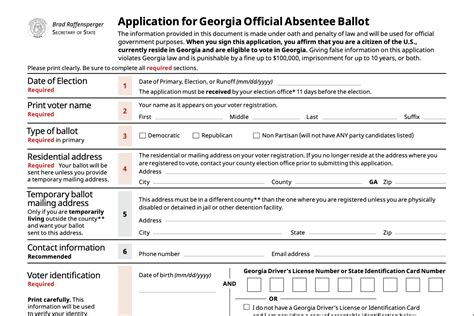
Bleeding Heart Flower
The Bleeding Heart Flower, scientifically known as Dicentra spectabilis, is a perennial flowering plant native to Asia. It is a member of the poppy family and is known for its unique, heart-shaped flowers that dangle from arching stems. The plant is a popular choice for gardeners due to its delicate, romantic appearance and its ability to thrive in shaded areas.
Characteristics and Growth Habits
The Bleeding Heart Flower typically grows to be around 2-3 feet tall and 1-2 feet wide, making it a great choice for smaller gardens or container plantings. The plant has delicate, fern-like foliage that is a deep green color and is often used as a backdrop for the showy flowers. The flowers themselves are a pale pink or white color and are shaped like hearts, with a drop of red or purple color at the base, giving the appearance of “bleeding”. The plant blooms in the spring and early summer, and the flowers are often followed by seed pods that contain small, fertile seeds.
Cultivation and Care
The Bleeding Heart Flower is a relatively low-maintenance plant that is easy to care for. It prefers well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter, and partial to full shade. The plant should be watered regularly, but the soil should not be allowed to become waterlogged. In terms of fertilization, the plant benefits from a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer applied in the spring. The plant can be pruned back after blooming to encourage new growth and prevent seed production.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Height | 2-3 feet |
| Width | 1-2 feet |
| Flower Color | Pale pink or white |
| Soil Preference | Well-draining, rich in organic matter |
| Sun Requirement | Partial to full shade |
Propagation and Division
The Bleeding Heart Flower can be propagated through division in the spring or fall. The plant should be dug up and the roots separated, with each division being replanted in a new location. The plant can also be grown from seed, but this method can be more challenging and may not result in plants that are true to the parent plant’s variety. In terms of pests and diseases, the Bleeding Heart Flower is generally a healthy plant, but it can be susceptible to slugs and snails as well as root rot if the soil is too wet.
Pest and Disease Management
To manage pests and diseases, gardeners can use a variety of techniques, including hand-picking slugs and snails, using copper barriers to deter these pests, and improving soil drainage to prevent root rot. The plant can also be treated with fungicides if it becomes infected with a fungal disease.
What is the ideal soil pH for the Bleeding Heart Flower?
+The ideal soil pH for the Bleeding Heart Flower is between 6.0 and 7.0, which is slightly acidic to neutral.
How often should I water my Bleeding Heart Flower?
+The Bleeding Heart Flower should be watered regularly, but the soil should not be allowed to become waterlogged. A good rule of thumb is to water the plant when the top 1-2 inches of soil feels dry to the touch.
Can I grow the Bleeding Heart Flower in a container?
+Yes, the Bleeding Heart Flower can be grown in a container. Choose a container that is at least 6-8 inches deep and has good drainage holes to prevent waterlogged soil.