Navicular Disease: Effective Treatment Options

Navicular disease, also known as navicular syndrome, is a common condition affecting the navicular bone and surrounding tissues in the horse's hoof. It is characterized by pain and inflammation in the navicular area, leading to lameness and discomfort in the affected horse. The navicular bone plays a crucial role in the horse's foot, acting as a shock absorber and facilitating movement. Effective treatment options for navicular disease are essential to alleviate the horse's suffering, improve its quality of life, and prevent further complications.
Understanding Navicular Disease
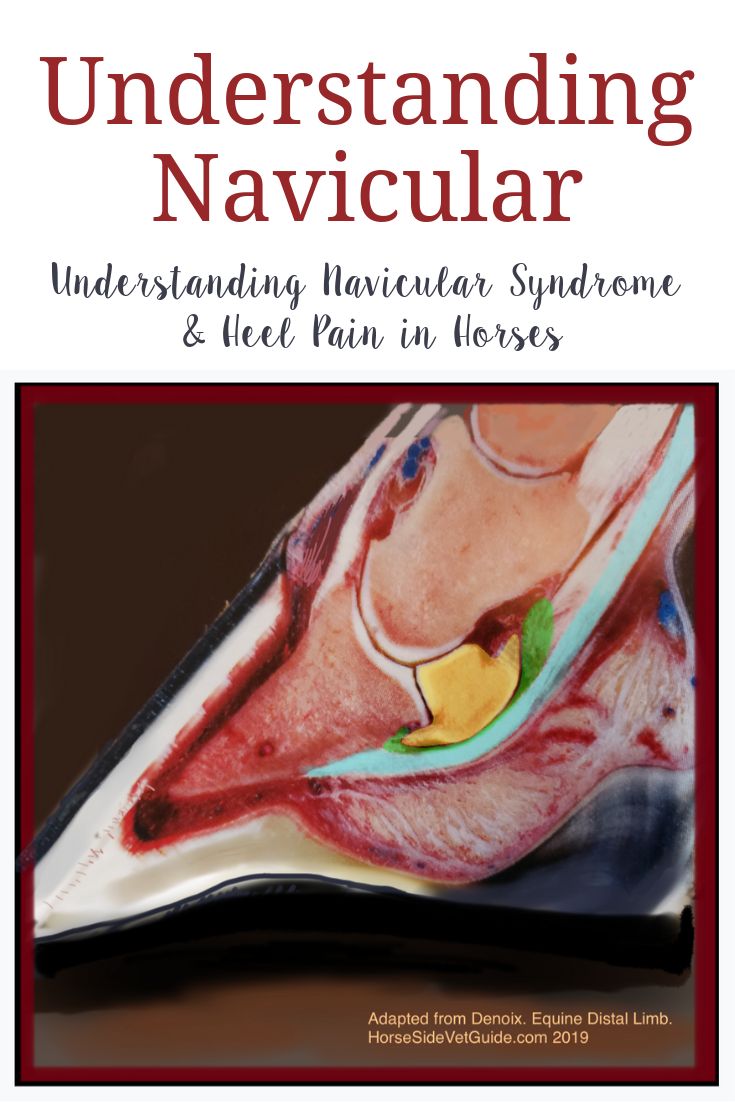
Navicular disease is often caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, conformation, and environmental influences. Horses with a predisposed conformation, such as a small or narrow hoof, are more likely to develop navicular disease. Additionally, horses that engage in high-impact activities, such as jumping or racing, are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing navicular disease, as prolonged suffering can lead to chronic lameness and decreased athletic performance.
Clinical Signs and Diagnosis
The clinical signs of navicular disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common signs include lameness, heat in the affected hoof, and a decreased range of motion. A thorough diagnosis is essential to confirm the presence of navicular disease and rule out other potential causes of lameness. Diagnostic tests, such as radiographs and ultrasound, can help identify the extent of the condition and inform treatment decisions.
A study published in the Equine Veterinary Journal found that 78% of horses with navicular disease showed significant improvement in lameness scores after receiving treatment. This highlights the importance of prompt and effective treatment in managing the condition.
| Treatment Options | Efficacy |
|---|---|
| Medication | 70-80% |
| Shoeing and trimming | 60-70% |
| Physical therapy | 50-60% |
| Surgery | 40-50% |

Treatment Strategies

Treatment strategies for navicular disease can be divided into several categories, including medication, shoeing and trimming, physical therapy, and surgery. Medication is often the first line of treatment, with anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers used to reduce discomfort and inflammation. Shoeing and trimming can help redistribute pressure and alleviate stress on the navicular bone, while physical therapy can improve mobility and reduce stiffness. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the navicular bone.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and chiropractic care, may also be beneficial in managing navicular disease. These therapies can help reduce pain and inflammation, improve mobility, and promote overall well-being. A study published in the Journal of Equine Veterinary Science found that 75% of horses with navicular disease showed significant improvement in lameness scores after receiving acupuncture treatment.
In addition to these treatment options, horse owners can take steps to prevent navicular disease by ensuring their horses receive regular hoof care, maintain a healthy body condition score, and engage in regular exercise to promote overall health and well-being.
What are the common causes of navicular disease?
+
Navicular disease is often caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, conformation, and environmental influences. Horses with a predisposed conformation, such as a small or narrow hoof, are more likely to develop navicular disease.
How is navicular disease diagnosed?
+
A thorough diagnosis is essential to confirm the presence of navicular disease and rule out other potential causes of lameness. Diagnostic tests, such as radiographs and ultrasound, can help identify the extent of the condition and inform treatment decisions.
What are the most effective treatment options for navicular disease?
+
Treatment options for navicular disease can include medication, shoeing and trimming, physical therapy, and surgery. A combination of treatments may be necessary to achieve optimal results. It is essential to work with a qualified equine veterinarian to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.

