Illinois Praying Mantis Facts: Identification Guide

The Illinois praying mantis is a fascinating insect that can be found throughout the state of Illinois. These incredible creatures are known for their impressive camouflage abilities, stealthy hunting tactics, and unique life cycle. In this article, we will delve into the world of the Illinois praying mantis, exploring their identification, habitat, behavior, and interesting facts.
Introduction to Illinois Praying Mantis
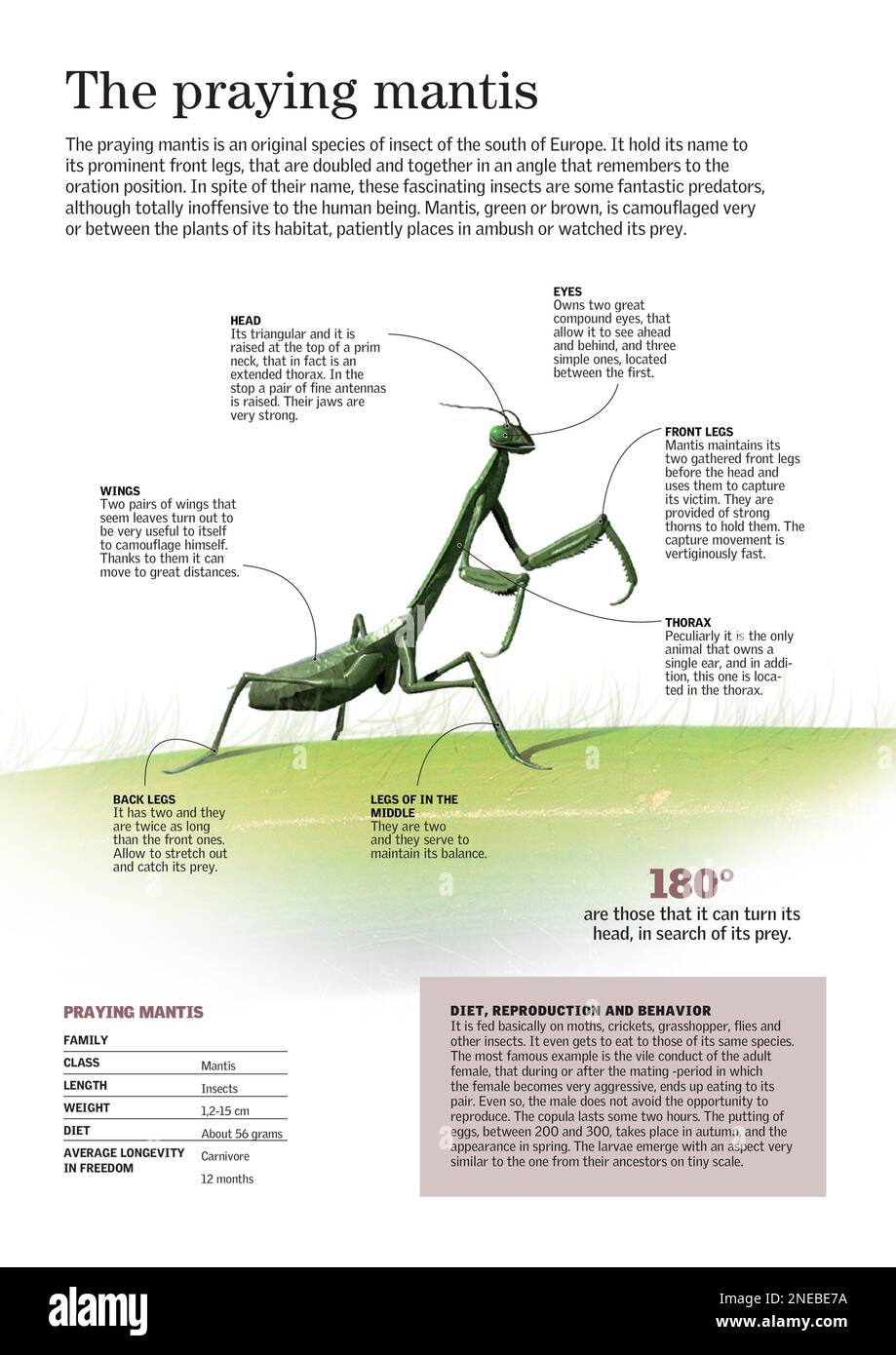
The Illinois praying mantis belongs to the family Mantidae, which comprises over 2,400 species of praying mantis worldwide. The most common species found in Illinois is the Carolina mantis (Stagmomantis carolina), which is native to the region. These insects are easily recognizable due to their elongated bodies, long legs, and distinctive prayer-like stance.
Physical Characteristics
Illinois praying mantis can grow up to 2-3 inches in length, with females typically being larger than males. They have a green or brown body, which provides excellent camouflage in their natural habitat. Their long, slender legs are equipped with spikes, allowing them to grasp and hold onto prey. The Illinois praying mantis also has large, triangular eyes that provide exceptional vision, helping them to detect movement and track their prey.
| Physical Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Body Length | 2-3 inches |
| Body Color | Green or brown |
| Legs | |
| Eyes | Large, triangular |

Habitat and Distribution

Illinois praying mantis can be found in a variety of habitats, including gardens, meadows, and forests. They are most commonly found in areas with an abundance of flowers, as these provide a source of food and shelter. The Illinois praying mantis is native to the southeastern United States, but can be found throughout the state of Illinois, particularly in the warmer months.
Life Cycle
The life cycle of the Illinois praying mantis typically begins in the spring, when adults emerge from their winter hiding places. Males will often engage in a complex courtship ritual, which involves vibrating their bodies and performing a series of intricate movements. After mating, the female will lay a batch of eggs, which will hatch into nymphs after several weeks. The nymphs will go through a series of molts, eventually reaching adulthood and beginning the cycle again.
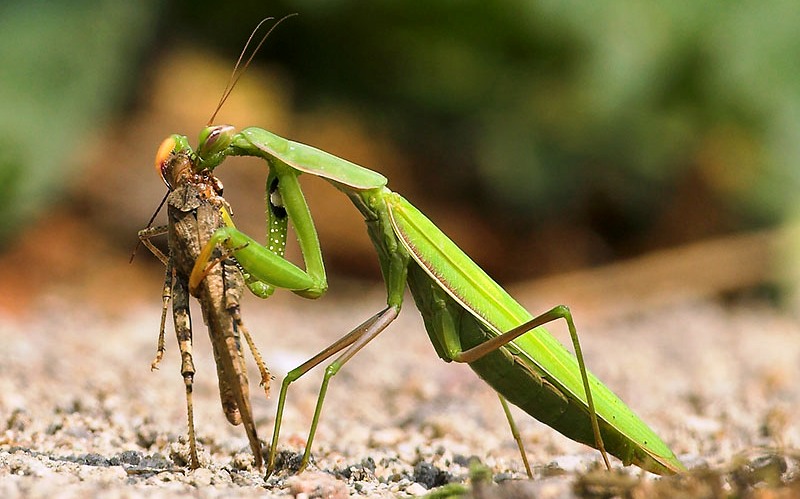
The Illinois praying mantis is a formidable predator, feeding on a variety of insects, including flies, bees, and butterflies. They are also known to feed on other small animals, such as spiders and snails. In terms of defense, the Illinois praying mantis is equipped with a range of strategies, including camouflage, stealth, and the ability to release a foul-tasting fluid to deter predators.
Conservation Status
The Illinois praying mantis is not currently considered to be a threatened species, although their populations can be affected by a range of factors, including habitat destruction, pesticide use, and climate change. Efforts can be made to conserve and protect the Illinois praying mantis, such as creating insect-friendly habitats and reducing the use of pesticides.
Predators and Threats
The Illinois praying mantis has a range of predators, including birds, spiders, and other insects. They are also susceptible to a range of threats, including habitat destruction, pesticide use, and climate change. In terms of disease, the Illinois praying mantis can be affected by a range of fungal and bacterial infections, which can have a significant impact on their populations.
| Predator/Threat | Description |
|---|---|
| Birds | Feed on Illinois praying mantis |
| Spiders | Feed on Illinois praying mantis |
| Pesticides | Can harm or kill Illinois praying mantis |
| Climate Change | Can affect habitat and populations |
What do Illinois praying mantis eat?
+
Illinois praying mantis are carnivorous insects that feed on a variety of small animals, including flies, bees, butterflies, and other insects. They are also known to feed on spiders and snails.
How long do Illinois praying mantis live?
+
The lifespan of an Illinois praying mantis varies depending on factors such as food availability and environmental conditions. On average, they can live for several months, with some individuals surviving up to a year.
Are Illinois praying mantis endangered?
+
No, the Illinois praying mantis is not currently considered to be an endangered species. However, their populations can be affected by a range of factors, including habitat destruction and pesticide use.

