10+ P Value Hacks For Statistics Success
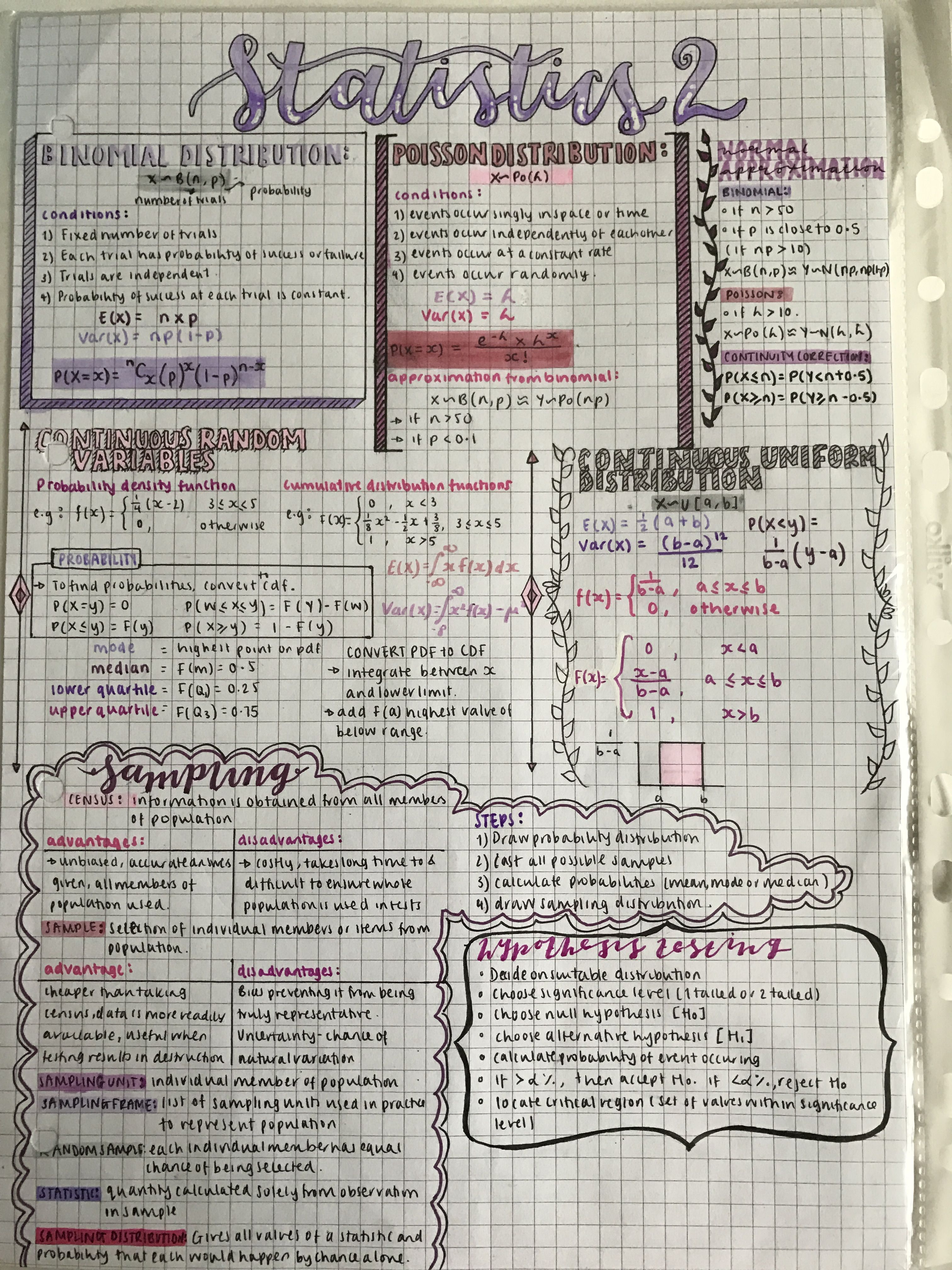
The p-value is a crucial concept in statistical analysis, representing the probability of obtaining the observed results (or more extreme) given that the null hypothesis is true. Understanding and correctly interpreting p-values is essential for drawing accurate conclusions from data. In this article, we will delve into 10+ p-value hacks for statistics success, providing you with a comprehensive guide to navigate the complexities of statistical significance.
Understanding the Basics of P-Value

Before diving into the hacks, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concept of p-value. The p-value, or probability value, is a number between 0 and 1 that indicates the strength of evidence against a null hypothesis. A small p-value (typically less than 0.05) suggests that the observed data would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis, leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis. On the other hand, a large p-value indicates that the data is consistent with the null hypothesis, and we fail to reject it.
P-Value Misinterpretations
One of the most common misinterpretations of p-values is that they represent the probability of the null hypothesis being true. However, the p-value only indicates the probability of observing the data (or more extreme) given that the null hypothesis is true. It does not provide information about the probability of the null hypothesis itself. Correctly interpreting p-values is crucial to avoid false positives or false negatives. Statistical significance should not be confused with practical significance, as a statistically significant result may not necessarily have practical implications.
| P-Value Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 0.00 - 0.05 | Statistically significant, reject null hypothesis |
| 0.05 - 0.10 | Marginal significance, caution when interpreting results |
| 0.10 - 1.00 | Not statistically significant, fail to reject null hypothesis |

P-Value Hacks for Statistics Success

Now that we have a solid understanding of p-values, let’s dive into the hacks to ensure statistics success:
- Understand the research question: Clearly define the research question and null hypothesis to ensure that the p-value is interpreted in the correct context.
- Choose the correct statistical test: Select a statistical test that is suitable for the research question and data type to avoid incorrect p-value interpretations.
- Consider multiple testing: When performing multiple tests, adjust the p-value threshold to account for the increased risk of false positives.
- Interpret p-values in context: Consider the research question, sample size, and effect size when interpreting p-values to avoid misinterpretations.
- Use confidence intervals: In addition to p-values, use confidence intervals to provide a range of plausible values for the population parameter.
- Avoid p-hacking: Refrain from selectively reporting p-values or manipulating data to achieve statistically significant results.
- Consider Bayesian alternatives: Bayesian methods can provide a more nuanced understanding of statistical significance and avoid some of the limitations of p-values.
- Use p-value distributions: Visualize p-value distributions to understand the distribution of p-values under the null hypothesis and detect potential biases.
- Account for sample size: Recognize that p-values are influenced by sample size and interpret results accordingly.
- Use robust statistical methods: Employ robust statistical methods that are resistant to outliers and non-normality to ensure reliable p-value interpretations.
Common P-Value Mistakes
Avoid common p-value mistakes, such as:
- Interpreting p-values as the probability of the null hypothesis being true
- Confusing statistical significance with practical significance
- Ignoring multiple testing and false discovery rates
- Failing to consider alternative hypotheses
- Overemphasizing p-values and neglecting other statistical measures
Best Practices for P-Value Interpretation
To ensure accurate p-value interpretation, follow these best practices:
Clear Research Questions
Clearly define the research question and null hypothesis to ensure that the p-value is interpreted in the correct context.
Transparent Reporting
Report p-values transparently, including the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and p-value. Avoid selectively reporting p-values or manipulating data to achieve statistically significant results.
Interpretation in Context
Interpret p-values in the context of the research question, sample size, and effect size. Consider the practical significance of the results and avoid overemphasizing p-values.
What is the difference between statistical significance and practical significance?
+Statistical significance refers to the probability of observing the data (or more extreme) given that the null hypothesis is true. Practical significance, on the other hand, refers to the magnitude and importance of the effect size in the context of the research question.
How do I avoid p-hacking?
+To avoid p-hacking, pre-register your study, use transparent reporting, and avoid selectively reporting p-values or manipulating data to achieve statistically significant results. Consider using Bayesian methods or robust statistical approaches to minimize the risk of p-hacking.
What is the role of confidence intervals in p-value interpretation?
+Confidence intervals provide a range of plausible values for the population parameter, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the results. They can be used in conjunction with p-values to provide a more complete picture of the data and avoid misinterpretations.



