10+ Collision Secrets To Master Elastic Impact

Understanding the dynamics of collision is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and materials science. Elastic impact, in particular, is a fundamental concept that describes the collision between two objects where the kinetic energy is preserved, and the objects revert to their original shape after the collision. Mastering elastic impact is essential for designing and optimizing systems that involve collisions, such as gears, bearings, and even vehicle safety features. In this article, we will delve into the secrets of elastic impact, exploring the key principles, factors, and techniques involved.
Introduction to Elastic Impact
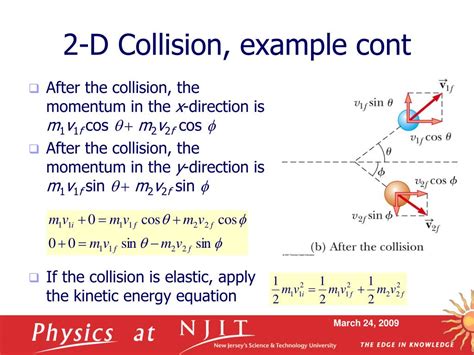
Elastic impact occurs when two objects collide, and the collision is characterized by a sudden change in momentum. The impact is considered elastic if the objects retain their shape and size after the collision, and the kinetic energy is conserved. This type of collision is commonly observed in situations where the objects are made of materials with high elasticity, such as metals or rubber. Understanding the principles of elastic impact is vital for predicting and controlling the behavior of objects during collisions.
Key Principles of Elastic Impact
Several key principles govern the behavior of elastic impact. These include:
- Conservation of momentum: The total momentum before and after the collision remains constant.
- Conservation of kinetic energy: The total kinetic energy before and after the collision remains constant.
- Elastic deformation: The objects deform during the collision but revert to their original shape after the collision.
These principles form the foundation of elastic impact and are essential for analyzing and predicting the behavior of objects during collisions.
Factors Affecting Elastic Impact

Several factors can influence the behavior of elastic impact, including:
Material Properties
The material properties of the objects involved in the collision play a significant role in determining the behavior of elastic impact. Factors such as young’s modulus, poisson’s ratio, and density can affect the elasticity and deformation of the objects during the collision.
| Material Property | Effect on Elastic Impact |
|---|---|
| Young’s Modulus | Affects the stiffness and elasticity of the material |
| Poisson’s Ratio | Affects the lateral strain and deformation of the material |
| Density | Affects the momentum and kinetic energy of the objects |

Understanding the material properties is crucial for predicting the behavior of elastic impact and designing systems that involve collisions.
Collision Geometry
The geometry of the collision can also affect the behavior of elastic impact. Factors such as the angle of incidence, the impact velocity, and the shape of the objects can influence the collision dynamics.
By analyzing the collision geometry, engineers and researchers can predict and control the behavior of objects during collisions, optimizing the design of systems such as gears, bearings, and vehicle safety features.
Techniques for Mastering Elastic Impact
Several techniques can be employed to master elastic impact, including:
Experimental Methods
Experimental methods, such as drop testing and impact testing, can be used to measure the behavior of elastic impact. These methods involve measuring the velocity, acceleration, and deformation of the objects during the collision.
By analyzing the experimental data, researchers can gain insight into the behavior of elastic impact and validate theoretical models.
Numerical Methods
Numerical methods, such as finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD), can be used to simulate the behavior of elastic impact. These methods involve discretizing the objects and the collision domain into smaller elements and solving the equations of motion using numerical algorithms.
By using numerical methods, researchers can predict the behavior of elastic impact and optimize the design of systems that involve collisions.
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic impact?
+Elastic impact occurs when the objects retain their shape and size after the collision, and the kinetic energy is conserved. Inelastic impact, on the other hand, occurs when the objects deform permanently, and the kinetic energy is dissipated.
How can elastic impact be measured experimentally?
+Elastic impact can be measured experimentally using techniques such as drop testing and impact testing. These methods involve measuring the velocity, acceleration, and deformation of the objects during the collision.
What are the applications of elastic impact in engineering?
+Elastic impact has numerous applications in engineering, including the design of gears, bearings, and vehicle safety features. Understanding the behavior of elastic impact is essential for optimizing the performance and safety of these systems.


