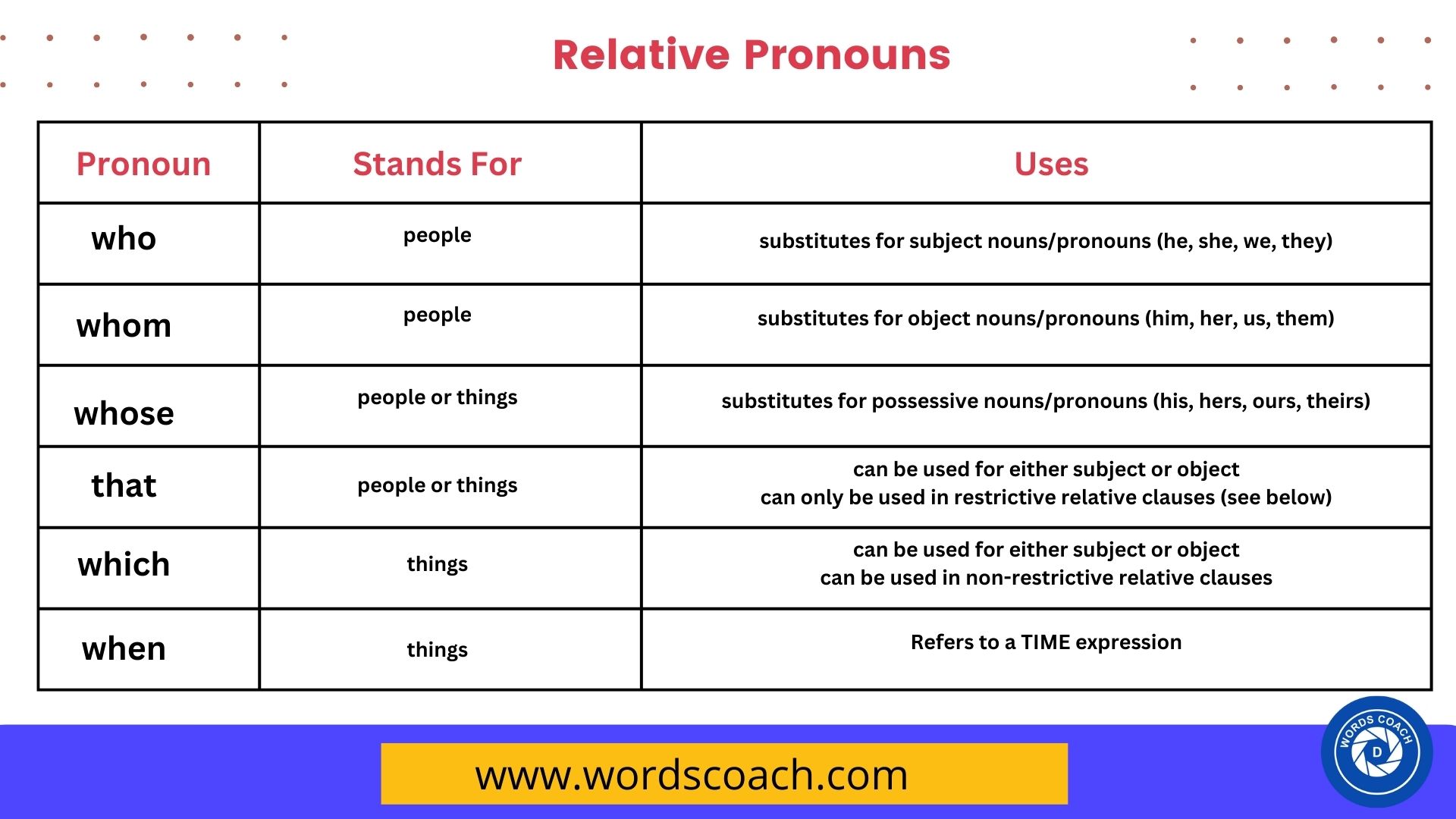
Cation Exchange Capacity
The cation exchange capacity (CEC) is a critical parameter in soil science, agronomy, and environmental studies, as it determines the soil's ability to retain and exchange cations, which are positively charged ions. CEC is a measure of the soil's capacity to hold onto these ions, such as calcium (Ca²⁺), magnesium (Mg²⁺), potassium (K⁺), and sodium (Na⁺), and to exchange them with other cations in the soil solution. In this article, we will delve into the concept of CEC, its importance, and its applications in various fields.
What is Cation Exchange Capacity?
Cation exchange capacity is the amount of cations that a soil can retain and exchange, expressed in terms of the amount of cations that can be exchanged per unit weight of soil, typically measured in milliequivalents per 100 grams of soil (meq/100g). CEC is a function of the soil’s clay content, organic matter, and pH, as these factors influence the availability of negatively charged sites on the soil particles that can attract and retain cations.
Factors Affecting Cation Exchange Capacity
Several factors affect the CEC of a soil, including:
- Clay content: Soils with high clay content tend to have higher CEC, as clay particles have a larger surface area and more negatively charged sites that can attract cations.
- Organic matter: Soils with high organic matter content also tend to have higher CEC, as organic matter can contribute to the formation of negatively charged sites that can attract cations.
- pH: The pH of the soil can also affect CEC, as some soils may have a higher CEC at certain pH ranges.
These factors can interact with each other and with other soil properties, such as the type and amount of clay minerals, the presence of other ions, and the soil's structure and porosity, to influence the overall CEC of the soil.
Importance of Cation Exchange Capacity
CEC is an important parameter in various fields, including:
- Agriculture: CEC is critical in agriculture, as it affects the soil’s ability to retain and supply nutrients to plants. Soils with high CEC can retain more nutrients, reducing the need for fertilizers and minimizing nutrient leaching into groundwater.
- Environmental studies: CEC is also important in environmental studies, as it can influence the transport and fate of pollutants, such as heavy metals and pesticides, in the soil and groundwater.
- Soil remediation: CEC can be used to assess the effectiveness of soil remediation strategies, such as the use of amendments to increase the soil’s CEC and retain pollutants.
Measurement of Cation Exchange Capacity
CEC can be measured using various methods, including:
- Ammonium acetate method: This method involves extracting the soil with ammonium acetate solution and measuring the amount of cations exchanged.
- Barium chloride method: This method involves extracting the soil with barium chloride solution and measuring the amount of cations exchanged.
These methods can provide accurate and reliable measurements of CEC, but they may require specialized equipment and expertise.
| Soil Type | CEC (meq/100g) |
|---|---|
| Sand | 1-5 |
| Silt | 5-15 |
| Clay | 15-30 |
| Organic soil | 30-50 |
Applications of Cation Exchange Capacity
CEC has various applications in agriculture, environmental studies, and soil remediation, including:
- Fertilizer management: CEC can be used to determine the optimal amount of fertilizer to apply to a soil, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Soil remediation: CEC can be used to assess the effectiveness of soil remediation strategies and to develop new strategies to increase the soil’s CEC and retain pollutants.
- Environmental modeling: CEC can be used to develop models that predict the transport and fate of pollutants in the soil and groundwater.
By understanding the CEC of a soil, we can develop effective strategies to manage soil fertility, minimize environmental impacts, and promote sustainable agriculture and environmental practices.
What is the importance of cation exchange capacity in agriculture?
+Cation exchange capacity is critical in agriculture, as it affects the soil’s ability to retain and supply nutrients to plants. Soils with high CEC can retain more nutrients, reducing the need for fertilizers and minimizing nutrient leaching into groundwater.
How is cation exchange capacity measured?
+Cation exchange capacity can be measured using various methods, including the ammonium acetate method and the barium chloride method. These methods involve extracting the soil with a solution and measuring the amount of cations exchanged.
What are the applications of cation exchange capacity in environmental studies?
+Cation exchange capacity has various applications in environmental studies, including the development of models that predict the transport and fate of pollutants in the soil and groundwater, and the assessment of the effectiveness of soil remediation strategies.