Hypokalemia Icd 10 Code Guide
Hypokalemia is a medical condition characterized by lower than normal potassium levels in the blood. Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve function, and heart rhythm. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), provides a standardized system for coding and classifying diseases, including hypokalemia. In this article, we will delve into the ICD-10 code guide for hypokalemia, exploring the different codes, their meanings, and the conditions they represent.
Understanding Hypokalemia and ICD-10 Codes
The ICD-10 coding system is used by healthcare professionals to classify and code diseases, symptoms, and procedures. For hypokalemia, the ICD-10 code is crucial for diagnosing, treating, and billing purposes. The code for hypokalemia is E87.1, which falls under the category of “Other disorders of electrolyte and fluid balance.” This category includes various conditions related to electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, and electrolyte imbalance unspecified.
ICD-10 Code for Hypokalemia: E87.1
The ICD-10 code E87.1 specifically represents hypokalemia, which is characterized by a serum potassium level below 3.5 mmol/L. This code is used to indicate a diagnosis of hypokalemia, regardless of the underlying cause. The code E87.1 is further subdivided into several subcodes, which provide more specific information about the condition. For example, E87.1A represents hypokalemia, unspecified, while E87.1B represents hypokalemia due to diuretic therapy.
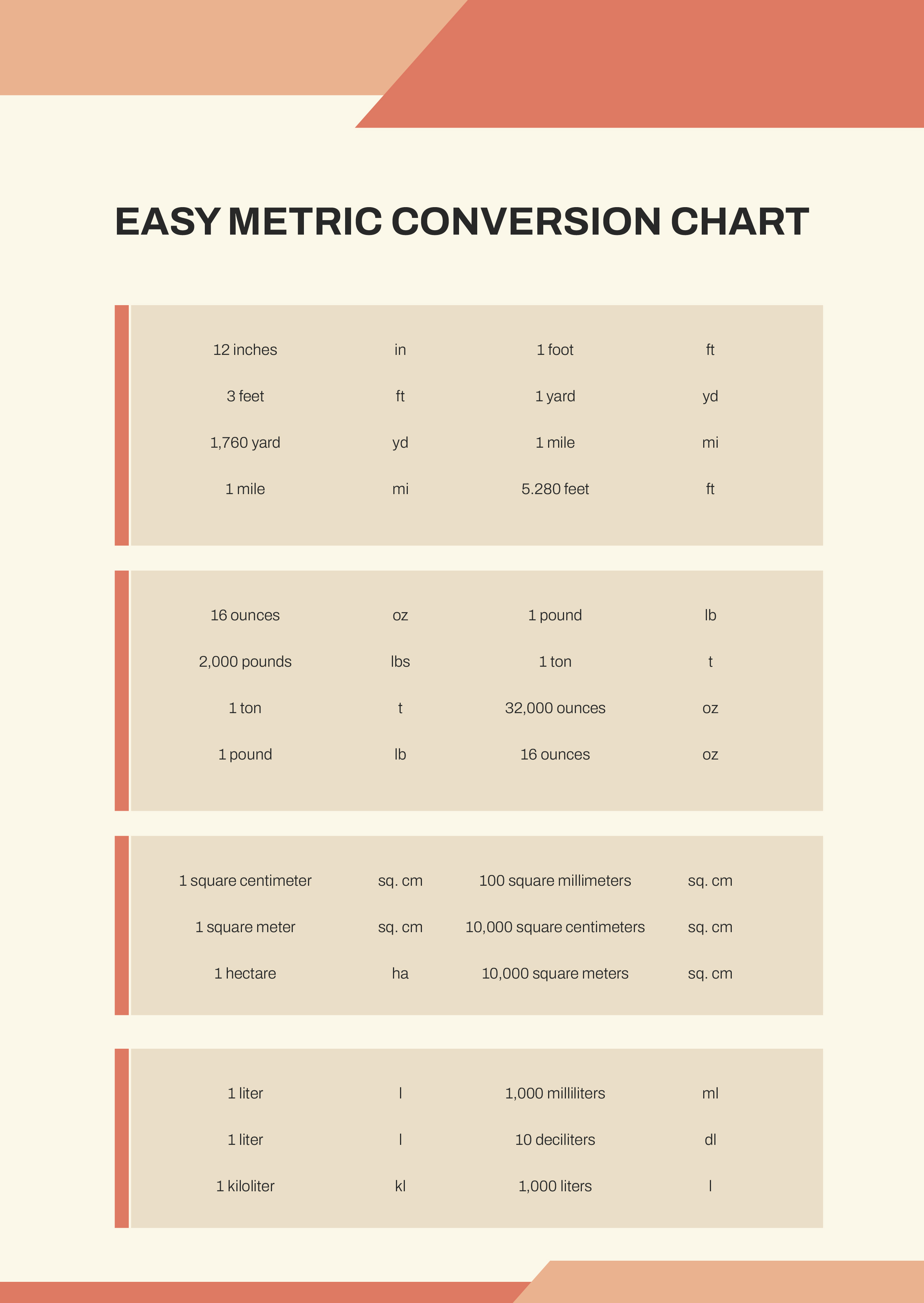
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| E87.1 | Hypokalemia |
| E87.1A | Hypokalemia, unspecified |
| E87.1B | Hypokalemia due to diuretic therapy |
| E87.1C | Hypokalemia due to gastrointestinal loss |
| E87.1D | Hypokalemia due to renal loss |
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia can present with a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, constipation, and palpitations. In severe cases, hypokalemia can lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrhythmias, and even paralysis. The diagnosis of hypokalemia is typically made based on laboratory tests, including serum potassium levels, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and clinical symptoms. The ICD-10 code for hypokalemia should be used in conjunction with other relevant codes, such as those for underlying conditions or symptoms.
Treatment and Management of Hypokalemia
The treatment and management of hypokalemia depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In general, treatment involves correcting the potassium imbalance through dietary changes, supplements, or medications. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor cardiac function and electrolyte levels. The ICD-10 code for hypokalemia can help healthcare professionals track the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of patients with this condition.
In conclusion, the ICD-10 code guide for hypokalemia provides a standardized system for coding and classifying this condition. The code E87.1 and its subcodes offer a detailed and specific way to represent hypokalemia, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose, treat, and bill for this condition. By understanding the ICD-10 code guide for hypokalemia, healthcare professionals can improve patient care and outcomes.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypokalemia?
+The ICD-10 code for hypokalemia is E87.1.
What are the symptoms of hypokalemia?
+The symptoms of hypokalemia include muscle weakness, fatigue, constipation, and palpitations. In severe cases, hypokalemia can lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrhythmias, and even paralysis.
How is hypokalemia diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of hypokalemia is typically made based on laboratory tests, including serum potassium levels, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and clinical symptoms.