Magnetic Quantum Number
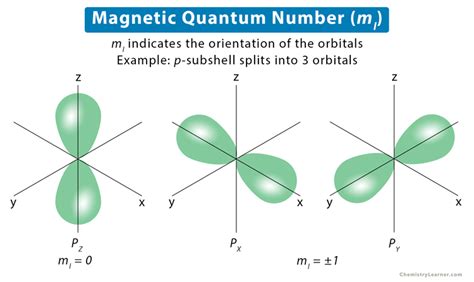
The magnetic quantum number is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics, playing a crucial role in describing the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules. It is one of the four quantum numbers that define the energy, shape, and orientation of an atomic orbital. In this article, we will delve into the world of magnetic quantum numbers, exploring their significance, properties, and applications in various fields of physics and chemistry.
Introduction to Quantum Numbers
In atomic physics, quantum numbers are used to describe the energy, shape, and orientation of atomic orbitals. The four quantum numbers are: principal quantum number (n), azimuthal quantum number (l), magnetic quantum number (m_l), and spin quantum number (m_s). Each quantum number provides unique information about the orbital, and together, they form a complete description of the electron’s state. The magnetic quantum number, in particular, is responsible for describing the orientation of the orbital in space.
Definition and Properties of Magnetic Quantum Number
The magnetic quantum number (m_l) is a measure of the orbital angular momentum of an electron. It can take on integer values ranging from -l to +l, where l is the azimuthal quantum number. The magnetic quantum number determines the number of nodes in the orbital, which are regions where the probability of finding the electron is zero. The value of m_l also affects the energy of the orbital, with different values corresponding to different energy levels. For example, in a 2p orbital, the magnetic quantum number can take on values of -1, 0, and +1, resulting in three distinct energy levels.
| Quantum Number | Description |
|---|---|
| n (Principal Quantum Number) | Energy level of the electron |
| l (Azimuthal Quantum Number) | Shape of the orbital |
| m_l (Magnetic Quantum Number) | Orientation of the orbital in space |
| m_s (Spin Quantum Number) | Spin of the electron |

Applications of Magnetic Quantum Number

The magnetic quantum number has numerous applications in various fields of physics and chemistry. In atomic physics, it is used to describe the energy levels and orbitals of electrons. In molecular physics, it is used to understand the bonding and structure of molecules. The magnetic quantum number is also crucial in understanding the behavior of electrons in magnetic fields, which has led to the development of technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Zeeman Effect and Magnetic Quantum Number
The Zeeman effect is the splitting of spectral lines in the presence of a magnetic field. The magnetic quantum number plays a crucial role in understanding the Zeeman effect, as it determines the energy shift of the spectral lines. The energy shift is proportional to the magnetic quantum number, and the resulting spectral lines are split into multiple components. This effect has been widely used in spectroscopy to study the properties of atoms and molecules.
- The Zeeman effect is used in atomic physics to study the energy levels and orbitals of electrons.
- The magnetic quantum number is used to understand the splitting of spectral lines in the presence of a magnetic field.
- The Zeeman effect has led to the development of technologies such as MRI and NMR spectroscopy.
Conclusion and Future Implications
In conclusion, the magnetic quantum number is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics, playing a crucial role in describing the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules. Its significance extends to various fields of physics and chemistry, including atomic physics, molecular physics, and spectroscopy. The understanding of magnetic quantum number has led to the development of technologies such as MRI and NMR spectroscopy, and its applications continue to grow. As research in quantum mechanics and its applications advances, the magnetic quantum number will remain a critical component in understanding the behavior of electrons and the properties of matter.
What is the magnetic quantum number?
+The magnetic quantum number is a measure of the orbital angular momentum of an electron, determining the orientation of the orbital in space.
What is the range of values for the magnetic quantum number?
+The magnetic quantum number can take on integer values ranging from -l to +l, where l is the azimuthal quantum number.
What is the significance of the magnetic quantum number in atomic physics?
+The magnetic quantum number is crucial in understanding the energy levels and orbitals of electrons, and its value determines the orientation of the orbital in space.