12 Wien's Displacement Law Secrets Revealed
Wien's Displacement Law, a fundamental principle in physics, describes the relationship between the temperature of a blackbody and the wavelength at which it emits the most intense radiation. This law, formulated by Wilhelm Wien in the late 19th century, has far-reaching implications in various fields, including astronomy, engineering, and climate science. In this article, we will delve into the secrets of Wien's Displacement Law, exploring its underlying principles, applications, and significance in modern physics.
Introduction to Wien’s Displacement Law
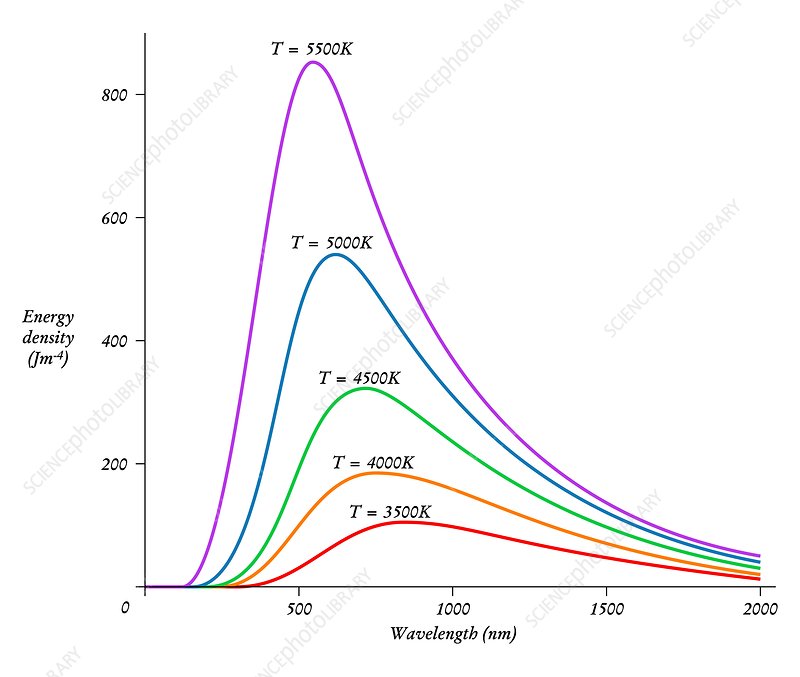
Wien’s Displacement Law states that the wavelength at which a blackbody emits the most intense radiation is inversely proportional to its temperature. Mathematically, this is expressed as λ_max = b / T, where λ_max is the peak wavelength, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and b is a constant of proportionality. This law provides a crucial link between the thermal properties of an object and its radiative behavior, enabling scientists to infer temperatures from spectral measurements.
Historical Context and Development
The development of Wien’s Displacement Law was a significant milestone in the history of physics. In the late 19th century, scientists were struggling to understand the nature of blackbody radiation. Wilhelm Wien, a German physicist, conducted a series of experiments and derived the displacement law, which was later refined by other researchers, including Max Planck. The law has since become a cornerstone of modern physics, with applications in diverse fields, including astrophysics, materials science, and engineering.
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| Wien's displacement law constant (b) | 2.897771955 × 10^(-3) m·K |

Applications of Wien’s Displacement Law

Wien’s Displacement Law has numerous applications in various fields. In astronomy, it is used to determine the temperatures of stars and other celestial objects from their spectral properties. In engineering, it is applied in the design of thermal systems, such as heat exchangers and radiative coolers. Additionally, the law is used in climate science to study the Earth’s energy balance and the effects of greenhouse gases on the planet’s temperature.
Temperature Measurements and Radiative Transfer
Wien’s Displacement Law is a crucial tool for temperature measurements. By measuring the peak wavelength of an object’s emission spectrum, scientists can infer its temperature. This technique is widely used in various fields, including materials science, biology, and medicine. Furthermore, the law is essential for radiative transfer calculations, which are critical in understanding the behavior of complex systems, such as atmospheric circulation and heat transfer in buildings.
Some of the key applications of Wien's Displacement Law include:
- Astronomy: determining the temperatures of stars and other celestial objects
- Engineering: designing thermal systems, such as heat exchangers and radiative coolers
- Climate science: studying the Earth's energy balance and the effects of greenhouse gases on the planet's temperature
- Materials science: measuring the temperatures of materials and understanding their thermal properties
Future Implications and Research Directions
Wien's Displacement Law continues to be an active area of research, with scientists exploring its implications in various fields. One of the key research directions is the development of new technologies that can harness the principles of the law to create more efficient thermal systems and radiative devices. Additionally, researchers are investigating the law's applications in emerging fields, such as nanotechnology and biophotonics.
Emerging Technologies and Applications
The future of Wien’s Displacement Law is closely tied to the development of new technologies and applications. Some of the emerging areas include:
- Nanotechnology: using the law to design and optimize nanoscale thermal systems and radiative devices
- Biophotonics: applying the law to understand and manipulate the thermal properties of biological systems
- Renewable energy: using the law to optimize the performance of solar cells and other renewable energy systems
What is Wien’s Displacement Law?
+Wien’s Displacement Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes the relationship between the temperature of a blackbody and the wavelength at which it emits the most intense radiation.
What are the applications of Wien’s Displacement Law?
+The applications of Wien’s Displacement Law are diverse and include astronomy, engineering, climate science, materials science, and biophotonics, among others.
What is the significance of Wien’s Displacement Law in modern physics?
+Wien’s Displacement Law is a cornerstone of modern physics, providing a crucial link between the thermal properties of an object and its radiative behavior. It has far-reaching implications in various fields and continues to be an active area of research.


