.
Biological Redox Reactions
Redox reactions play a crucial role in various biological processes, including metabolism, respiration, and photosynthesis. In these processes, electrons are transferred between molecules, often with the help of enzymes, to generate energy or synthesize complex molecules. For example, in cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to produce energy in the form of ATP, while in photosynthesis, light energy is used to reduce carbon dioxide to form glucose.
Industrial Applications of Redox Reactions
Redox reactions have numerous industrial applications, including:
- Electroplating: This involves the use of redox reactions to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a surface, often to protect it from corrosion or to enhance its appearance.
- Battery production: Redox reactions are used to generate electricity in batteries, such as lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries.
- Water treatment: Redox reactions are used to remove impurities from water, such as chlorine and ozone disinfection.
Environmental Significance of Redox Reactions
Redox reactions play a crucial role in various environmental processes, including the degradation of pollutants, the formation of ozone, and the cycling of nutrients. Understanding these reactions is essential in predicting the fate and transport of pollutants in the environment and in developing strategies for mitigating their impact.
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
+Oxidation is the loss of one or more electrons, while reduction is the gain of one or more electrons. These two processes are often coupled, resulting in a transfer of electrons between species.
What are the different types of redox reactions?
+Redox reactions can be classified into combination reactions, decomposition reactions, and displacement reactions, among others.
What is the significance of redox reactions in biology?
+Redox reactions play a crucial role in various biological processes, including metabolism, respiration, and photosynthesis, and are essential in generating energy and synthesizing complex molecules.