Buoyant Force Formula: Simplify Fluid Dynamics

The buoyant force is a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, playing a crucial role in understanding the behavior of objects when immersed in fluids. The buoyant force formula, derived from Archimedes' Principle, provides a mathematical framework for calculating the magnitude of this force. In this article, we will delve into the world of fluid dynamics, exploring the intricacies of the buoyant force formula and its applications in various fields.
Introduction to Buoyant Force

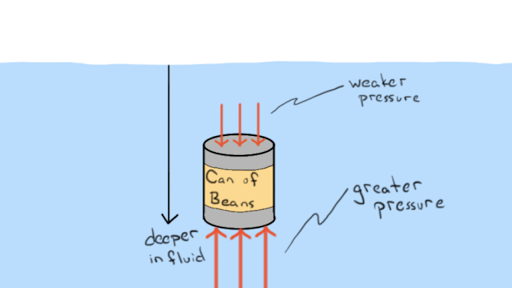
The buoyant force, also known as the upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid on an object partially or fully submerged in it. This force is a result of the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the object, causing it to experience an upward or downward force. The buoyant force formula, Fb = ρVg, where Fb is the buoyant force, ρ is the fluid density, V is the volume of the displaced fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity, provides a quantitative measure of this force.
Derivation of the Buoyant Force Formula
The derivation of the buoyant force formula can be attributed to Archimedes, who first discovered the principle that bears his name. According to Archimedes’ Principle, the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Mathematically, this can be expressed as Fluid Displacement = ρV, where ρ is the fluid density and V is the volume of the displaced fluid. By applying the force equation, F = mg, where m is the mass of the displaced fluid and g is the acceleration due to gravity, we arrive at the buoyant force formula, Fb = ρVg.
| Fluid Property | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Density | ρ | kg/m³ |
| Volume of Displaced Fluid | V | m³ |
| Acceleration due to Gravity | g | m/s² |
Applications of the Buoyant Force Formula

The buoyant force formula has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and marine biology. In engineering, the formula is used to design and optimize systems, such as buoyancy control devices, submarines, and oil rigs. In physics, the formula is employed to study the behavior of objects in fluids, including the motion of ships and aircraft. In marine biology, the formula is used to understand the behavior of marine animals, such as fish and dolphins, and their interactions with their aquatic environment.
Calculating Buoyant Force
To calculate the buoyant force on an object, we need to know the fluid density, the volume of the displaced fluid, and the acceleration due to gravity. For example, if we want to calculate the buoyant force on a cube with a side length of 1 meter, immersed in water with a density of 1000 kg/m³, we can use the following values: ρ = 1000 kg/m³, V = 1 m³, and g = 9.8 m/s². Plugging these values into the buoyant force formula, we get Fb = (1000 kg/m³)(1 m³)(9.8 m/s²) = 9800 N.
- Fluid density: The density of the fluid, typically measured in kg/m³.
- Volume of displaced fluid: The volume of the fluid displaced by the object, typically measured in m³.
- Acceleration due to gravity: The acceleration due to gravity, typically measured in m/s².
What is the buoyant force formula?
+The buoyant force formula is Fb = ρVg, where Fb is the buoyant force, ρ is the fluid density, V is the volume of the displaced fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What are the applications of the buoyant force formula?
+The buoyant force formula has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and marine biology, such as designing buoyancy control devices, studying the behavior of objects in fluids, and understanding the behavior of marine animals.
How do I calculate the buoyant force on an object?
+To calculate the buoyant force on an object, you need to know the fluid density, the volume of the displaced fluid, and the acceleration due to gravity. You can then use the buoyant force formula, Fb = ρVg, to calculate the buoyant force.