How Does Genetic Variation Affect Self Pollination? Expert Tips
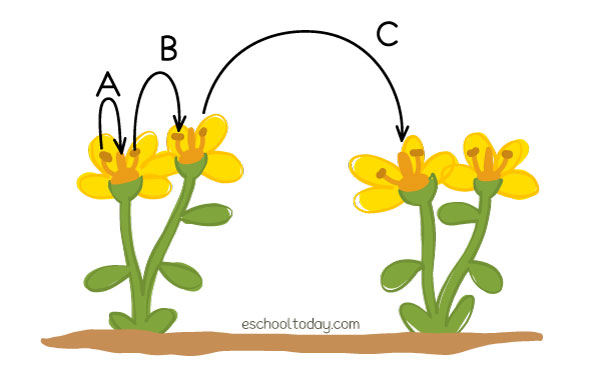
Genetic variation plays a crucial role in the process of self-pollination, which is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same plant. This process is essential for the reproduction of many plant species, and understanding the impact of genetic variation on self-pollination is vital for plant breeding and genetics. In this article, we will delve into the effects of genetic variation on self-pollination, exploring the mechanisms, advantages, and limitations of this process.
Genetic Variation and Self-Pollination: An Introduction
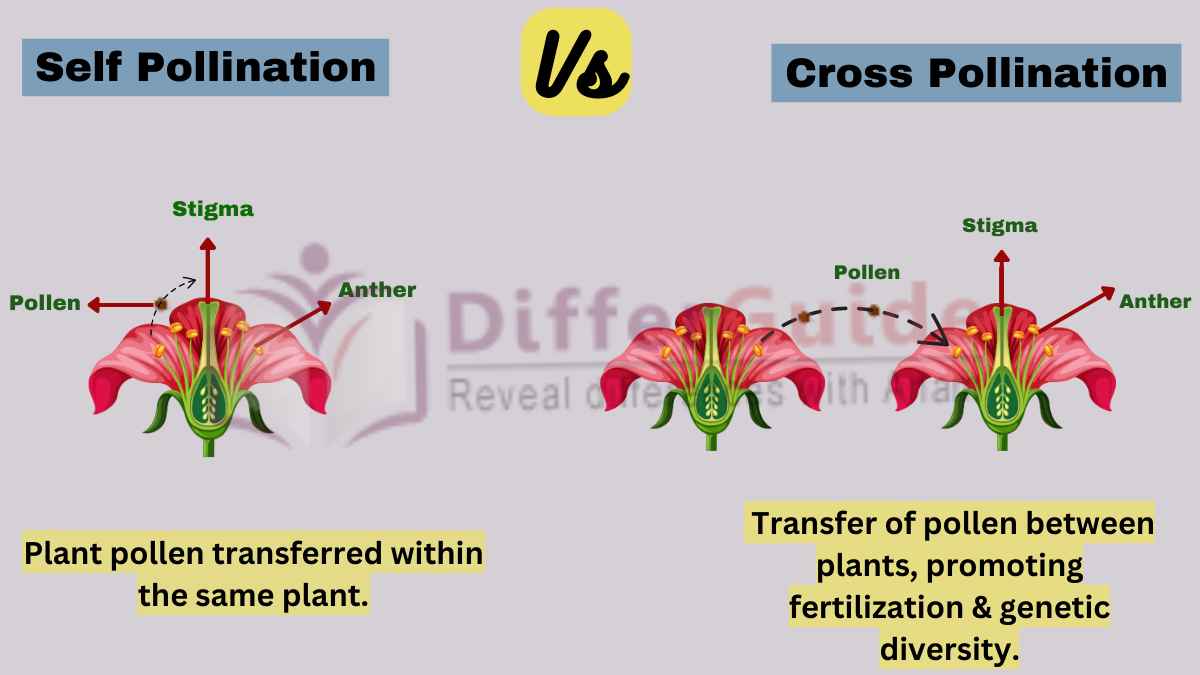
Genetic variation refers to the differences in the DNA sequence of individuals within a population or species. This variation can arise from various sources, including mutation, genetic recombination, and gene flow. Self-pollination, on the other hand, is a type of pollination where the pollen from the anther of a flower is transferred to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant. This process can lead to the production of offspring with reduced genetic diversity, as the pollen and egg cells are genetically similar.
Mechanisms of Genetic Variation in Self-Pollination
Several mechanisms contribute to genetic variation in self-pollination, including:
- Mutation: Random changes in the DNA sequence can occur during replication, leading to the creation of new alleles and increased genetic variation.
- Genetic recombination: The shuffling of genetic material during meiosis can result in the creation of new combinations of alleles, increasing genetic diversity.
- Gene flow: The movement of individuals with different genotypes into a population can introduce new alleles and increase genetic variation.
These mechanisms can lead to the creation of new genetic variants, which can affect the self-pollination process. For example, genetic variation in the S-locus region can influence the compatibility of pollen and stigma, affecting the success of self-pollination.
Advantages of Genetic Variation in Self-Pollination

Genetic variation in self-pollination can have several advantages, including:
- Increased fitness: Genetic variation can lead to the creation of offspring with improved fitness, as they may inherit beneficial traits from their parents.
- Improved disease resistance: Genetic variation can provide plants with increased resistance to diseases, as different alleles may confer varying levels of resistance.
- Enhanced adaptability: Genetic variation can enable plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity.
However, genetic variation in self-pollination can also have limitations, such as reduced genetic diversity and increased inbreeding depression.
Limitations of Genetic Variation in Self-Pollination
The limitations of genetic variation in self-pollination include:
- Reduced genetic diversity: Self-pollination can lead to the production of offspring with reduced genetic diversity, as the pollen and egg cells are genetically similar.
- Inbreeding depression: The increased homozygosity of self-pollinated offspring can lead to inbreeding depression, resulting in reduced fitness and increased susceptibility to disease.
- Loss of genetic variation: The repeated use of self-pollination can lead to the loss of genetic variation, as the same alleles are repeatedly selected and fixed in the population.
To mitigate these limitations, plant breeders and geneticists use various techniques, such as cross-pollination and genetic mapping, to introduce new genetic variation and increase genetic diversity.
Expert Tips for Managing Genetic Variation in Self-Pollination
Based on our understanding of the effects of genetic variation on self-pollination, we can provide the following expert tips for managing genetic variation in self-pollination:
- Maintain genetic diversity: Use cross-pollination and genetic mapping to introduce new genetic variation and increase genetic diversity.
- Monitor inbreeding depression: Regularly monitor the fitness and disease resistance of self-pollinated offspring to detect signs of inbreeding depression.
- Use genetic techniques: Utilize genetic techniques, such as marker-assisted selection and genomic selection, to select for desirable traits and increase genetic variation.
| Genetic Mechanism | Effect on Self-Pollination |
|---|---|
| Mutation | Increased genetic variation |
| Genetic recombination | Increased genetic diversity |
| Gene flow | Introduction of new alleles |

In conclusion, genetic variation plays a crucial role in the process of self-pollination, influencing the success and limitations of this process. By understanding the mechanisms, advantages, and limitations of genetic variation in self-pollination, plant breeders and geneticists can develop effective strategies to manage genetic variation and improve the fitness and adaptability of plants.
What is genetic variation, and how does it affect self-pollination?
+Genetic variation refers to the differences in the DNA sequence of individuals within a population or species. It can affect self-pollination by influencing the compatibility of pollen and stigma, as well as the fitness and disease resistance of offspring.
What are the advantages of genetic variation in self-pollination?
+The advantages of genetic variation in self-pollination include increased fitness, improved disease resistance, and enhanced adaptability. Genetic variation can lead to the creation of offspring with improved traits, making them better suited to their environment.
How can plant breeders and geneticists manage genetic variation in self-pollination?
+Plant breeders and geneticists can manage genetic variation in self-pollination by using techniques such as cross-pollination, genetic mapping, and marker-assisted selection. These techniques can help introduce new genetic variation, increase genetic diversity, and select for desirable traits.

