How Is Klein Waardenburg Syndrome Diagnosed?
Klein-Waardenburg syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by hearing loss, skin and hair pigmentation abnormalities, and other distinct physical features. Diagnosing this condition involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory investigations. Early diagnosis is crucial for providing appropriate management and support to affected individuals.
Clinical Evaluation
A thorough clinical evaluation is the first step in diagnosing Klein-Waardenburg syndrome. This involves a detailed medical history and physical examination to identify the characteristic features of the condition. The evaluation should include an assessment of hearing, vision, and skin pigmentation, as well as an examination for any other associated physical anomalies. Skilled clinicians should be involved in this process to ensure that all relevant features are identified and documented.
Key Diagnostic Features
The diagnosis of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome is based on the presence of specific clinical features, which may include:
- Sensorineural hearing loss, which can range from mild to profound and is often bilateral
- Abnormalities of skin and hair pigmentation, such as white forelock or patches of skin that are lighter or darker than the surrounding areas
- Heterochromia iridum, where there are differences in eye color between the two eyes or within the same eye
- Other physical features, such as a broad and high nasal root, microphthalmia (small eyes), or premature graying of the hair
Genetic Testing

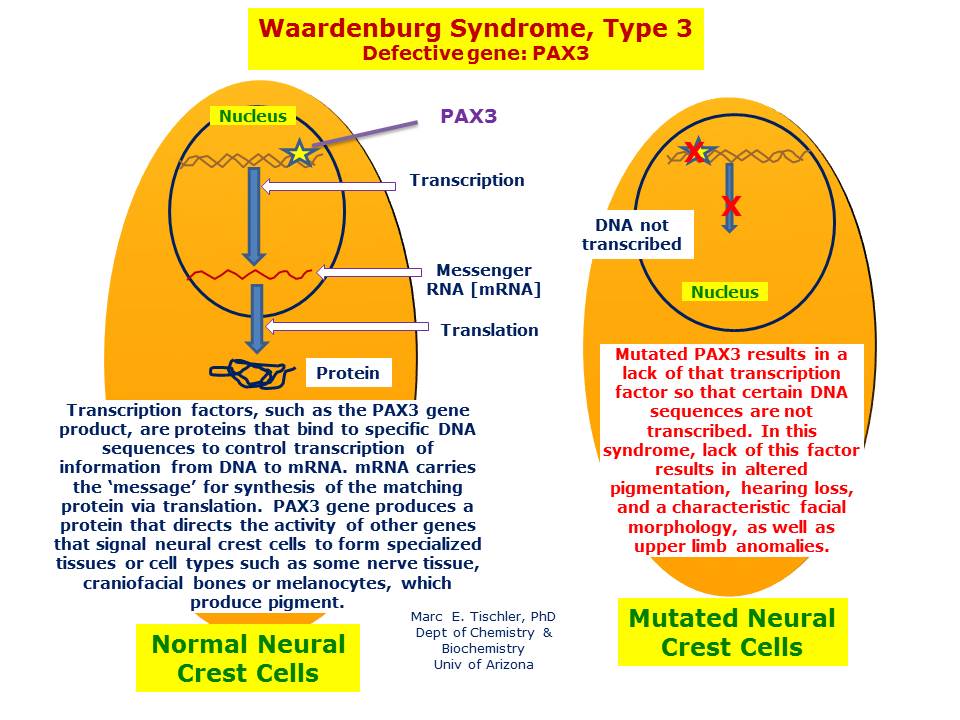
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome. The condition is caused by mutations in the PAX3 gene, and testing can identify these mutations in affected individuals. Genetic counseling should be offered to families to discuss the risks of transmission and the options for prenatal testing in future pregnancies.
Molecular Genetics
The PAX3 gene provides instructions for making a protein that is involved in the development of the auditory system, skin, and hair. Mutations in this gene disrupt the normal development of these tissues, leading to the characteristic features of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome. Molecular genetic testing can identify the specific mutation responsible for the condition in an affected individual.
| Diagnostic Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Audiometry | Assesses hearing thresholds and identifies any hearing loss |
| Ophthalmologic examination | Evaluates vision and identifies any abnormalities of the eyes |
| Genetic testing | Identifies mutations in the PAX3 gene responsible for the condition |

The diagnosis of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving clinicians from various specialties, including genetics, audiology, ophthalmology, and dermatology. By combining clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory investigations, healthcare professionals can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective management plan for individuals with this rare and complex condition.
What are the common symptoms of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome?
+The common symptoms of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome include sensorineural hearing loss, abnormalities of skin and hair pigmentation, heterochromia iridum, and other distinct physical features such as a broad and high nasal root, microphthalmia, or premature graying of the hair.
How is Klein-Waardenburg syndrome diagnosed?
+Klein-Waardenburg syndrome is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory investigations. A thorough medical history and physical examination are performed to identify the characteristic features of the condition, and genetic testing is used to confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the PAX3 gene.
What are the implications of a diagnosis of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome?
+A diagnosis of Klein-Waardenburg syndrome has significant implications for the management of the condition and the quality of life of affected individuals. Early diagnosis and intervention can help to address the symptoms of the condition, and genetic counseling can provide information about the risks of transmission and the options for prenatal testing in future pregnancies.


