Electric Dipole In 3D
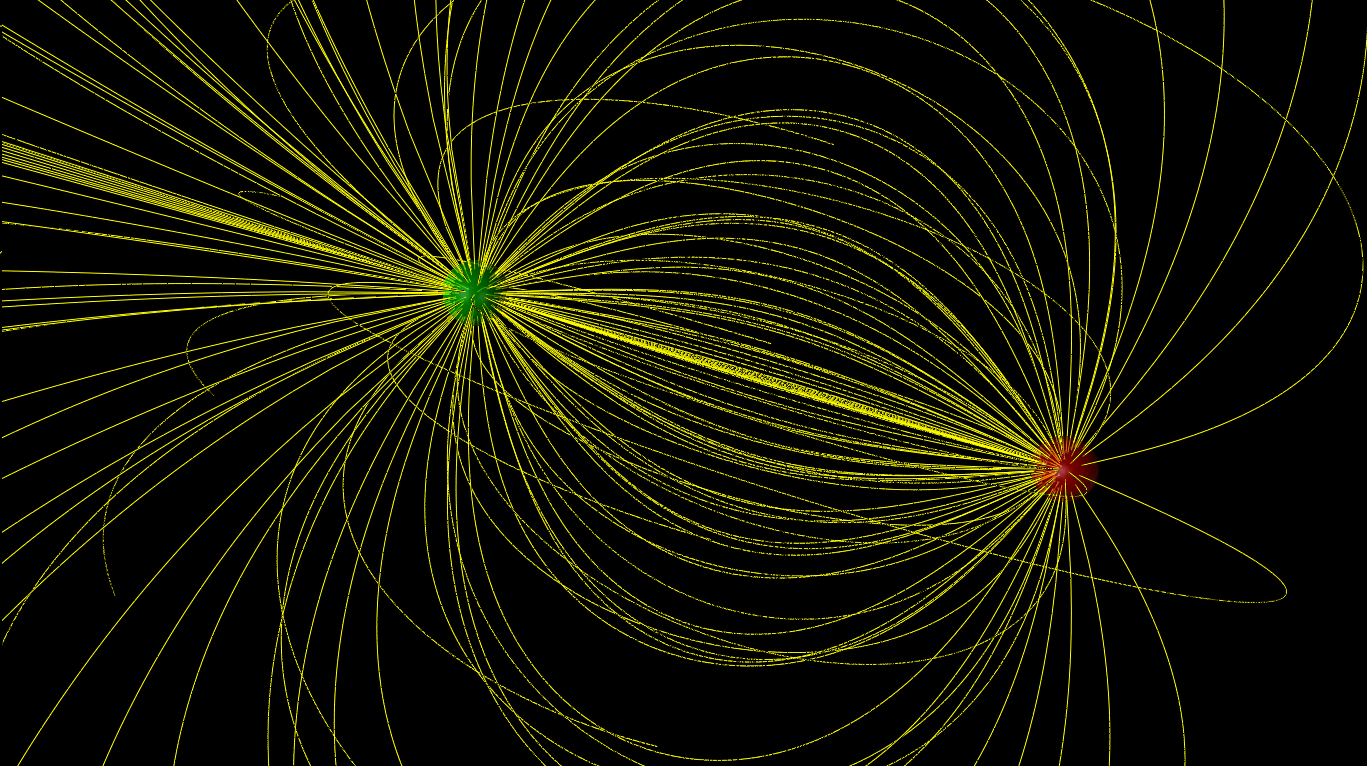
The concept of an electric dipole is a fundamental aspect of electromagnetism, playing a crucial role in understanding various phenomena in physics and engineering. In three-dimensional space, an electric dipole is characterized by a pair of point charges, one positive and one negative, separated by a distance. This separation of charges creates an electric field around the dipole, which can be visualized and analyzed using vector calculus and electromagnetic theory.
Definition and Properties of an Electric Dipole

An electric dipole is defined by its dipole moment, a vector quantity that depends on the magnitude of the charges and the distance between them. The dipole moment (p) is given by the product of the charge (q) and the distance (d) between the charges, p = qd. The direction of the dipole moment vector is from the negative charge to the positive charge. The electric dipole moment is a measure of the distribution of charge in space and is used to calculate the electric field produced by the dipole at any point in 3D space.
Electric Field of a Dipole
The electric field (E) produced by an electric dipole at a point in space can be calculated using the formula E = k * p / r^3, where k is Coulomb’s constant, p is the dipole moment, and r is the distance from the center of the dipole to the point where the field is being measured. The direction of the electric field vector at any point is tangential to the electric field line passing through that point. Understanding the electric field of a dipole is crucial for analyzing its interactions with other charges and dipoles in 3D space.
The electric field lines emerge from the positive charge and terminate on the negative charge. For a dipole in 3D space, these lines are not confined to a single plane but radiate outward in all directions, forming a complex pattern. The intensity of the field decreases with the cube of the distance from the dipole, making the dipole's influence significant only at close range.
| Property | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dipole Moment | p = qd | Vector quantity characterizing the dipole |
| Electric Field | E = k \* p / r^3 | Electric field at a distance r from the dipole |

Applications of Electric Dipoles

Electric dipoles have numerous applications in physics, chemistry, and engineering. In chemistry, the concept of electric dipoles is used to understand the properties of polar molecules, which have a permanent electric dipole moment. This polarity affects the physical and chemical properties of the molecule, such as its boiling point, solubility, and reactivity. In materials science, the alignment of electric dipoles in dielectric materials influences their electrical properties, including capacitance and piezoelectricity.
Molecular Polarization
In the context of molecular physics, the electric dipole moment of a molecule is a key factor in understanding its polarizability and the intermolecular forces it experiences. Polar molecules can form dipole-dipole interactions, which are stronger than the London dispersion forces acting between non-polar molecules. This difference in intermolecular forces significantly affects the physical properties of substances, such as their melting and boiling points.
Electric dipoles are also crucial in the design and operation of electromagnetic devices, including antennas, capacitors, and sensors. The ability to manipulate and control electric dipoles at the molecular or macroscopic level enables the development of advanced technologies with specific electromagnetic properties.
What is the significance of the direction of the dipole moment vector?
+The direction of the dipole moment vector, from the negative to the positive charge, is crucial for understanding the orientation of the dipole in an electric field and its interactions with other dipoles or charges.
How does the electric field of a dipole decrease with distance?
+The electric field of a dipole decreases with the cube of the distance from the dipole. This rapid decrease means that the influence of a dipole is significant only at relatively close distances.
What are some applications of electric dipoles in materials science?
+Electric dipoles play a crucial role in understanding the properties of dielectric materials, including their capacitance, piezoelectricity, and polarization behavior. These properties are essential for the design of capacitors, sensors, and other electromagnetic devices.