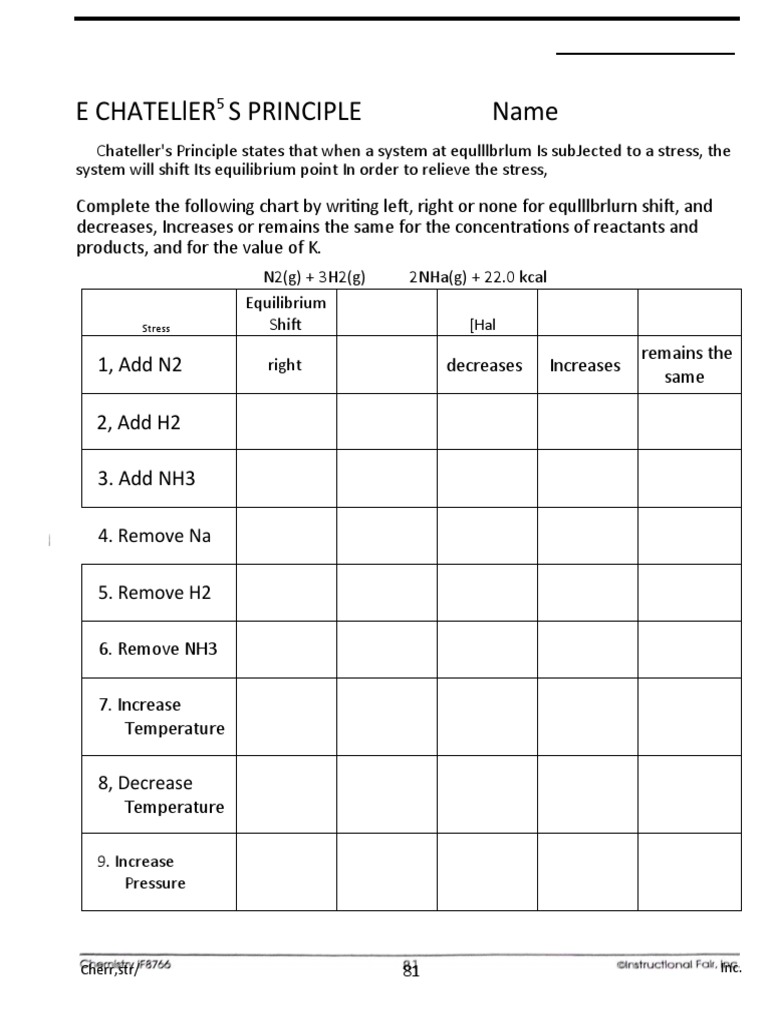
9 Years In Dog Years
The concept of "dog years" is a popular way to estimate a dog's age in human years, but it's not as simple as it sounds. The idea behind dog years is that dogs age at a faster rate than humans, especially during the early years of their life. However, the traditional method of calculating dog years, which is to multiply a dog's age by 7, is not entirely accurate.
Understanding Dog Years
The notion of dog years originated from the fact that dogs mature and age at a different rate than humans. While humans take about 20 years to reach physical maturity, dogs can reach adulthood in just 2-3 years. This rapid growth and development mean that dogs experience a faster pace of life, which can affect their physical and mental health. For example, a 1-year-old dog is equivalent to a human teenager, while a 2-year-old dog is similar to a human in their early twenties.
Calculating Dog Years
A more accurate way to calculate dog years is to consider the dog’s breed, size, and health status. Small breeds, such as Chihuahuas and Poodles, tend to live longer than large breeds, like Great Danes and Mastiffs. According to the American Kennel Club, the first two years of a dog’s life are equivalent to about 10-14 human years, while each subsequent year is equivalent to about 5-7 human years. Using this method, a 9-year-old dog would be equivalent to a human in their mid-to-late fifties.
| Dog Age | Human Equivalent |
|---|---|
| 1 year | 10-14 years |
| 2 years | 20-24 years |
| 3 years | 25-29 years |
| 4 years | 30-34 years |
| 5 years | 35-39 years |
| 6 years | 40-44 years |
| 7 years | 45-49 years |
| 8 years | 50-54 years |
| 9 years | 55-59 years |
Factors Affecting Dog Longevity
A dog’s lifespan is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Breed, size, and health status are significant contributors to a dog’s longevity. For example, genetic disorders can affect certain breeds, such as hip dysplasia in large breeds or eye problems in small breeds. Additionally, nutrition and exercise play crucial roles in maintaining a dog’s physical and mental health. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help prevent obesity, diabetes, and other health issues that can shorten a dog’s lifespan.
Health Considerations
As dogs age, they become more prone to certain health issues, such as arthritis, cancer, and kidney disease. Regular veterinary check-ups and preventative care, such as vaccinations and parasite control, can help identify and manage these conditions. Furthermore, mental health is also essential, as dogs can experience anxiety and depression, especially in their senior years. Providing a comfortable and stimulating environment, including socialization and cognitive stimulation, can help mitigate these issues.
In conclusion, 9 years in dog years is equivalent to a human in their mid-to-late fifties, but this is only an estimate. By understanding the factors that affect dog longevity and taking proactive steps to maintain their physical and mental health, dog owners can help their furry friends live a long, happy, and healthy life.
How accurate is the traditional method of calculating dog years?
+The traditional method of calculating dog years, which is to multiply a dog’s age by 7, is not entirely accurate. A more accurate method is to consider the dog’s breed, size, and health status.
What factors affect a dog’s longevity?
+A dog’s longevity is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including breed, size, health status, nutrition, and exercise.
How can I help my dog live a long and healthy life?
+By providing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and preventative care, such as vaccinations and parasite control, you can help maintain your dog’s physical and mental health. Regular veterinary check-ups and a comfortable and stimulating environment can also contribute to a long and healthy life.