Asn Amino Acid
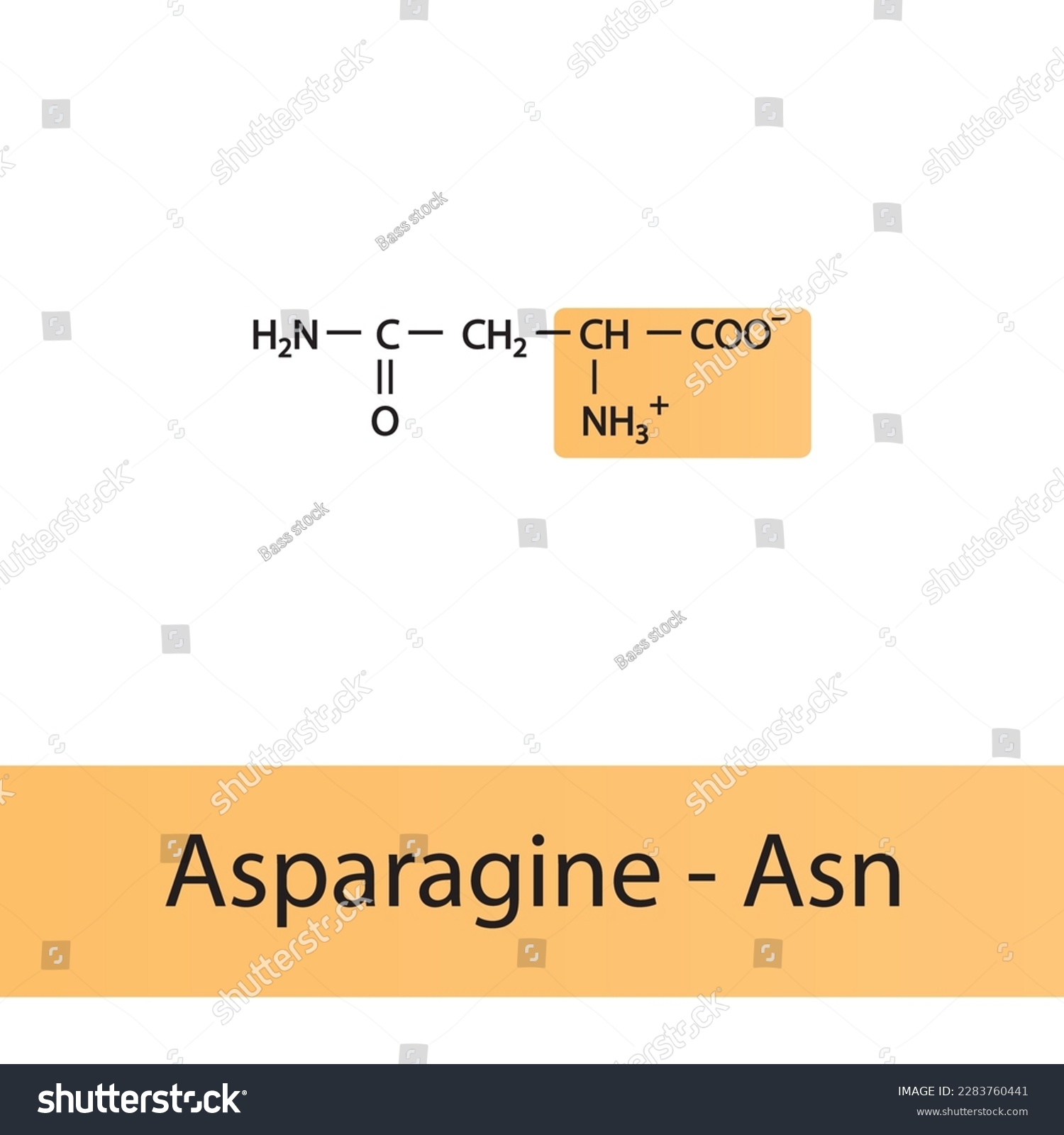
The amino acid Asn, also known as Asparagine, is a non-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various biological processes. It is encoded by the codons AAC and AAU and is one of the 20 standard amino acids found in proteins. Asparagine is an amide derivative of the amino acid aspartic acid, and its side chain contains a carboxamide group.
Structure and Properties of Asn

Asn has a molecular formula of C4H8N2O3 and a molecular weight of 132.12 g/mol. It is a polar, uncharged amino acid with a pKa value of 2.02, which is the pH at which the amino acid exists in its zwitterionic form. Asn is soluble in water and has a melting point of 221-222°C. Its structure consists of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain containing a carboxamide group.
Biological Functions of Asn
Asn is involved in various biological processes, including protein synthesis, metabolism, and cell signaling. It is a precursor to the synthesis of other amino acids, such as aspartic acid and arginine, and is also involved in the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids. Asn is also a key component of the pentose phosphate pathway, which generates NADPH and pentoses from glucose-6-phosphate.
| Amino Acid | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Asn (Asparagine) | C4H8N2O3 | 132.12 g/mol |
| Asp (Aspartic Acid) | C4H7NO4 | 133.10 g/mol |
| Arg (Arginine) | C6H14N4O2 | 174.20 g/mol |

Asn is also involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as aspartate and glutamate, which play a crucial role in neurotransmission. It is also a precursor to the synthesis of N-acetylglutamate, which is involved in the regulation of the urea cycle.
Metabolism of Asn

The metabolism of Asn involves its conversion to aspartic acid, which is then converted to oxaloacetate and entered into the citric acid cycle. Asn can also be converted to arginine, which is then converted to urea and excreted. The metabolism of Asn is regulated by various enzymes, including asparaginase, which converts Asn to aspartic acid, and arginase, which converts arginine to urea.
Regulation of Asn Expression
The expression of Asn is regulated by various factors, including hormones, growth factors, and nutrients. Insulin, for example, stimulates the expression of Asn, while glucagon inhibits its expression. The expression of Asn is also regulated by the availability of amino acids, with high levels of Asn inhibiting its own expression.
Asn is also involved in the regulation of gene expression, and its expression is altered in response to various environmental stimuli, including stress, hypoxia, and nutrient deprivation. The regulation of Asn expression is complex and involves the coordinated action of multiple transcription factors and signaling pathways.
What is the molecular formula of Asn?
+
The molecular formula of Asn is C4H8N2O3.
What is the biological function of Asn?
+
Asn is involved in various biological processes, including protein synthesis, metabolism, and cell signaling.
What is the role of Asn in cancer?
+
Asn is involved in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation, and its expression is altered in various types of cancer.