Antibiotics Side Effects Guide

Antibiotics are a crucial part of modern medicine, used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. However, like all medications, they can have side effects. Understanding these side effects is essential for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment and for healthcare providers to prescribe antibiotics safely and effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of antibiotics, exploring their mechanism of action, common side effects, and strategies for mitigating these effects.
Introduction to Antibiotics

Antibiotics are medicines that are designed to kill bacteria or inhibit their growth. They are prescribed for various infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. The discovery of antibiotics revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people worldwide. However, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, making it crucial to use these medications judiciously.
How Antibiotics Work
Antibiotics work by targeting specific processes essential for bacterial survival. For example, beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillins and cephalosporins, inhibit the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell lysis and death. Macrolides and quinolones interfere with protein synthesis and DNA replication, respectively, in bacteria. Understanding how antibiotics work is key to understanding their side effects and potential interactions with other medications.
Common Side Effects of Antibiotics
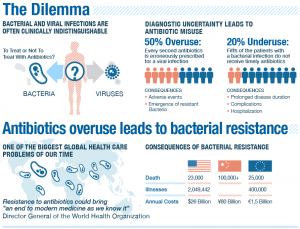
While antibiotics are generally safe, they can cause a range of side effects. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms are often mild and transient but can sometimes be severe enough to warrant discontinuation of the antibiotic. Other common side effects include rash, headache, and fatigue. In rare cases, antibiotics can cause more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, liver toxicity, and Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) infection.
Antibiotic Resistance and Its Implications
The overuse and misuse of antibiotics have accelerated the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. When bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, infections become harder to treat, increasing the risk of complications and death. Antibiotic stewardship programs have been implemented in many healthcare settings to promote the appropriate use of antibiotics and combat resistance. These programs involve strategies such as using the narrowest spectrum antibiotic possible, limiting the duration of antibiotic treatment, and ensuring that antibiotics are only prescribed when necessary.
| Antibiotic Class | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Penicillins | Diarrhea, rash, allergic reactions |
| Cephalosporins | Nausea, vomiting, headache |
| Macrolides | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue |
| Quinolones | Dizziness, nausea, liver toxicity (rare) |

Strategies for Minimizing Side Effects
To minimize the side effects of antibiotics, patients should take their medication exactly as prescribed and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the antibiotics. It is also important to maintain good hygiene, especially handwashing, to prevent the spread of infections. Additionally, probiotics may help mitigate gastrointestinal side effects by supporting the balance of gut flora.
Future Directions in Antibiotic Development
The development of new antibiotics is critical to addressing the challenge of antibiotic resistance. Researchers are exploring novel targets and mechanisms of action, such as inhibiting bacterial virulence factors or targeting the bacterial cell membrane. Furthermore, antibiotic adjuvants that enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics are being investigated. These advancements hold promise for improving the treatment of bacterial infections and reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
What are the most common side effects of antibiotics?
+The most common side effects of antibiotics include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rash, headache, and fatigue. These symptoms are usually mild and temporary but can sometimes be severe.
How can I minimize the side effects of antibiotics?
+To minimize side effects, take antibiotics exactly as prescribed, complete the full course of treatment, and consider taking probiotics to support gut health. It’s also important to maintain good hygiene practices.
What is antibiotic resistance, and why is it a concern?
+Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve to withstand the effects of antibiotics, making infections harder to treat. This is a significant concern because it increases the risk of treatment failure, complications, and death. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics accelerate resistance, highlighting the need for responsible antibiotic use.
