12+ Icd 10 Tinea Versicolor Tips For Accurate Coding

Tinea versicolor is a common skin condition characterized by patches of discoloration on the skin, typically caused by a fungal infection. Accurate coding of this condition is crucial for medical billing and insurance purposes. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), provides a standardized system for coding diseases, including tinea versicolor. In this article, we will provide 12+ tips for accurate coding of tinea versicolor using ICD-10.
Understanding Tinea Versicolor and ICD-10 Coding

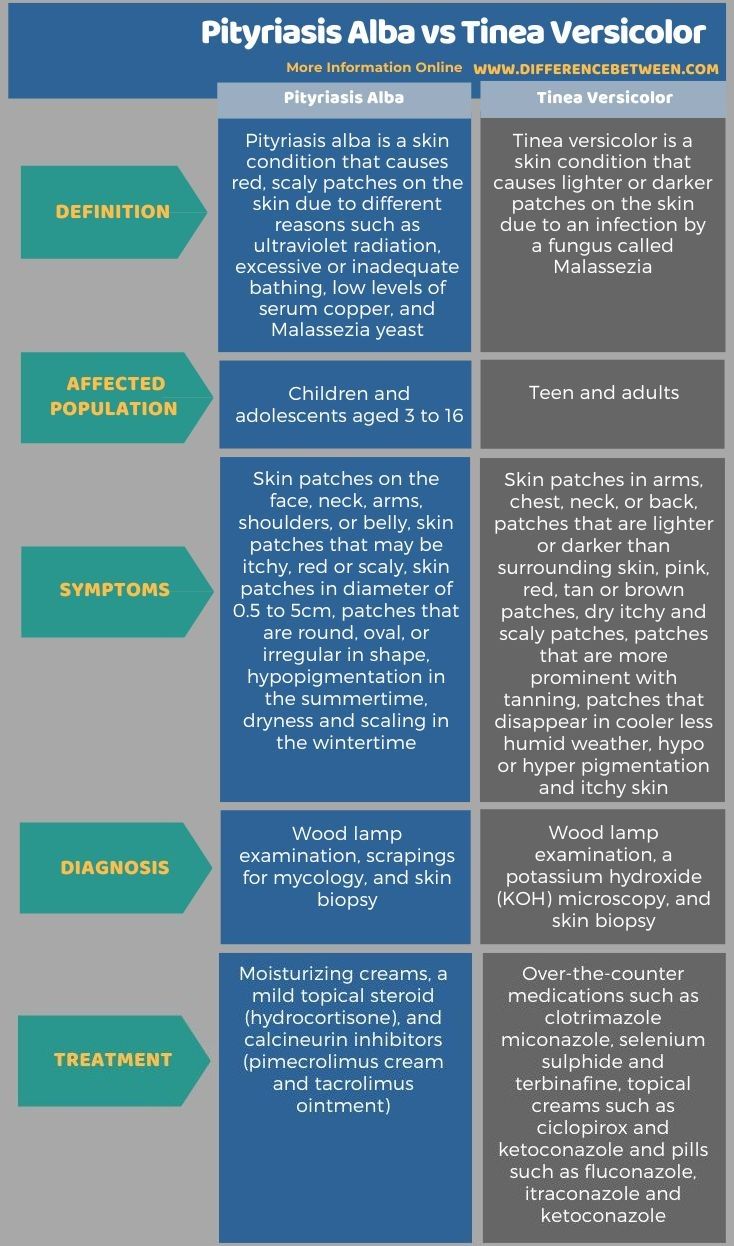
Tinea versicolor is a condition caused by the overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus on the skin, typically in areas with high oil production, such as the chest, back, and arms. The condition is also known as pityriasis versicolor. ICD-10 coding for tinea versicolor requires an understanding of the condition’s symptoms, severity, and location on the body. The ICD-10 code for tinea versicolor is B36.0, which is classified under the category of “Other fungal diseases” in the ICD-10 manual.
Tip 1: Identify the Correct Code for Tinea Versicolor
The correct ICD-10 code for tinea versicolor is B36.0. This code should be used for all cases of tinea versicolor, regardless of the location on the body or the severity of the condition. It’s essential to note that tinea versicolor is a type of fungal infection, and the code B36.0 specifically represents this condition.
Tip 2: Specify the Location of the Condition
While the code B36.0 covers tinea versicolor in general, it’s essential to specify the location of the condition on the body. ICD-10 codes for tinea versicolor can be further specified using additional codes to indicate the location, such as:
| Location | ICD-10 Code |
|---|---|
| Face | B36.0 + L71.1 |
| Chest | B36.0 + L71.2 |
| Back | B36.0 + L71.3 |
It’s crucial to use the correct combination of codes to accurately represent the condition and its location.
Tip 3: Document the Severity of the Condition
ICD-10 coding for tinea versicolor also requires documentation of the condition’s severity. The severity can be indicated using additional codes, such as:
- B36.0 for mild cases
- B36.1 for moderate cases
- B36.2 for severe cases
Tip 4: Consider Additional Codes for Associated Conditions
Tinea versicolor can be associated with other conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis. In these cases, additional codes may be required to accurately represent the associated conditions. For example:
| Associated Condition | ICD-10 Code |
|---|---|
| Eczema | L20.9 |
| Psoriasis | L40.9 |
Additional Tips for Accurate Coding
In addition to the tips mentioned above, here are some additional tips for accurate coding of tinea versicolor:
Tip 5: Use the Correct Code for Recurrent Cases
For recurrent cases of tinea versicolor, the code B36.0 can be used with an additional code to indicate the recurrence, such as Z87.09.
Tip 6: Consider Codes for Complications
Complications of tinea versicolor, such as secondary bacterial infection, can be coded using additional codes, such as B95.0.
Tip 7: Use Codes for Associated Symptoms
Associated symptoms of tinea versicolor, such as pruritus, can be coded using additional codes, such as R21.0.
Tip 8: Document the Treatment
Documentation of the treatment for tinea versicolor is essential for accurate coding. The treatment can be coded using additional codes, such as Z51.89 for antifungal medication.
Tip 9: Consider Codes for Prevention
Prevention of tinea versicolor can be coded using additional codes, such as Z29.1 for prophylactic antifungal medication.
Tip 10: Use Codes for Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care for tinea versicolor can be coded using additional codes, such as Z09.89 for follow-up examination.
Tip 11: Document the Patient’s History
Documentation of the patient’s history, including previous episodes of tinea versicolor, is essential for accurate coding.
Tip 12: Use Codes for Patient Education
Patient education on the prevention and treatment of tinea versicolor can be coded using additional codes, such as Z91.89 for patient education on skin care.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for tinea versicolor?
+The correct ICD-10 code for tinea versicolor is B36.0.
How do I specify the location of the condition on the body?
+The location of the condition can be specified using additional codes, such as L71.1 for the face, L71.2 for the chest, and L71.3 for the back.
What is the difference between the codes B36.0, B36.1, and B36.2?
+The codes B36.0, B36.1, and B36.2 represent different severities of tinea versicolor, with B36.0 representing mild cases, B36.1 representing moderate cases, and B36.2 representing severe cases.

