37 Degree Fahrenheit: Know When It's Freezing
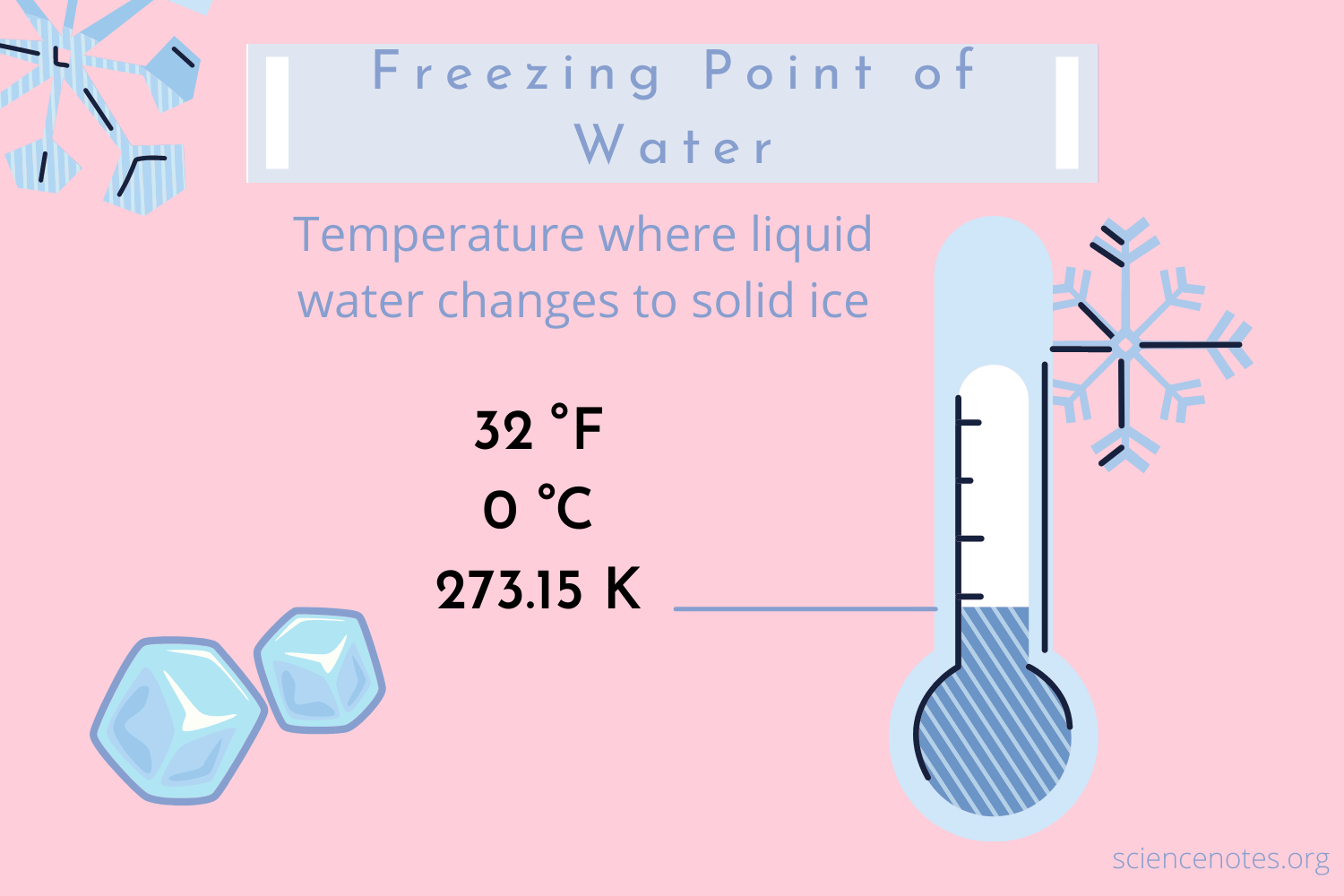
The concept of freezing is often associated with temperatures at or below 32 degrees Fahrenheit (0 degrees Celsius), which is the freezing point of water. However, the perception of cold and the onset of freezing conditions can vary significantly depending on several factors, including humidity, wind speed, and the specific context in which the temperature is being considered. For instance, when discussing the freezing of water or the impact of cold temperatures on various materials and living organisms, the precise temperature can be critical. In this article, we will explore the implications of a temperature of 37 degrees Fahrenheit, which, while above the freezing point of water, can still have significant effects on both the natural world and human activities.
Understanding Temperature Scales

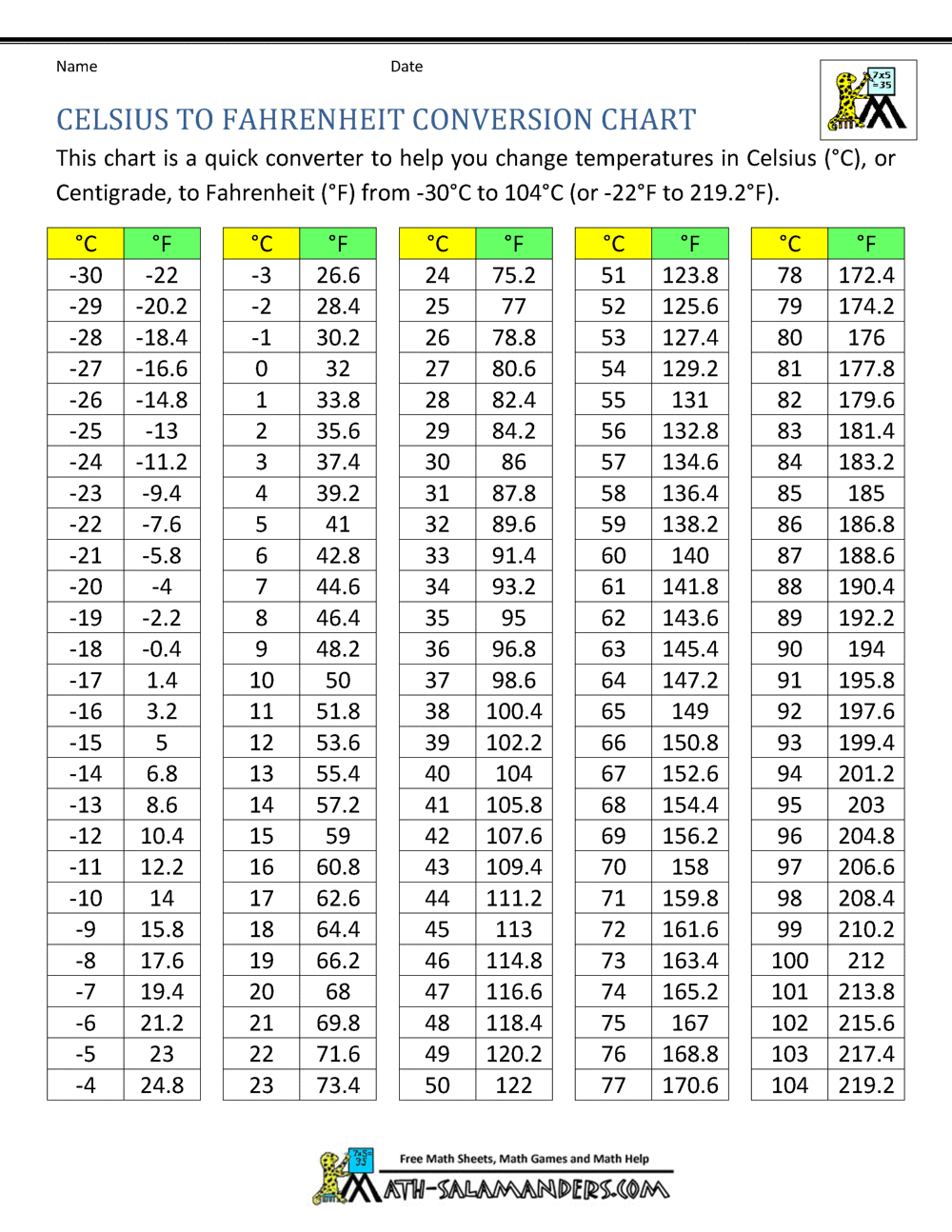
Temperature is a fundamental physical quantity that is measured using various scales, with the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales being the most commonly used. The Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32 degrees and the boiling point at 212 degrees, while the Celsius scale sets these points at 0 degrees and 100 degrees, respectively. A temperature of 37 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 2.78 degrees Celsius. This temperature is notably close to the average human body temperature, which is around 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius), highlighting the relatively narrow range of temperatures that are considered comfortable for human habitation.
Implications for Human Health
Temperatures around 37 degrees Fahrenheit can have implications for human health, particularly in terms of hypothermia and the preservation of perishable medical supplies. Hypothermia, a condition where the body’s core temperature drops below 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius), can occur even in temperatures above freezing if an individual is wet or exposed to cold for an extended period. Understanding the risks associated with cold temperatures is crucial for preventing and treating hypothermia. Additionally, certain medical supplies and vaccines must be stored at specific temperatures to remain effective, and temperatures around 37 degrees Fahrenheit can be within the acceptable range for some of these products, depending on their formulation and storage requirements.
| Temperature (Fahrenheit) | Equivalent Celsius | Human Health Implications |
|---|---|---|
| 37 | 2.78 | Comfortable for storage of certain medical supplies, potential for hypothermia in specific conditions |
| 32 | 0 | Freezing point of water, increased risk of hypothermia and frostbite |
| 95 | 35 | Threshold for hypothermia, significant risk to health if body temperature drops below this point |
Environmental and Material Implications

Temperatures around 37 degrees Fahrenheit can have significant implications for the environment and various materials. For plants, temperatures below 40 degrees Fahrenheit (4.44 degrees Celsius) can lead to frost damage, affecting growth and productivity. In construction and engineering, the freezing point of water is crucial because water expands when it freezes, which can cause damage to structures and infrastructure. Although 37 degrees Fahrenheit is above the freezing point, understanding the thermal properties of materials and the potential impacts of temperature fluctuations is vital for designing and maintaining resilient infrastructure.
Applications in Science and Technology
In scientific research and technological applications, precise temperature control is often necessary. For instance, in laboratories, certain experiments and the storage of biological samples require temperatures to be maintained within narrow ranges. A temperature of 37 degrees Fahrenheit, being close to the human body temperature, is particularly relevant in biomedical research, where simulating human physiological conditions is essential. Furthermore, in the development of materials and technologies intended for use in cold environments, understanding how materials behave at temperatures around 37 degrees Fahrenheit can provide valuable insights into their performance under more extreme conditions.
In conclusion, while 37 degrees Fahrenheit may not be considered "freezing" in the traditional sense, it is a temperature that can have significant implications for human health, environmental conditions, and various technological and scientific applications. Understanding these implications and the factors that influence our perception and experience of cold temperatures is essential for a wide range of fields, from medicine and environmental science to materials engineering and beyond.
What is the significance of 37 degrees Fahrenheit in human health?
+
37 degrees Fahrenheit is significant in human health because it is close to the average human body temperature, and temperatures around this point can be relevant for the storage of medical supplies and the prevention of hypothermia.
How does a temperature of 37 degrees Fahrenheit affect plants?
+
Temperatures around 37 degrees Fahrenheit are generally not harmful to most plants, but temperatures below 40 degrees Fahrenheit can lead to frost damage, affecting plant growth and productivity.
What are the implications of 37 degrees Fahrenheit for materials and infrastructure?
+
Although 37 degrees Fahrenheit is above the freezing point of water, understanding thermal properties and potential temperature fluctuations is crucial for designing and maintaining resilient infrastructure, as water expansion upon freezing can cause structural damage.
