How To Use Tap & Drill Chart? Instant Guide
The tap and drill chart is a fundamental tool used in various industries, including manufacturing, engineering, and construction. It provides a comprehensive guide for determining the correct drill bit size and tap size for creating threaded holes in different materials. In this article, we will delve into the world of tap and drill charts, exploring their importance, how to read them, and practical applications.
Understanding the Tap and Drill Chart

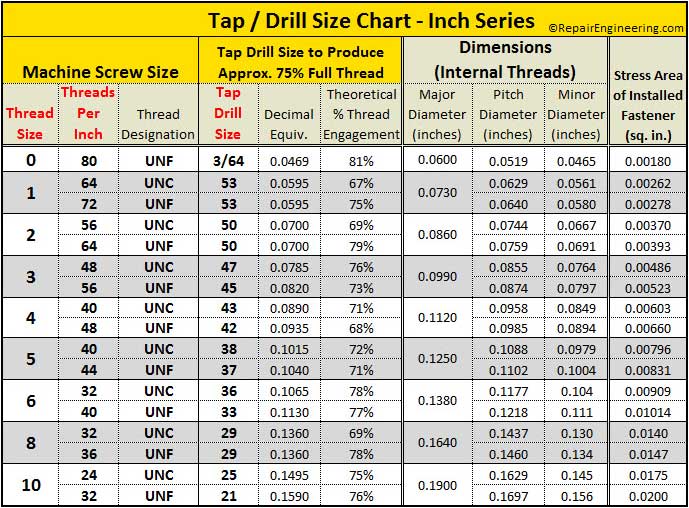
A tap and drill chart is a table or diagram that lists the standard drill bit sizes and corresponding tap sizes for various thread sizes and types. The chart takes into account the material being worked with, such as steel, aluminum, or brass, and provides the necessary information to ensure accurate and precise threading. The chart is usually organized by thread size, with columns for drill bit size, tap size, and other relevant information. By using a tap and drill chart, individuals can avoid common mistakes, such as using the wrong drill bit size or tap size, which can result in damaged threads, stripped screws, or other problems.
Reading the Tap and Drill Chart
Reading a tap and drill chart requires attention to detail and a basic understanding of threading concepts. Thread size refers to the diameter of the thread, while thread pitch refers to the distance between threads. The chart will typically list the thread size, thread pitch, and corresponding drill bit size and tap size. For example, a chart might list a thread size of 1⁄4-20, with a recommended drill bit size of #7 and a tap size of 1⁄4-20. It is essential to note that different materials may require different drill bit sizes and tap sizes, even for the same thread size.
| Thread Size | Thread Pitch | Drill Bit Size | Tap Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4-20 | 20 | #7 | 1/4-20 |
| 1/2-13 | 13 | 1/2 | 1/2-13 |
| 3/4-10 | 10 | 5/8 | 3/4-10 |

Practical Applications of Tap and Drill Charts

Tap and drill charts have numerous practical applications in various industries. In manufacturing, they are used to ensure accurate and precise threading of parts, such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, and other components. In construction, tap and drill charts are used for threading anchor bolts, screws, and other fasteners. By using a tap and drill chart, individuals can save time and reduce costs associated with rework, repairs, and material waste. Additionally, tap and drill charts can help prevent accidents and injuries caused by faulty or damaged threads.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When using a tap and drill chart, there are several common mistakes to avoid. One of the most critical mistakes is using the wrong drill bit size or tap size, which can result in damaged threads or stripped screws. Another mistake is failing to consider the material being worked with, which can affect the threading process. Over-tightening or under-tightening threads can also lead to problems, such as stripped threads or loose fasteners. By following the recommendations outlined in the tap and drill chart and taking the necessary precautions, individuals can avoid these common mistakes and ensure accurate and precise threading.
What is the purpose of a tap and drill chart?
+
A tap and drill chart provides a comprehensive guide for determining the correct drill bit size and tap size for creating threaded holes in different materials, ensuring accurate and precise threading.
How do I read a tap and drill chart?
+
Reading a tap and drill chart requires attention to detail and a basic understanding of threading concepts. The chart will typically list the thread size, thread pitch, and corresponding drill bit size and tap size, taking into account the material being worked with.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when using a tap and drill chart?
+
Common mistakes to avoid include using the wrong drill bit size or tap size, failing to consider the material being worked with, and over-tightening or under-tightening threads. By following the recommendations outlined in the tap and drill chart and taking the necessary precautions, individuals can avoid these common mistakes and ensure accurate and precise threading.