Biology Is Science
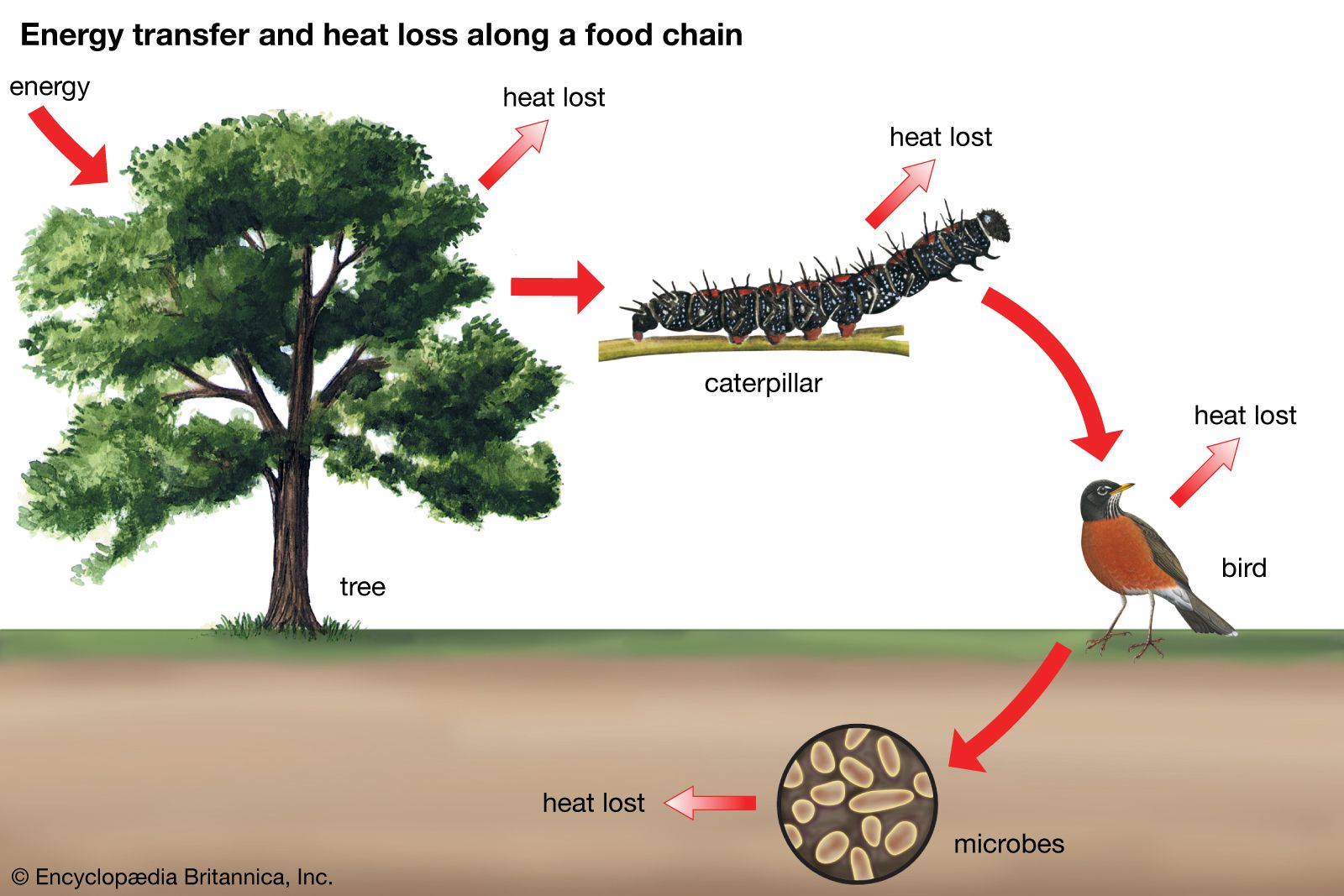
Biology, the scientific study of life and living organisms, is a vast and fascinating field that encompasses various disciplines, from the molecular mechanisms of cells to the complex interactions of entire ecosystems. As a branch of science, biology is grounded in the principles of observation, experimentation, and evidence-based reasoning. The study of biology has led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of the natural world and has significant implications for fields such as medicine, conservation, and agriculture.
The Foundations of Biology

The core of biology is built around several key concepts, including the cell theory, genetics, evolution, and the structure and function of biomolecules. The cell theory, which states that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, provides a fundamental framework for understanding the organization and function of life. Genetics, the study of heredity and variation, has revealed the mechanisms by which traits are inherited from one generation to the next. Evolution, the process by which species change over time through natural selection, genetic drift, and other mechanisms, explains the diversity of life on Earth. Furthermore, the study of biomolecules, such as DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates, has elucidated the chemical basis of life and its processes.
Branches of Biology
Biology is a diverse field that is divided into several branches, each focusing on a specific aspect of life. Molecular biology explores the structure and function of biomolecules, while cell biology examines the behavior and interactions of cells. Ecology, the study of the interactions between organisms and their environment, is crucial for understanding the delicate balance of ecosystems. Genetics and evolutionary biology provide insights into the mechanisms of inheritance and the history of life on Earth. Other branches, such as botany, zoology, and microbiology, focus on specific groups of organisms, from plants and animals to microorganisms.
| Branch of Biology | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecular Biology | Study of the structure and function of biomolecules |
| Cell Biology | Examination of the behavior and interactions of cells |
| Ecology | Study of the interactions between organisms and their environment |
| Genetics | Study of heredity and variation |
| Evolutionary Biology | Study of the history and processes of evolution |

Biology has numerous applications in real-world scenarios, from the development of new medicines and agricultural practices to the conservation of ecosystems and the management of natural resources. For instance, advances in genetic engineering have enabled the creation of crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, potentially increasing food security. Similarly, the study of ecology has informed conservation efforts, helping to protect endangered species and preserve biodiversity.
Applications of Biology

The applications of biology are diverse and widespread. In medicine, biological knowledge is used to develop new treatments for diseases, understand the mechanisms of disease progression, and improve human health. In agriculture, biology informs the development of more efficient and sustainable farming practices, enhancing food production and reducing environmental impact. Conservation biology applies ecological principles to protect and restore ecosystems, preserving biodiversity and ecosystem services. Additionally, biology has significant implications for biotechnology, where biological systems are used to develop new products and technologies.
Future Directions in Biology
As biology continues to evolve as a field, several areas are expected to see significant advancements in the coming years. Synthetic biology, which involves the design and construction of new biological systems, has the potential to revolutionize biotechnology and bioengineering. Systems biology, an approach that focuses on the study of complex biological systems, will continue to provide insights into the intricate interactions within cells and ecosystems. Furthermore, the integration of biology with other disciplines, such as physics, chemistry, and computer science, will lead to new methodologies and technologies that can tackle complex biological questions.
In conclusion, biology is a dynamic and multifaceted science that underpins our understanding of life and the natural world. Through its various branches and applications, biology has the power to address some of humanity's most pressing challenges, from improving human health and food security to conserving biodiversity and mitigating the effects of climate change.
What is the importance of biology in everyday life?
+Biology plays a crucial role in everyday life, from the food we eat to the medicines we take. It informs agricultural practices, helps us understand and treat diseases, and underpins conservation efforts. Biology is essential for developing new technologies and products, such as biofuels and bioplastics, and for addressing global challenges like climate change and biodiversity loss.
How does biology contribute to medical advancements?
+Biology is fundamental to medical advancements, providing insights into the mechanisms of disease, the development of new treatments, and the improvement of human health. Through the study of genetics, molecular biology, and cell biology, scientists can understand the underlying causes of diseases and develop targeted therapies. Biology also informs the development of vaccines, diagnostic tools, and personalized medicine.
What is the role of biology in conservation and environmental management?
+Biology is essential for conservation and environmental management, as it provides the scientific basis for understanding ecosystems, species, and their interactions. By studying ecology, conservation biology, and evolutionary biology, scientists can identify areas of high conservation value, develop strategies to protect endangered species, and manage natural resources sustainably. Biology informs policies and practices aimed at preserving biodiversity, mitigating the effects of climate change, and maintaining ecosystem services.



