How To Convert Fahrenheit To Celsius? Instant Results

Converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius is a common task in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday life. The process involves a simple mathematical formula that can be applied to obtain instant results. In this article, we will delve into the world of temperature conversion, exploring the history behind the two scales, the conversion formula, and providing examples to illustrate the process.
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
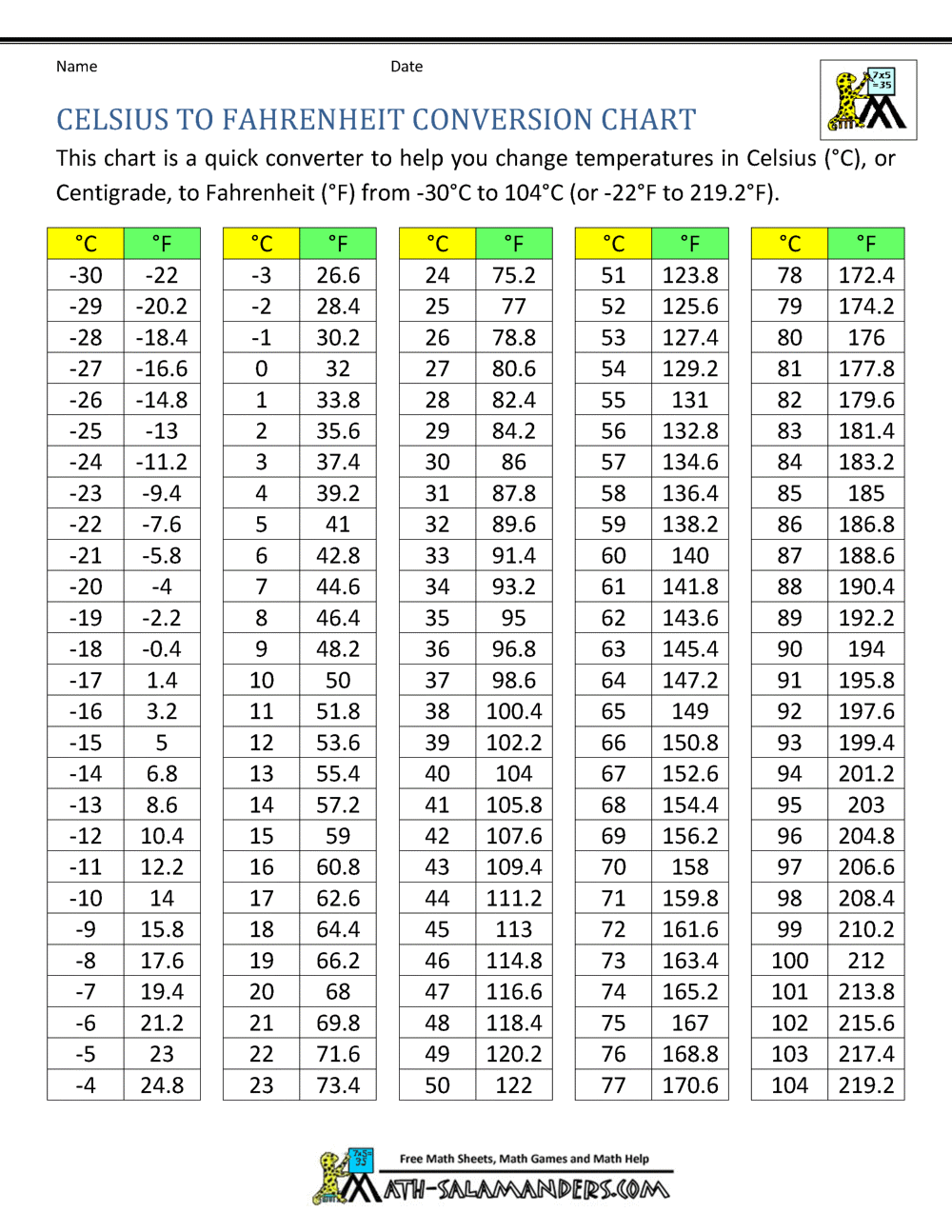
The Fahrenheit scale was introduced by German physicist Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, while the Celsius scale was developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. The main difference between the two scales lies in their reference points: the Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32 degrees and the boiling point at 212 degrees, whereas the Celsius scale sets the freezing point at 0 degrees and the boiling point at 100 degrees.
The Conversion Formula
To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, the following formula is used: °C = (°F - 32) × 5⁄9. This formula can be applied to any temperature reading in Fahrenheit to obtain the equivalent temperature in Celsius. For instance, to convert 80 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, the calculation would be: °C = (80 - 32) × 5⁄9 = 26.67°C.
The conversion formula can also be expressed in a more detailed step-by-step process:
- Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature reading.
- Multiply the result by 5.
- Divide the product by 9.
By following these steps, you can easily convert any Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius.
| Fahrenheit Temperature | Celsius Temperature |
|---|---|
| 32°F | 0°C |
| 100°F | 37.78°C |
| 212°F | 100°C |
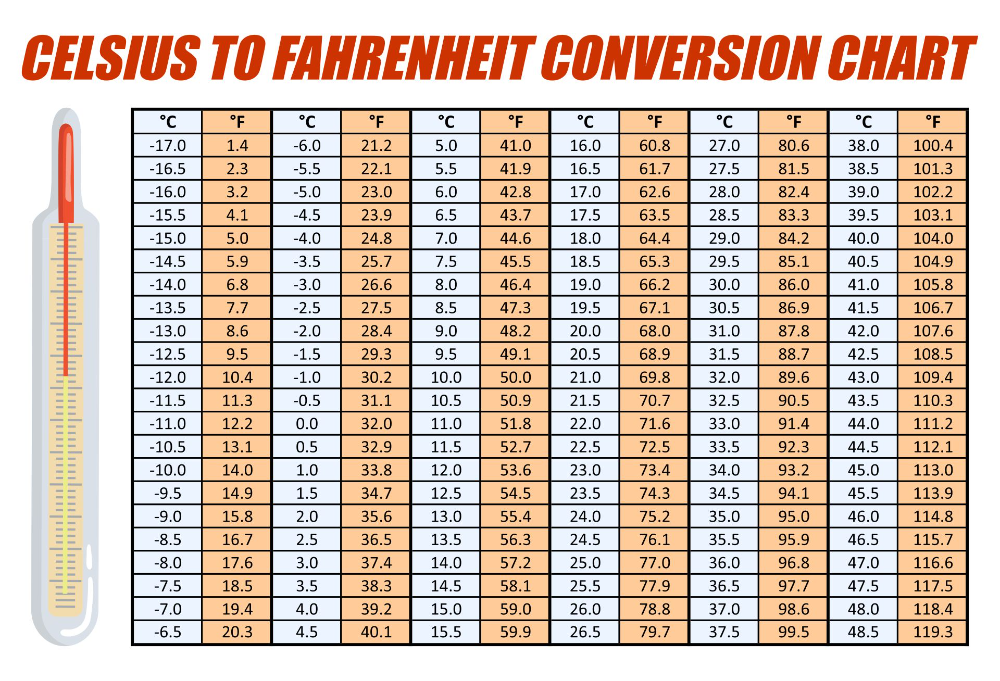
Examples and Applications

The Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion has numerous applications in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday life. For instance, in weather forecasting, temperature readings are often reported in both Fahrenheit and Celsius to cater to different audiences. In scientific research, the Celsius scale is widely used due to its more intuitive and decimal-based nature.
Real-World Examples
In the United States, the Fahrenheit scale is still widely used in everyday applications, such as cooking and weather forecasting. However, in most other countries, the Celsius scale is preferred. To illustrate the conversion process, consider the following examples:
- Convert 90°F to Celsius: °C = (90 - 32) × 5⁄9 = 32.22°C.
- Convert 25°C to Fahrenheit: °F = (25 × 9⁄5) + 32 = 77°F.
These examples demonstrate the ease of converting between the two temperature scales using the formula.
What is the difference between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales?
+The main difference between the two scales lies in their reference points: the Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32 degrees and the boiling point at 212 degrees, whereas the Celsius scale sets the freezing point at 0 degrees and the boiling point at 100 degrees.
How do I convert 100°F to Celsius?
+To convert 100°F to Celsius, use the formula: °C = (°F - 32) × 5⁄9. Therefore, °C = (100 - 32) × 5⁄9 = 37.78°C.
Why is the Celsius scale preferred in scientific research?
+The Celsius scale is widely used in scientific research due to its more intuitive and decimal-based nature, making it easier to perform calculations and comparisons.


