Covalent Bonds Examples
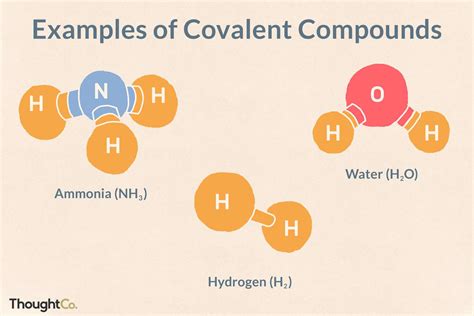
Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. This type of bonding is typically seen in molecules, where two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a stable compound. Covalent bonds are often found in organic compounds, such as methane, ammonia, and water, and are also present in many inorganic compounds, including carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid.
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds

Covalent bonds have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types of chemical bonds. One of the most important characteristics of covalent bonds is that they involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. This sharing of electrons allows the atoms to achieve a more stable electronic configuration, which is often referred to as a noble gas configuration. Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved in the bond. Polar covalent bonds involve the unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other atom.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are several types of covalent bonds, including single, double, and triple bonds. A single covalent bond involves the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms, while a double covalent bond involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons. A triple covalent bond involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons. The type of covalent bond that forms between two atoms depends on the number of electrons that each atom needs to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
For example, in the molecule methane (CH4), there are four single covalent bonds between the carbon atom and the four hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom shares one pair of electrons with the carbon atom, resulting in a stable electronic configuration for both atoms. In contrast, in the molecule ethene (C2H4), there is a double covalent bond between the two carbon atoms, resulting in a planar, unsaturated molecule.
| Type of Covalent Bond | Example |
|---|---|
| Single covalent bond | Methane (CH4) |
| Double covalent bond | Ethene (C2H4) |
| Triple covalent bond | Ethyne (C2H2) |

Examples of Covalent Bonds in Different Compounds
Covalent bonds are found in a wide range of compounds, including organic and inorganic molecules. Some examples of covalent bonds in different compounds include:
- Water (H2O): In water, there are two single covalent bonds between the oxygen atom and the two hydrogen atoms.
- Ammonia (NH3): In ammonia, there are three single covalent bonds between the nitrogen atom and the three hydrogen atoms.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): In carbon dioxide, there are two double covalent bonds between the carbon atom and the two oxygen atoms.
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4): In sulfuric acid, there are two single covalent bonds between the sulfur atom and the two oxygen atoms, and two double covalent bonds between the sulfur atom and the other two oxygen atoms.
These examples illustrate the diversity of covalent bonds in different compounds and highlight the importance of understanding the different types of covalent bonds in predicting the properties and reactivity of molecules.
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds can be classified as polar or nonpolar, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved in the bond. Polar covalent bonds involve the unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other atom. Nonpolar covalent bonds involve the equal sharing of electrons, resulting in no net charge on either atom.
For example, in the molecule hydrogen fluoride (HF), there is a polar covalent bond between the hydrogen atom and the fluorine atom. The fluorine atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, resulting in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the fluorine atom. In contrast, in the molecule oxygen (O2), there is a nonpolar covalent bond between the two oxygen atoms, resulting in no net charge on either atom.
What is a covalent bond?
+
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. This type of bonding is typically seen in molecules, where two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a stable compound.
What are the different types of covalent bonds?
+
There are several types of covalent bonds, including single, double, and triple bonds. A single covalent bond involves the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms, while a double covalent bond involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons. A triple covalent bond involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
+
Polar covalent bonds involve the unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other atom. Nonpolar covalent bonds involve the equal sharing of electrons, resulting in no net charge on either atom.