Anatomy Physiology: Master Human Body Functions

The human body is a complex and fascinating system, comprising numerous organs, tissues, and cells that work together to maintain overall health and function. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body is essential for medical professionals, researchers, and individuals seeking to improve their overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of human body functions, exploring the various systems, organs, and processes that enable us to live, grow, and thrive.
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology

Human anatomy refers to the study of the structure and organization of the body, including the relationships between different organs, tissues, and cells. Physiology, on the other hand, focuses on the functions and processes that occur within the body, such as movement, digestion, and respiration. Together, anatomy and physiology provide a comprehensive understanding of the human body, enabling us to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that maintain homeostasis and overall health.
Body Systems and Organs
The human body is composed of 11 major systems, each comprising various organs and tissues that work together to perform specific functions. These systems include:
- Nervous system: responsible for controlling and coordinating body functions, including movement, sensation, and cognition
- Circulatory system: transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products
- Respiratory system: brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide through breathing
- Digestive system: breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized by the body
- Endocrine system: produces hormones that regulate various bodily functions, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction
- Integumentary system: protects the body from external damage and regulates body temperature
- Muscular system: enables movement, maintains posture, and regulates body temperature
- Skeletal system: provides support, protection, and movement for the body
- Urinary system: removes waste and excess fluids from the body
- Reproductive system: produces sex cells and supports the development of a fetus during pregnancy
- Immune system: protects the body against pathogens and foreign substances
Each system is composed of various organs and tissues that work together to perform specific functions. For example, the circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood, which work together to transport oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove waste products.
Physiological Processes

Physiological processes refer to the functions and activities that occur within the body, such as movement, digestion, and respiration. These processes are essential for maintaining homeostasis and overall health. Some key physiological processes include:
Movement and Locomotion
Movement and locomotion are essential for maintaining posture, balance, and overall mobility. The muscular system, skeletal system, and nervous system work together to enable movement, with muscles contracting and relaxing to produce movement, bones providing support and leverage, and the nervous system coordinating and controlling muscle activity.
Digestion and Absorption
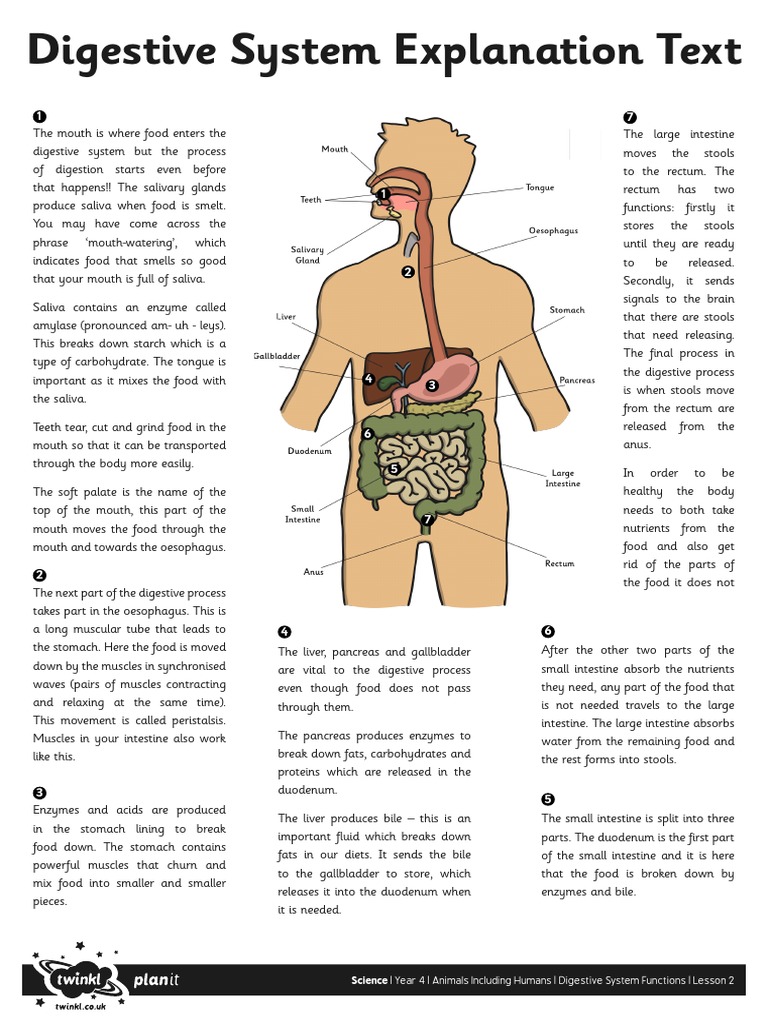
Digestion and absorption are critical for breaking down food into nutrients that can be utilized by the body. The digestive system, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, works together to break down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Respiration and Gas Exchange
Respiration and gas exchange are essential for bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide. The respiratory system, including the lungs, trachea, bronchi, and diaphragm, works together to bring oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide through breathing.
| System | Organs | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Nervous System | Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves | Controls and coordinates body functions |
| Circulatory System | Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood | Transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products |
| Respiratory System | Lungs, Trachea, Bronchi, Diaphragm | Brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide |
| Digestive System | Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine | Breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized by the body |
Homeostasis and Regulation
Homeostasis refers to the ability of the body to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions. The body uses various mechanisms to regulate and maintain homeostasis, including negative feedback loops, positive feedback loops, and hormonal regulation. For example, the body regulates blood sugar levels through the release of insulin and glucagon, which work together to maintain a stable blood sugar level.
Negative Feedback Loops
Negative feedback loops are mechanisms that counteract changes in the body, such as the regulation of blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin, which stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells and reduces blood sugar levels. Conversely, when blood sugar levels fall, the pancreas releases glucagon, which stimulates the release of glucose from stored energy sources and increases blood sugar levels.
Positive Feedback Loops
Positive feedback loops are mechanisms that amplify changes in the body, such as the regulation of blood clotting. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets are activated, which triggers a cascade of reactions that ultimately leads to the formation of a blood clot. This process is an example of a positive feedback loop, where the activation of platelets amplifies the response to injury and promotes the formation of a blood clot.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the human body is a complex and fascinating system, comprising numerous organs, tissues, and cells that work together to maintain overall health and function. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body is essential for medical professionals, researchers, and individuals seeking to improve their overall well-being. Future research directions may include the development of new treatments and therapies for diseases and disorders, as well as a greater understanding of the intricate mechanisms that maintain homeostasis and overall health.
What is the importance of understanding human anatomy and physiology?
+
Understanding human anatomy and physiology is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. It enables individuals to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that maintain homeostasis and overall health, and take steps to promote healthy habits and prevent disease.
What are the major systems of the human body?
+
The human body is composed of 11 major systems, including the nervous system, circulatory system, respiratory system, digestive system, endocrine system, integumentary system, muscular system, skeletal system, urinary system, reproductive system, and immune system.
How does the body maintain homeostasis?
+
The body maintains homeostasis through various mechanisms, including negative feedback loops, positive feedback loops, and hormonal regulation. These mechanisms work together to regulate and maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions.
